* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 1 Exam
Survey
Document related concepts
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Symbiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
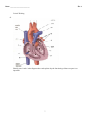
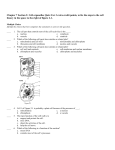
Name: ________________________ Class: ___________________ Date: __________ ID: A Unit I Exam True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. False Response ____ 1. Cellular respiration takes place in animal cells but not in plant cells. Critical Thinking ____ 2. Bacteria can be helpful to humans as well as harmful. ____ 3. A virus is not able to perform any life functions for itself, but requires a host cell to do these for it. Knowledge ____ 4. Potassium is an essential nutrient responsible for maintaining good muscle and nerve activity. ____ 5. Saliva is not part of the digestive process and is only responsible for moistening the food so that it will go down the system more easily. ____ 6. Veins contain valve structures to keep the blood from flowing back to the venules and capillaries. Application ____ 7. Only blood that is low in oxygen flows into the chambers of the heart. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Knowledge ____ 8. Bacteria ... a. are single-celled life forms. b. are one of the oldest life forms found on Earth. c. can affect how our body systems work. d. all of the above are true. ____ 9. Which of the structures in the cell is responsible for storing waste for the cell? a. vacuole c. Golgi body b. mitochondrion d. chloroplast ____ 10. Which cell structure is responsible for the energy provided to the cell? a. nucleus c. ribosome b. mitochondria d. cell membrane ____ 11. When cell parts such as organelles break down, they are recycled by the ... a. ribosomes. c. vacuoles. b. lysosomes. d. Golgi bodies. 1 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 12. A cell with no organelles that passes its genetic material on to another cell in order to have that cell reproduce the genetic material is called a ... a. virus. c. parasite. b. bacterium. d. fungus. ____ 13. Bacteria are ... a. single-celled organisms. c. only disease causers. b. small sections of DNA only. d. a kind of virus. ____ 14. The process that allows you to smell supper cooking in the kitchen when you walk into the house is called ... a. osmosis. c. evaporation. b. diffusion. d. permeation. ____ 15. When a group of similar cells work together in the body, they are described as ... a. a tissue. c. an organ system. b. a muscle. d. a cell system. ____ 16. Nutrients come in the form of ... a. carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and vitamins. b. fibre, fats, protein, and minerals. c. carbohydrates, fats, fibre, and vitamins. d. fats, fibre, proteins, and water. ____ 17. During the process of digesting food, your body ... a. takes food into the system. b. chemically breaks down the food. c. takes nutrients from the digestive system into the body. d. eliminates material the body cannot use. ____ 18. The process of chewing your food is part of the process referred to as ... a. chemical digestion. c. nutrient absorption. b. mechanical digestion. d. food intake. ____ 19. Gas exchange (oxygen and carbon dioxide) in the respiratory system takes place in the ... a. trachea. c. alveoli. b. bronchi. d. pharynx. ____ 20. The dirt and other particles trapped by the cilia and mucus in the respiratory system are ... a. absorbed through the lining of the respiratory system. b. pushed back out into the surrounding air or down into the digestive system. c. pushed down into the trachea and bronchi. d. held by the cilia until you blow your nose. Application ____ 21. An example of a response to a stimulus might be ... a. answering this question. b. blinking when a bright light is suddenly shone in your face. c. staring at a blank TV screen. d. waking up naturally in the morning. ____ 22. Plant cells can be distinguished from animal cells because only plant cells have ... a. a cell wall. c. a cell membrane. b. vacuoles. d. cytoplasm. 2 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 23. A cell in which there are very few organelles and those organelles are not enclosed in a membrane is a ... a. prokaryotic cell. c. plant cell. b. eukaryotic cell. d. an animal. ____ 24. A cell in which the organelles are enclosed in a membrane is a ... a. prokaryotic cell. c. plant cell. b. eukaryotic cell. d. an animal. ____ 25. Carbohydrates are used by the body to provide ... a. fuel for the body. b. materials for building body parts such as muscles. c. stored energy. d. support for the body in processes such as muscles and nerve activity. ____ 26. When blood is pumped through the blood vessels of the lungs, it becomes ... a. oxygenated. b. lighter in colour. c. thinner than when it is returned from the body to the heart. d. all of the above. ____ 27. From the nasal cavity the air passes to the ... a. pharynx, then past the epiglottis, then through the larynx, then into the trachea. b. trachea, then past the epiglottis, then through the pharynx, then into the bronchioles. c. pharynx, then past the larynx, then through the treachea, then into the larynx. d. bronchus, then past the epiglottis, then through the trachea, then into the larynx. ____ 28. What are the capillaries in the alveoli responsible for? a. There are no capillaries in the alveoli. b. Cleaning the air in the lungs. c. Exchanging gases between the blood and the air in the alveoli. d. Providing mucus to line the walls of the alveoli. Critical Thinking ____ 29. A living thing would exhibit the following characteristics: a. the ability to grow, reproduce, and communicate with others b. the ability to grow, respond to its environment, and communicate with others c. the ability to use energy, eliminate waste material, and mate with another living thing d. the ability to use energy, eliminate waste, and reproduce ____ 30. Normal reproduction provides a way for a single type of organism to ... a. replace organisms that die off. b. allow organisms to grow bigger. c. create many new types of organisms. d. create many new organisms with different characteristics. ____ 31. The most abundant chemical compound in a cell is ... a. protein. c. water. b. glucose. d. carbon dioxide. ____ 32. Cells extract energy from their food by means of ... a. chlorophyll. c. photosynthesis. b. cellular respiration. d. osmosis. 3 Name: ________________________ ID: A Completion Complete each statement. Knowledge 33. For 33 to 37 choose from following list: diffusion, magnification power, selectively permeable, resolving power, cells, osmosis, and objective lens. The ability of a microscope to distinguish between two objects that are close together is referred to as its____________________. 34. The number of times that an objective lens can magnify an object is referred to as the____________________. 35. The movement of ink within a glass of water when the water has been left undisturbed (not shaken or stirred) could be the result ____________________. 36. Because the cell membrane allows some materials to pass through it but keeps others out, it is a ____________________. 37. For 37 to 41 choose from the following list: cartilidge, enzymes, saturated, tendons, unsaturated, alveoli, cilia, and peristalsis. Muscles are attached to the bones by means of ____________________. 38. A fat that is a liquid at room temperature is called a(n) ____________________. 39. Many chemical processes in digestion can occur only because special types of proteins are present to speed up the reactions. These proteins are called ____________________. 40. A series of muscle contractions that moves food along a passage in the digestive system such as the esophagus is called ____________________. 41. The actual places in the body where the exchange of gases between the blood and the air takes place are the____________________. Application 42. When organisms carry out life activities, including responding to their environment, they must use ____________________. Matching Match the correct term to each of the following descriptions. a. energy d. response b. growth e. stimulus c. reproduction f. waste ____ 43. a reaction to something in an organism’s environment ____ 44. something that is eliminated from an organism since it is not needed ____ 45. something that is needed by an organism to carry out life’s activities 4 Name: ________________________ ID: A ____ 46. the creation of new members of a group of organisms ____ 47. something that causes an organism to respond or react ____ 48. an organism getting larger in size Identify the part of the blood that performs the function described. a. plasma c. red blood cells b. platelets d. white blood cells ____ ____ ____ ____ 49. 50. 51. 52. contains hemoglobin for carrying oxygen and carbon dioxide is used to fight disease and infection is a clear yellowish liquid containing proteins and minerals assist in the clotting of blood by causing it to thicken Short Answer Knowledge 53. Identify each of the microscope parts indicated in the diagram. 54. Briefly describe the characteristics of a system. 55. Identify five systems in the human body. 5 Name: ________________________ ID: A Application 56. Identify each of the following cell parts, giving the number and the name of the part in your answer: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) the part that is a jelly substance containing the organelles of the cell the part that traps sunlight and stores the energy in chemical form the part that is a rigid structure surrounding the cell membrane the part that sometimes stores waste material the part that is a network of folded channels that transports proteins Critical Thinking 57. Describe two examples of where bacteria could be helpful to humans. 58. Explain why you would not find chloroplasts in a cell taken from the root of a fir tree. Problem Application 59. You have just discovered a new cell in a sample you have been looking at under a very powerful microscope. How would you determine if the cell was a prokaryotic or a eukaryotic cell? 60. Arrange the following parts of the respiratory system in order from smallest to largest: - bronchiole cell - organ - organism - organ system - respiratory tissue smallest → → → largest → 6 Name: ________________________ ID: A Critical Thinking 61. Identify parts ii and v in the diagram above and explain why the functioning of these two parts is so important. 7 ID: A Unit I Exam Answer Section TRUE/FALSE 1. ANS: F Cellular respiration takes place in all cells so that energy can be released for use in life functions. 2. 3. 4. 5. PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 1.2 LOC: LS-CS-B2 TOP: Cells KEY: cellular respiration MSC: Knowledge ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 1.2 LOC: LS-CS-B2 TOP: Cells KEY: bacteria MSC: Knowledge ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 1.2 LOC: LS-CS-B2 TOP: Cells KEY: virus | life functions | host MSC: Knowledge ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 2.2 LOC: LS-CS-B3 TOP: The Digestive and Excretory Systems KEY: potassium | muscle | nerve MSC: Knowledge ANS: F Saliva carries the enzyme called amylase, which starts the chemical digestion of the food. PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 2.2 LOC: LS-CS-B3 TOP: The Digestive and Excretory Systems KEY: saliva | amylase | digestion MSC: Knowledge 6. ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Easy OBJ: Section 2.3 LOC: LS-CS-B3 TOP: The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems KEY: vein | capillary | venule | valve MSC: Knowledge 7. ANS: F Oxygen-rich blood from the lungs flows into the left side of the heart for pumping out to the body. PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 2.3 TOP: The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems MSC: Knowledge LOC: LS-CS-B3 KEY: heart | oxygen | lung MULTIPLE CHOICE 8. ANS: LOC: MSC: 9. ANS: LOC: MSC: 10. ANS: LOC: MSC: D LS-CS-B2 Knowledge A LS-CS-B2 Knowledge B LS-CS-B2 Knowledge PTS: 1 DIF: Easy TOP: Cells and Systems OBJ: Unit Introduction KEY: bacteria PTS: 1 TOP: Cells DIF: Average OBJ: Section 1.2 KEY: cell | waste | vacuole PTS: 1 TOP: Cells DIF: Average OBJ: Section 1.2 KEY: cell | mitochondria 1 ID: A 11. ANS: LOC: MSC: 12. ANS: LOC: MSC: 13. ANS: LOC: MSC: 14. ANS: LOC: KEY: 15. ANS: LOC: MSC: 16. ANS: LOC: KEY: 17. ANS: LOC: KEY: 18. ANS: LOC: KEY: 19. ANS: LOC: KEY: 20. ANS: LOC: KEY: 21. ANS: LOC: MSC: 22. ANS: LOC: MSC: 23. ANS: LOC: MSC: 24. ANS: LOC: MSC: 25. ANS: LOC: KEY: 26. ANS: LOC: KEY: B PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 1.2 LS-CS-B2 TOP: Cells KEY: organelle | lysosome Knowledge A PTS: 1 DIF: Easy OBJ: Section 1.2 LS-CS-B2 TOP: Cells KEY: cell | organelle | virus Knowledge A PTS: 1 DIF: Easy OBJ: Section 1.2 LS-CS-B2 TOP: Cells KEY: bacteria | virus | organism Knowledge B PTS: 1 DIF: Easy OBJ: Section 1.3 LS-CS-B2 TOP: Diffusion, Osmosis, and the Cell Membrane diffusion MSC: Knowledge A PTS: 1 DIF: Easy OBJ: Section 2.1 LS-CS-B3 TOP: Body Systems KEY: cells | tissue Knowledge A PTS: 1 DIF: Easy OBJ: Section 2.2 LS-CS-B3 TOP: The Digestive and Excretory Systems nutrients MSC: Knowledge B PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 2.2 LS-CS-B3 TOP: The Digestive and Excretory Systems digestion MSC: Knowledge B PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 2.2 LS-CS-B3 TOP: The Digestive and Excretory Systems digestion | mechanical MSC: Knowledge C PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 2.3 LS-CS-B3 TOP: The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems respiratory | alveoli MSC: Knowledge B PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 2.3 LS-CS-B3 TOP: The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems respiratory | cilia | digestive MSC: Knowledge B PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 1.1 LS-CS-B1 TOP: Observing Living Things KEY: stimulus | response Skills A PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 1.2 LS-CS-B2 TOP: Cells KEY: cell | cell wall Knowledge A PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 1.2 LS-CS-B2 TOP: Cells KEY: cell | prokaryotic Knowledge B PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 1.2 LS-CS-B2 TOP: Cells KEY: cell | prokaryotic Knowledge A PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 2.2 LS-CS-B3 TOP: The Digestive and Excretory Systems carbohydrates MSC: Knowledge D PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 2.3 LS-CS-B3 TOP: The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems blood | oxygenated MSC: Knowledge 2 ID: A 27. ANS: LOC: KEY: 28. ANS: LOC: KEY: 29. ANS: LOC: KEY: 30. ANS: LOC: MSC: 31. ANS: LOC: MSC: 32. ANS: LOC: MSC: A PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: LS-CS-B3 TOP: The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems nasal cavity | pharynx | epiglottis | larynx | trachea MSC: C PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: LS-CS-B3 TOP: The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems capillaries | alveoli MSC: Knowledge D PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: LS-CS-B1 TOP: Observing Living Things growth | reproduce | eliminate waste | use energy MSC: A PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: LS-CS-B1 TOP: Observing Living Things KEY: Knowledge C PTS: 1 DIF: Difficult OBJ: LS-CS-B2 TOP: Cells KEY: cell | water | protein Knowledge B PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: LS-CS-B2 TOP: Cells KEY: cellular respiration Knowledge Section 2.3 Knowledge Section 2.3 Section 1.1 Knowledge Section 1.1 reproduction | characteristics Section 1.2 Section 1.2 COMPLETION 33. ANS: resolving power PTS: TOP: MSC: 34. ANS: 1 DIF: Average Observing Living Things Knowledge magnification power OBJ: Section 1.1 LOC: POS-A5 KEY: resolving power | microscope PTS: TOP: MSC: 35. ANS: 1 DIF: Easy Observing Living Things Knowledge diffusion OBJ: Section 1.1 LOC: POS-A5 | POS-A8 KEY: magnification power PTS: TOP: MSC: 36. ANS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 1.3 Diffusion, Osmosis, and the Cell Membrane Knowledge selectively permeable membrane LOC: LS-CS-B2 KEY: diffusion PTS: TOP: MSC: 37. ANS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 1.3 Diffusion, Osmosis, and the Cell Membrane Knowledge tendons LOC: LS-CS-B2 KEY: selectively permeable membrane PTS: 1 DIF: Easy TOP: Body Systems OBJ: Section 2.1 KEY: tendons 3 LOC: LS-CS-B3 MSC: Knowledge ID: A 38. ANS: unsaturated fat PTS: TOP: MSC: 39. ANS: 1 DIF: Easy OBJ: Section 2.2 The Digestive and Excretory Systems Knowledge enzymes LOC: LS-CS-B3 KEY: unsaturated fat PTS: TOP: MSC: 40. ANS: 1 DIF: Easy OBJ: Section 2.2 The Digestive and Excretory Systems Knowledge peristalsis LOC: LS-CS-B3 KEY: enzymes | proteins PTS: TOP: MSC: 41. ANS: 1 DIF: Easy OBJ: Section 2.2 The Digestive and Excretory Systems Knowledge alveoli LOC: LS-CS-B3 KEY: digestive | peristalsis PTS: TOP: MSC: 42. ANS: 1 DIF: Easy OBJ: Section 2.3 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Knowledge energy LOC: LS-CS-B3 KEY: alveoli PTS: 1 DIF: Average TOP: Observing Living Things OBJ: Section 1.1 KEY: energy LOC: LS-CS-B1 MSC: Knowledge MATCHING 43. ANS: LOC: MSC: 44. ANS: LOC: MSC: 45. ANS: LOC: MSC: 46. ANS: LOC: MSC: 47. ANS: LOC: MSC: 48. ANS: LOC: MSC: D LS-CS-B1 Knowledge F LS-CS-B1 Knowledge A LS-CS-B1 Knowledge C LS-CS-B1 Knowledge E LS-CS-B1 Knowledge B LS-CS-B1 Knowledge PTS: 1 DIF: Average TOP: Observing Living Things OBJ: Section 1.1 KEY: response | reaction PTS: 1 DIF: Easy TOP: Observing Living Things OBJ: Section 1.1 KEY: waste | elimination PTS: 1 DIF: Easy TOP: Observing Living Things OBJ: Section 1.1 KEY: energy PTS: 1 DIF: Easy TOP: Observing Living Things OBJ: Section 1.1 KEY: reproduction PTS: 1 DIF: Average TOP: Observing Living Things OBJ: Section 1.1 KEY: stimulus | response PTS: 1 DIF: Easy TOP: Observing Living Things OBJ: Section 1.1 KEY: growth 4 ID: A 49. ANS: LOC: KEY: 50. ANS: LOC: KEY: 51. ANS: LOC: KEY: 52. ANS: LOC: KEY: C PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: LS-CS-B3 TOP: The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems red blood cell | hemoglobin MSC: Knowledge D PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: LS-CS-B3 TOP: The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems white blood cell | disease | infection MSC: A PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: LS-CS-B3 TOP: The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems plasma | protein | minerals MSC: Knowledge B PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: LS-CS-B3 TOP: The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems platelets | clotting MSC: Knowledge Section 2.3 Section 2.3 Knowledge Section 2.3 Section 2.3 SHORT ANSWER 53. ANS: (1) eyepiece (2) revolving nosepiece (3) objective lenses (4) stage (5) light source (6) base (7) fine focus knob (8) coarse focus knob (9) arm PTS: 9 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 1.1 LOC: LS-CS-B2 | POS-A8 TOP: Observing Living Things KEY: microscope | eyepiece | nosepiece | objective lenses | stage MSC: Knowledge NOT: Answers are based on the diagram on page 12 of the text and will depend on the numbering system of the diagram. An alternative is to use the diagram from page 21 of the text. 54. ANS: - A system is made of individual parts that work together as a whole. - One system is usually connected to one or more other systems. - If one part of a system is missing or not functioning, the system will not function well or may not function at all. PTS: 3 DIF: Average TOP: Body Systems OBJ: Section 2.1 KEY: system 5 LOC: LS-CS-B3 MSC: Knowledge ID: A 55. ANS: - respiratory - circulatory - digestive - excretory - nervous - immune - endocrine - reproductive - integumentary - skeletal - muscular PTS: 5 DIF: Easy TOP: Body Systems 56. ANS: (a) 9 - cytoplasm (b) 7 - chloroplast (c) 4 - cell wall (d) 2 - vacuole (e) 8 - endoplasmic reticulum OBJ: Section 2.1 KEY: system LOC: LS-CS-B3 MSC: Knowledge PTS: 5 DIF: Difficult OBJ: Section 1.2 LOC: LS-CS-B2 TOP: Cells KEY: cell | cytoplasm | chloroplast | cell wall | vacuole | endoplasmic reticulum MSC: Knowledge NOT: This is the diagram from page 27 of the text with the names of the parts removed and numbers placed in their stead. 57. ANS: Any two of the following: - Some bacteria work in our digestive systems to help break down food and release nutrients. - Some bacteria are used to produce foods such as cheese and yogurt. - Some bacteria are used to produce medicines such as insulin. PTS: 1 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 1.2 LOC: LS-CS-B2 TOP: Cells KEY: bacteria MSC: Knowledge 58. ANS: Chloroplasts use sunlight to produce food for a plant and the roots are not exposed to the Sun so they would not need chloroplasts in them. PTS: 1 TOP: Cells DIF: Average OBJ: Section 1.2 KEY: cell | chloroplast 6 LOC: LS-CS-B2 MSC: Knowledge ID: A PROBLEM 59. ANS: If the cell you were looking at had organelles such as a nucleus or mitochondria, then it is a eukaryotic cell. However, if the DNA was simply coiled in the cell without a membrane around it to form a nucleus and there were no other organelles such as chloroplasts, mitochondria, or lysosomes, then it is likely a prokaryotic cell. PTS: 2 TOP: Cells 60. ANS: bronchiole cell DIF: Difficult OBJ: Section 1.2 KEY: cell | prokaryotic | eukaryotic → respiratory tissue → organ → LOC: LS-CS-B2 MSC: Knowledge organ system → organism PTS: 3 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 2.1 LOC: LS-CS-B3 TOP: Body Systems KEY: system | cell | tissue | organ | organism MSC: Knowledge 61. ANS: Parts ii and v are valves that prevent the blood from flowing from the ventricles back into the atriums. This is important so that all the blood in the ventricles is moved on to the lungs or the rest of the body in order to provide oxygen to the rest of the body. If these valves do not function properly, the heart will not be able to move as much blood as possible on to the lungs or the rest of the body, so the heart will have to work harder to do its job. PTS: 2 DIF: Average OBJ: Section 2.3 TOP: The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems MSC: Knowledge 7 LOC: LS-CS-B3 KEY: heart | ventricle