* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4: Congruent Triangles
Survey
Document related concepts
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Riemann–Roch theorem wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
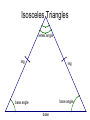
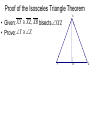
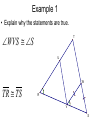
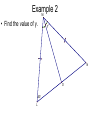
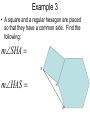
Chapter 4: Congruent Triangles 4.5 Isosceles & Equilateral Triangles Isosceles Triangles vertex angle leg leg base angle base angle base Theorem 4-3 • Isosceles Triangle Theorem – If two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the angles opposite those sides are congruent. Theorem 4-4 • Converse of Isosceles Triangle Theorem – If two angles of a triangle are congruent, then the sides opposite the angles are congruent. Theorem 4-5 • The bisector of the vertex angle of an isosceles triangle is the perpendicular bisector of the base. Proof of the Isosceles Triangle Theorem • Given: XY XZ , XB bisects YXZ • Prove: Y Z Y X B Z Example 1 • Explain why the statements are true. WVS S T U W TR TS R V S Example 2 M • Find the value of y. y N O 63 L Corollary • a statement that follows immediately from a theorem • like a “side note” Corollaries • Corollary to Theorem 4-3: – If a triangle is equilateral, then the triangle is equiangular. • Corollary to Theorem 4-4: – If a triangle is equiangular, then the triangle is equilateral. Example 3 • A square and a regular hexagon are placed so that they have a common side. Find the following: mSHA S mHAS H A Example 4 • Five fences meet at a point to form angles with measures x, 2x, 3x, 4x, and 5x around the point. Find the measure of each angle. Homework • p. 230 • 1-7, 10-13, 15, 20-22, 28, 30-32