* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIOLOGY Level L Basic Questions Chapter 1: 1) a) Contains
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
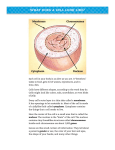
BIOLOGY Level L Basic Questions Chapter 1: 1) a) Contains chromosomes which carry hereditary information. Controls quantity and type of proteins/ regulates the chemical changes in the cell. Controls cell division. b) One; cytoplasm; chromosome. 2) a) Manufacture energy from food substances. b) They serve as working surfaces: ‐ they are folded thereby increasing their surface area for chemical reactions. ‐ they contain enzymes for respiration. c) the more active a cell is the more mitochondria it has. 3) site of proteins synthesis. 4) a) plant cells, single celled organisms and algae. b) chlorophyll 5) a) refer to fig 1 page 1. b) holds the cell contents together and controls which substances are allowed to enter and leave the cell; it maintains the structure of cells and chemical reactions of the cytoplasm. 6) a) fig 2 page 1 b) It is a food stores for plant cells. 7) Refer to table 1 page 5 for structural differences. Functional differences: plant cells can make their own foods while animal cells can’t and plant cells make their cell walls from cellulose while animal cells don’t. 8) a) to stain nucleus in plant cells. b)to stain nucleus in animal cells. 9) a) 41 mm b) 41mm/10mm x 1mm = 4.1 mm c) 4.1mm/ 100 = 0.041mm 10) i) chloroplast ii) mitochondria iii) cell membrane iv) nucleus v) vacuole vi) cell wall 11) Refer to table 1 page5 Chapter 2 1. Source of illumination Magnification Resolution Electron microscope Beams of electrons 500,000 times Very high resolution Light microscope Beams of light 1500times low resolution 2. Advantages: Very high resolution, very high magnification, and some microscopes allow an external view of the cell or organism Disadvantages: Cells are killed or dehydrated, some preparation procedures produce artificial features, very expensive and the use of the microscopes and preparation of specimens require specialist training. 3. ‐The growth of new plants and animals ‐Repair and replacement of damaged and worn out cells ‐It is a form of reproduction for simpler organisms 4. a) They have a high concentration of contractile fibers which enable the cells to contract, to move bones, move food along the gut and cause the heart to pump blood. b) They have flexible cell membranes , cytoplasm but no nucleus and other organelles so more space for hb would be available to carry oxygen. The cells are biconcave in shape resulting in larger surface area for oxygen exchange. c) They are dead and hollow (no cell membrane, cytoplasm or nucleus) and their cell wall contains lignin to provide support transport water. d) They have tiny tube‐like outgrowths from the cells to increase their surface area. They have a large vacuole and a selectively permeable with a thin cytoplasm for uptake of water & mineral salts. e) They have tiny hairs called cilia on the outer surface which flicking movement allows to move the mucus carrying bacteria away from lungs. 5. a) The process by which a cell becomes adapted to do one particular job. b) The specialization of cells to carry out particular functions in an organism. 6. a) bone and muscle b) lungs, heart and root c) gut (alimentary canal) 7. ‐A system is a group of organs whose functions are closely related . ‐An organism comprises of different organs and systems working together to produce a plant or animal 8. a) Samples of developing animal tissues or plant cells are taken, separated by enzymes and the cells are made to grow and divide in shallow dishes containing a nutrient solution. b) They are used to study the cells and cell division, to test new drugs and vaccines, to culture viruses, or to test the effect of possible harmful chemicals. Chapter 3: 1. Chemical reactions 2. Refer to fig.2 Pg.26 Proton: positive charge, mass of one amu. Electron: negative charge, 2000 times lighter that a proton. 3. a) Elements, atoms . b) 2N is two separate Nitrogen atoms while N2 is two chemically bonded Nitrogen atoms forming a molecule . 4. a) that a hydrogen molecule has two atoms bonded together. b) 2 hydrogen atoms joined together by a bond which represents a pair of electrons shared between them. 5. Organic compounds are substances that contain Carbon and often Hydrogen while inorganic compounds are substances that do not contain Carbon. 6. a) ‐COOH b) ‐NH2 7. a) refer to fig. in 3.3.3 b) 20; R‐group 8. a) Surface tension is the force of attraction which causes water molecules on the surface to resist separation. When water is gets attracted to and travels up the walls of the narrow capillary tube we call this capillary action. b) Water dissolves many organic substances and inorganic substances that are essential to life. c) The amount of heat needed to increase the temperature of a liquid. d) The density increases to reach its maximum at 4°C , and then decreases from 4°C to 0°C . 9. a) Hydrogen ions (H+) b) pH is a way used to express the acidity of a solution. It is measured by using a pH meter or a chemical indicator. c) High 10. a) Glucose and Oxygen b) Water, Carbon dioxide and energy 3. (Pg.34) ‐Electrical attraction ‐electrons ‐protons ‐electrons ‐nuclei Basic questions chapter 4: 1 a) Structural proteins and functional proteins. b) Structural proteins are used for building purposes such as muscle, hair and fingernails. Functional proteins are used as chemical tools such as enzymes and insulin hormone. 2 a) N, O,C, H b) amino acids ; ribosomes. c) by the radical (R) d) Dipeptide ; polypeptide e) peptide. 3. a) it allows a protein to perform its function. b) denatured c) increase in temperature above 50 degrees Celsius. 4. a) made of 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol. b) energy store , keeps body warm, essential to the structure and formation of cell membrane and internal membrane structure. c) fats, oils and steroids. d) C , H , O e) lipid; glycerol ;ester 5 a) C, H , O b)by size (number of simple sugars) monosaccharide, disaccharide and polysaccharides. c) by combining two glucose molecule using a glycosidic bond. d) glycosidic bond e) food store in animals as glycogen, in plants as starch/ cellulose makes the cell wall/ they provide primary source of energy. 6 a) nucleotide b) DNA found in nucleus and RNA found in nucleus and cytoplasm c) a simple sugar and a phosphate group. d) adenine, guanine, thymine and cytosine.