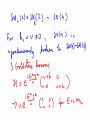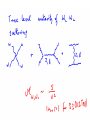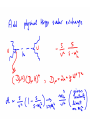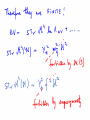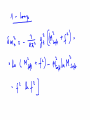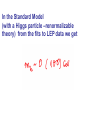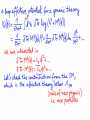* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What breaks electroweak symmetry
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Relational approach to quantum physics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Identical particles wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Weakly-interacting massive particles wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Yang–Mills theory wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear structure wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
ATLAS experiment wikipedia , lookup
Event symmetry wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
An Exceptionally Simple Theory of Everything wikipedia , lookup
Theory of everything wikipedia , lookup
Large Hadron Collider wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Quantum chromodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Higgs boson wikipedia , lookup
Future Circular Collider wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
Search for the Higgs boson wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Technicolor (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Supersymmetry wikipedia , lookup
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
Higgs mechanism wikipedia , lookup
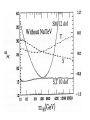
WHAT BREAKS ELECTROWEAK SYMMETRY ? We shall find the answer in experiments at the LHC? Most likely it will tells us a lot about the physics beyond the SM Electroweak symmetry breaking in the SM by the Higgs sector (renormalizable lagrangian) Properties of the Higgs potential crucial for the electroweak theory: SU(2)xSU(2) global symmetry of V : Spontaneously broken to the diagonal subgroup SU(2) The Higgs mechanism then ensures that the Goldstone bosons become the longitudinal modes of the gauge bosons W,Z which acquire masses. Renormalizability not crucial for EWSB But crucial for ensuring unitarity of e.g. WW scattering by exchange of one physical Higgs particle h INDEED, In the Standard Model, the EWSB is described but not explained Can we better understand the Fermi scale? e.g. calculate it in terms of some more fundamental parameters? The hierarchy problem of the Standard Model. SUPERSYMMETRY ------MANY VIRTUES Higgs sector of the MSSM: two Higgs doublets; Fermi scale calculated in terms of the soft supersymmetry breaking parameters; generated by quantum corrections to the Higgs potential due to the large top quark mass (Ibanez, Ross) The lightest physical scalar has similar properties as the Higgs particle in the SM; DOUBLE PROTECTION FOR THE HIGGS POTENTIAL SUPERSYMMETRY PLUS LOW ENERGY GLOBAL SYMMETRY; NO STRONGLY INTERACTING NEW PHYSICS Prediction – new fermionic states needed by global symmetry, e.g. new top quark around 1 TeV Non –supersymmetric „solutions” to the origin of the Fermi scale. Revival of those approaches inspired by various theoretical ideas (extra dimensions, AdS/CFT correspondence, deconstruction,… General picture –new strong interactions that provide a low-scale cut-off to the (non-renormalisable) electroweak theory and are responsible for electroweak symmetry breaking Well-known example : rescaled QCD (technicolour) CONCLUSION Barrel organ: the power source is commonly assumed to be a crank, turned by the operator or by his monkey. A barrel organ player has been asked how to compose good music. Just smoothly turn the crank, he replied. Supersymmetry – elementary scalars Minimal supersymmetric model – renormlizable extension of the SM UV behaviour improved due to fermionboson cancellations; Superpartner masses- cut off in the SM Higgs potential The impact of physics beyond the Standard Model on precision electroweak data can be studied in a model independent way by adding to the SM lagrangian higher dimension operators In the Standard Model (with a Higgs particle –renormalizable theory) from the fits to LEP data we get