* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electromagnet activity page
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
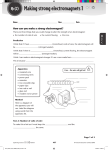
Electromagnet Age: 3rd grade and up; can be enjoyed by almost anyone! Concepts: Electricity, Magnetism Materials: 1 wire segment (about 3 feet) 1 metal bolt (not intrinsically magnetic) 1 D battery (more will increase the intensity of the magnet) 1 D battery holder (if you use more batteries, you will need more holders) Lots of paper clips Instructions: 1. Strip about one inch of the plastic coating off of each end of the wire (this should be done by an adult). 2. Snap the battery into the holder, being careful to align the ends correctly. After the activity is completed, feel free to return to this step and experiment with the number of batteries used to see how this affects the strength of the electromagnet. 3. Leaving about 4 inches on either end, wrap the wire around the bolt as much as you can. After the kids have finished building the electromagnet, feel free to return to this step and experiment with different numbers of wraps and see how this affects the strength of the electromagnet. 4. Bend the bare wire ends so that one is attached to each of the metal ends of the battery holder. 5. Hold a paper clip next to the wrapped wire and watch it stick! Continue adding more paper clips until they no longer stick and then record the number of clips your electromagnet held. Compare your number with those of other students and see whose electromagnet worked best. 6. For an extra activity, as hinted above, have the students unwrap their wires and record a table with number of wraps and number of paper clips held. They can also keep the number of wraps constant and try adding more batteries. 7. For another variation, try replacing the metal bolt with a wooden dowel or a plastic straw. How it Works/Discussion Questions: What seems to affect how strong the electromagnet is? Discuss how magnets work and how a wire wrapped around certain materials creates an electromagnet. All wires carrying current produce a magnetic field which is circular and perpendicular to the wire. By wrapping the wire in loops, you align the small magnetic field lines so that they point in the same direction, greatly amplifying the magnetic field produced. The bolt is affected by this magnetic field; it is transformed into a temporary magnet. http://science.howstuffworks.com/electromagnet4.htm