* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2 Reproduction of Flowering Plants
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
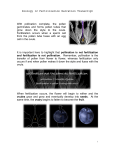
Name CHAPTER 13 Class Date Plant Processes SECTION 2 Reproduction of Flowering Plants National Science Education Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: LS 1a, 2a, 2b, 2d, 5b • What are pollination and fertilization? • How do seeds and fruits form? • How can flowering plants reproduce asexually? What Are Pollination and Fertilization? Flowering plants are most noticeable to us when they are in bloom. As flowers bloom, they surround us with bright colors and sweet fragrances. However, flowers are not just for us to enjoy. They are the structures for sexual reproduction in flowering plants. Pollination and fertilization take place in flowers. STUDY TIP Summarize As you read, write out or draw the steps of pollination and fertilization. Pollination and Fertilization 1 Pollen grains land on the stigma and begin to grow pollen tubes. Stigma Pollen tube Anther Pollen Sperm Style Ovary TAKE A LOOK Ovary Ovule Ovule containing egg 2 Sperm travel down pollen tubes and fertilize the eggs. 1. Identify Circle the part of the flower where pollination occurs. 2. Identify Draw an arrow to show where fertilization will take place. Sexual reproduction begins in flowers when wind or animals move pollen from one flower to another. Pollination occurs when pollen from an anther lands on a stigma. Each pollen grain grows a tube through the style to the ovary. The ovary has ovules, each of which contains an egg. Fertilization occurs when a sperm joins with the egg inside an ovule. Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Interactive Textbook 201 Plant Processes Name SECTION 2 Class Date Reproduction of Flowering Plants continued What Happens After Fertilization? a A mature plant produces a flower. Pollination and fertilization take place. b After fertilization, each ovule within the ovary contains a fertilized egg. STANDARDS CHECK LS 2a Reproduction is a characteristic of all living systems; because no living organism lives forever, reproduction is essential to the continuation of every species. Some organisms reproduce asexually. Others reproduce sexually. Ovary 3. Explain Where do seeds and fruits come from? Ovule c Petals and stamens fall away. e Each seed contains TAKE A LOOK 4. Identify In step C, circle the structures that will become seeds. a tiny plant. If a seed sprouts, or begins to grow, it can become a new plant. d The ovary becomes the fruit, and each ovule becomes a seed. After the fruit ripens, seeds are dispersed. THE FUNCTIONS OF FRUITS READING CHECK 5. List What are two functions of a fruit? When people think of fruit, they often think of apples or bananas. However, many things we call vegetables, such as tomatoes or green beans, are also fruits! A fruit is the ovary of the flower that has grown larger. Fruits have two major functions. They protect seeds while the seeds develop. Fruits also help a plant spread its seeds to new environments. For example, an animal might eat a fruit and drop the seeds far from the parent plant. Fruits such as burrs spread when they get caught in an animal’s fur. Other fruits are carried to new places by the wind or even by water. Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Interactive Textbook 202 Plant Processes Name SECTION 2 Class Date Reproduction of Flowering Plants continued How Do Seeds Grow into New Plants? The new plant inside a seed, called the embryo, stops growing once the seed is fully developed. However, the seed might not sprout right away. To sprout, most seeds need water, air, and warm temperatures. A seed might become dormant, or inactive, if the conditions are not right for a new plant to grow. For example, if the environment is too cold or too dry, a young plant will not survive. Dormant seeds often survive for long periods of time during droughts or freezing weather. Some seeds actually need extreme conditions, such as cold winters or forest fires, to germinate, or sprout. READING CHECK 6. Explain Why would a seed become dormant? Seeds grow into new plants. First, the roots begin to grow. Then, the shoots grow up through the soil. TAKE A LOOK 7. Identify Which part of a new plant grows first? How Else Can Flowering Plants Reproduce? Flowering plants can also reproduce asexually, or without flowers. In asexual reproduction, sperm and eggs do not join. A new plant grows from a plant part such as a root or stem. These plant parts include plantlets, tubers, and runners. Three Structures for Asexual Reproduction Critical Thinking 8. Infer When would asexual reproduction be important for the survival of a flowering plant? Kalanchoe produces plantlets along the edges of their leaves. The plantlets will fall off and take root in the soil. A potato is a tuber, or underground stem. The “eyes” of potatoes are buds that can grow into new plants. The strawberry plant produces runners, or stems that grow along the ground. Buds along the runners take root and grow into new plants. Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Interactive Textbook 203 Plant Processes Name Class Section 2 Review Date NSES LS 1a, 2a, 2b, 2d, 5b SECTION VOCABULARY dormant describes the inactive state of a seed or other plant part when conditions are unfavorable to growth 1. Apply Concepts Is fertilization part of asexual reproduction or sexual reproduction? Explain your answer. 2. Compare What is the difference between pollination and fertilization? 3. Summarize Complete the Process Chart below to summarize how sexual reproduction produces new plants. A mature plant produces flowers. Eggs are fertilized. 4. Identify Name two environmental conditions that can cause a seed to become dormant. 5. List What are three structures a flowering plant can use to reproduce asexually? 6. Infer Why do you think roots are the first part of a plant to grow? Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Interactive Textbook 204 Plant Processes Life Science Answer Key continued 8. If no other plant of the same species were 2. Taproot systems have one main root that available for pollination, a plant could still reproduce, asexually. can get water from deep underground. Fibrous root systems have many small roots that get water from close to the soil surface. 3. Stems support the body of a plant; allow for transport of water, minerals, and food; and store materials for the plant. 4. roots, stems, leaves, flowers Review 1. Sexual—it involves the joining of a sperm and an egg. 2. In pollination, pollen lands on the stigma. In Chapter 13 Plant Processes 3. SECTION 1 PHOTOSYNTHESIS 1. 2. 3. 4. a green pigment that absorbs light energy in the grana of chloroplasts glucose and oxygen mitochondria 5. The plant couldn’t take in carbon dioxide. It couldn’t make food. 6. Circles should be around the structures on the sides of the stoma; they open and close stomata. 7. chemical energy 4. 5. 6. SECTION 3 PLANT RESPONSES TO THE ENVIRONMENT Review 1. It reflects the green wavelengths of sunlight. 2. Mitochondria break down food to provide 1. anything that causes a reaction in your body 2. The X should be on the right side of the energy. They take part in cellular respiration. 3. Photosynthesis Cellular respiration Cells make food for the plant. Cells break down food to provide energy. Oxygen is produced. Oxygen is used to break down food. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 4. stomata and cuticle 5. They form the base of almost all food chains on Earth. They also produce oxygen, which most organisms need for cellular respiration. 6. They would lose too much water. 2. 1. stigma 2. ovule 3. Seeds are fertilized ovules. Fruits are ovaries 6. 7. picture. A plant will grow toward light. Arrow points down. It must have been growing upside down. Plant stems grow away from gravity. 7.2 h chlorophyll orange and yellow pigments Review 1. A negative tropism is growth away from SECTION 2 REPRODUCTION OF FLOWERING PLANTS 4. 5. fertilization, a sperm joins with an egg. A mature plant produces flowers. Flowers are pollinated. Eggs are fertilized. The ovary becomes a fruit, and ovules become seeds. Seeds are spread. They sprout and grow into new plants. very cold weather, very dry weather plantlets, tubers, runners Plants need roots first so they can start to get nutrients from the soil. Also, the roots hold the plant in place. 3. 4. 5. that have grown larger to protect the seeds. The ovules should be circled. Protect the seed and spread seeds to new environments. if conditions were not right for a new plant to grow the root 6. 7. a stimulus. A positive tropism is growth toward a stimulus. Cells farthest from the light grow longer than cells facing the light. This causes the shoot to bend toward the light. plant growth in response to gravity change in the length of days Short-day plants need short days and long nights in order to start reproducing. Long-day plants need longer day lengths to reproduce. Chlorophyll hides the other pigments in the summer. Evergreen leaves are covered with a thick cuticle that protects them from cold and dry weather. Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Interactive Textbook Answer Key 14 Life Science