* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Word Work File L_987757493
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Loading coil wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
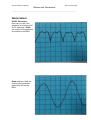
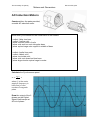
KICKSTART PHYSICS The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators MOTORS AND GENERATORS SCHOOL OF PHYSICS 1. THE MOTOR EFFECT 2. LENZ’S LAW 3. GENERATORS 4. TRANSFORMERS 5. AC INDUCTION MOTORS Kickstart would like to acknowledge and pay respect to the traditional owners of the land– the Gadigal people of the Eora Nation. It is upon their ancestral lands that the University of Sydney is built. As we share our own knowledge, teaching, learning, and research practices within this University may we also pay respect to the knowledge embedded forever within the Aboriginal Custodianship of For more information head to http://sydney.edu.au/science/physics/schools_community/kickstart.shtml The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators Generate some motor-vation List three risks in the 2nd year lab Risk Electricity Radiation Equipment Water LN2 Consequence Electrocution Radiation sickness Injury Slip/injury Frostbite Precaution Safety Switch Low dose, shielding Don’t touch No food drink in lab PPE Careers with Motors and Generators Your demonstrator might be able to help with this. What sort of career do you think you could get if you studied this topic at the University of Sydney? Industry Research • Finance/Tech companies • University • Gaming • Any research field • Solar/energy • • Veritasium Public service • CSIRO, DSTO, NMI, Geoscience, Questacon • Government • Teachers The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators The Motor Effect An electric charge experiences a force when it moves in a magnetic field. Thus, a current-carrying conductor feels a force from a magnetic field. This is the motor effect. Label the parts of the motor on the pictures below. Are these DC motors or AC? Or both? How can you tell? Rotor Stator Power source Brushes Commutator Describe the application of the motor effect in the galvanometer and the loudspeaker Galvanometer Loudspeaker Features: - Permanent Magnet - Coil - Spring - Power source Features: - Permanent Magnet - Coil - Diaphragm - Power source Characteristics: - Current in wire moves in magnetic field - Spring resists motion of coil - When force from spring is equal to force from motor, needle is still - Depending on resistance of circuit, different scale is read Characteristics: - Current in wire moves in magnetic field up or down - Wire connected to diaphragm - Depending on current, different sounds are produced The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators Electromagnetic Induction and Lenz’s Law Lenz’s Law There are 5 parts to Lenz’s Law. A changing Magnetic flux generates an electro-motive force which induces a current that produces its own magnetic field that opposes the original change that caused it. Predict Observe Apply Magnet and coil Student makes their own predictions Student makes their own observations Electricity generation Falling magnet Student makes their own predictions Student makes their own observations Magnetic dampening Jumping rings Student makes their own predictions Student makes their own observations Projectiles, launching Pendulum Student makes their own predictions Student makes their own observations Magnetic braking Arago’s disk Student makes their own predictions Student makes their own observations Induction motor The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators Generators AC/DC Generator How can you tell if the generator is producing AC or DC electricity? Draw the output of the generator as viewed on the DSO Draw what you think the output of the generator would look like on the DSO: The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators Transformers Transformers use the ideas of electromagnetic induction to transform one voltage into another. We can use experimentation to determine the relationship between the voltage and the number of turns in the coil. First we can count the number of turns in the coil, then use the multimetre to measure the voltage. What is the best way to represent this data? Volts, Vs (V) Number of coils, Ns ~0.4 1 ~0.9 2 ~1.5 4 ~2.3 6 ~3.2 8 Conclusion: From this graph, what can you say about the relationship between the voltage and number of turns in the secondary coil? - direct positive relationship How would you represent this mathematically? Hint, it’s a straight line. - 𝑦 = 𝑚𝑥 + 𝑏 Discussion: You have the relationship between the secondary voltage and coils, Calculate the relationship between the primary voltage and coils? 𝑉! 3.2 = = 0.4 𝑛! 8 Are they the same? Can you write a general expression for all of these 4 terms? 𝑉! 𝑉! = 𝑛! 𝑛! The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators AC Induction Motors Construct from the parts provided, a model AC induction motor. Write down your method for the construction of the models - collect 3 blue iron bars - collect 3 yellow coils - place iron into centre of coils - place coils and iron onto triangular base - place squirrel cage onto support in middle of base - collect 4 radial iron parts - collect 4 black coils - place iron inside coils - place coils onto dowel on blue base - place large circular squirrel cage in centre Calculate the Synchronous speed: 𝑛! = !"#×! ! = where 𝑓 is the motor supply's frequency in hertz and 𝑝 is the number of magnetic poles. Draw the output of the 2 phases on the Digital Signal Oscilloscope at 90 out of phase The University of Sydney School of Physics Motors and Generators Title: Voltage Vs # of coils