* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Magnetic Flux Faraday`s Law
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
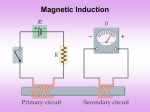
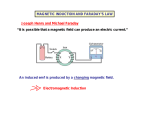
2/25/2014 Magnetic Flux • Recall: when you put a loop of wire in a magnetic field it will rotate until the magnetic moment (the vector normal to area) is aligned with the field. • The degree of alignment with the field is measured using magnetic flux Φ : Φ ≡ ܣ ܤcos ߠ • Magnetic flux tells us how much field is passing through the loop given the angle between field and normal • Magnetic flux is measured in Tmଶ 2 Faraday’s Law • Principle of EM induction: A change in the magnetic flux through a loop produces an a induced ‘EMF’ or electromotive force (voltage) ℰ and therefore an induced current in the loop is given by Faraday’s Law: ∆Φ ℰ = −ܰ ∆ݐ • The minus sign tells us that the induced emf would be created so that its own field points in a direction opposite to the change in the field causing it in the first place. (Lenz’s Law; coming up shortly) • Simulation: http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/faraday 3 1 2/25/2014 Example • For a coil with ܰ = 2, = ܣ0.0050 mଶ , ܤ = 0.010 T, ߠ = 0°, the field changes to ܤ = 0.030 T still in the same direction. What’s the resulting emf ℰ if the change took one ∆ second? ℰ = −ܰ ∆௧ಳ ∆Φ = Φ − Φ 4 5 Lenz’s Law • Lenz’s Law: The direction of the induced emf and induced current will be such as to produce a magnetic field which opposes the original change in magnetic flux • This is needed to prevent a violation of the conservation of energy! 6 2 2/25/2014 7 8 9 3 2/25/2014 Examples 10 Applications: 1. Induction Motor • As the coil is rotated in the magnetic field flux changes and induces current to flow in the coil • What is the direction of the current in the coil? 11 Applications: 2. Magnetic Induction Stoves • Magnetic induction cooking. • The magnetic field induces an electric field in the metal of the pan. • never use aluminum foil on it! 12 4 2/25/2014 Electrical Resistance • We have already seen in lab that current and potential difference (voltage) are related through Ohm’s Law: ∆ܸ =ܫ ܴ • where ܴ is the resistance measured in ohms Ω = V/A • Since emf (ℰ) is a potential difference, for a coil where flux is changing we have: ℰ ܰ ∆Φ ܫௗ௨ௗ = = − ܴ ܴ ∆ݐ 13 5