* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reciprocating Saw Dissection: Motor Description
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Electrical injury wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Brushless DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Commutator (electric) wikipedia , lookup
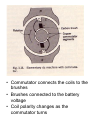
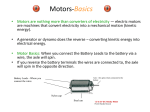
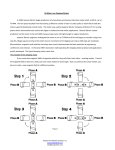
Reciprocating Saw Dissection: Motor Description Thomas Snowdon DC Electrical Principles • When power is from a battery the current is called DC for direct current • Motors that operate from battery power are called DC motors • Current flow from a battery is always in the same direction • Current magnitude in a coil is dependant on battery voltage and wire resistance Design Principles • Driven by electromagnetics • Like magnetic poles repel, opposite magnetic poles attract • Current passed through a coil of wire produces a magnetic field • Changing the direction of current in a coil reverses the magnetic field • The amount of current in a coil will determine the strength of the poles or magnetic field. Motor Construction Major Components • Frame • Stator Coils • Rotor • Commutator and Brushes • Frame is made of metal and supports the other parts • Stator can be made of either permanent magnets or coils of wire on a steel core • Rotor is made up of a shaft, a set of wire coils, and the commutator • Rotor shaft is supported by bearings in the frame • Shaft extends out of the motor to drive tool • Commutator connects the coils to the brushes • Brushes connected to the battery voltage • Coil polarity changes as the commutator turns Operation • Motor creates a rotating motion from the battery power • As the motor rotor turns the commutator switches the current flow in the rotor coils • Motor shaft has a gear attached to drive the next piece of the tool • Speed of the motor is dependant on the current flow through the coils Advantages and Disadvantages of DC Motors Advantages: • Variable speed control • Portable • Can handle heavy torque loads Disadvantages • Complex to build and expensive • Not as reliable as other motors • Difficulty keeping a constant speed Conclusion • The motor used in this tool is a DC type motor • Operates on battery power • Runs at variable speeds • Can handle heavy torque loads created by tool use References • Fitzgerald, A. E., Charles Kingsley, and Alexander Kusko. Electric Machinery. 3rd ed. McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1971. • http://www.ni.com/ References • Fitzgerald, A. E., Charles Kingsley, and Alexander Kusko. Electric Machinery. 3rd ed. McGraw-Hill Book Company, 1971. • http://www.ni.com/