* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parent Signature_____________________ Ocean Unit
Survey
Document related concepts
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
History of navigation wikipedia , lookup
Marine biology wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
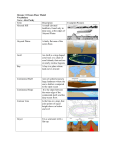
Name ______________________ Parent Signature_____________________ Ocean Unit Study Guide Test Date: A Day: Friday, April 1 B Day: Thursday, March 31 Study your notebook notes, study guide, and review pgs. C82-C95 in your textbook. SOL5.6 The student will investigate and understand characteristics of the ocean environment. Key concepts include a) geological characteristics (continental shelf, slope, rise); b) physical characteristics (depth, salinity, major currents); and c) biological characteristics (ecosystems). Key Ideas and Terms: There are 4 major oceans on Earth. They are: The Atlantic Ocean, the Pacific Ocean, The Arctic Ocean, and the Indian Ocean. The nearest ocean to Virginia is the Atlantic Ocean. 70% of the earth is covered by the oceans. Oceans are important because of the habitat that they provide for many types of fish and aquatic plants. They also benefit humans as a source of food, minerals, recreation, and employment. Basin- another name for the Ocean floor. Continental Shelf- the underwater edge of the continent. This area is rich in fish, underwater plants, and minerals such as oil and natural gas. Continental Slope – The steep slope that goes from the edge of the Continental Shelf to the sea floor. Continental Rise- The buildup of sediments on the sea floor at the bottom of the continental slope. Abyssal Plain- the flat area of the ocean floor after the continental rise that covers almost half the ocean floor. Deep Sea Trench – a deep valley on the sea floor sometimes caused by a convergent boundary. Some of the deepest areas of the ocean floor are trenches. The Marianas Trench is 36,000 ft. deep and is the deepest part of the oceans known to man. Seamount- A huge underwater volcanic mountain. Some may emerge from the ocean as an island. The Hawaiian Islands are an example of seamounts. Mid-Atlantic Ocean Ridge – a chain of undersea mountains that were formed by a divergent boundary. Salinity – a measure of how much salt is in the ocean water. Saltier water is more dense and tends to sink to the bottom while fresh water tends to rise to the top of a waterway. Brackish water – a mixture of salt and fresh water. Estuary – an environment where fresh water such as a river meets salty water such as an ocean. Current – the movement of water. A major current near the coast of Virginia is The Gulf Stream. It is a warm current and keeps the climate in Virginia warmer. Sample Questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.6a 5. What part of the ocean are you unlikely to find plant life? A in a ocean trench B on the continentai slope C on the abyssal plain D on the continental shelf 5.6a 6. Where in the ocean do we find petroleum, sand and gravel deposits, and most of our fisheries? A continental rise B ocean trench C continental slope D continental shelf 5.6b 7. Which of the following does NOT happen as you go down deeper into the oceans: A pressure decreases B light decreases OCEAN DEPTH VS. LIVING C temperature decreases ORGANISMS D depth increases 5.6b 8. Currents in the oceans are created by wind and E underwater earthquakes. F Plate boundaries G differences in temperature and salt content. H runoff from rivers. 5.6c 9. What conclusion could you make from the chart on the right? A B C D When When When When ocean ocean ocean ocean depth depth depth depth DEPTH OF OCEAN # OF LIVING SPECIES 10 meters 3,000 100 meters 1,500 1,000 meters 300 3,000 meters 100 increases, the number of organisms increases. increases, the number of organisms is constant. decreases, the number of organisms decreases. decreases, the number of organisms increases.