* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Psychological Disorders
Involuntary commitment internationally wikipedia , lookup
History of psychopathy wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Anti-psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Dodo bird verdict wikipedia , lookup
Lifetrack Therapy wikipedia , lookup
Psychiatric survivors movement wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mental status examination wikipedia , lookup
Psychological trauma wikipedia , lookup
Mental health professional wikipedia , lookup
Eating disorder wikipedia , lookup
Deinstitutionalisation wikipedia , lookup
Moral treatment wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatric institutions wikipedia , lookup
Homelessness and mental health wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
Pyotr Gannushkin wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Externalizing disorders wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
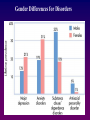
Psychological Disorders: An Introduction Defining Disorder Psychological Disorders •Psychopathology—scientific study of the origins, symptoms, and development of psychological disorders •Psychological disorder - a pattern of behavioral and psychological symptoms that causes significant personal distress, impairs the ability to function in one or more important areas of daily life, or both Psychological Disorder • A “harmful dysfunction” in which behaviors are maladaptive, unjustifiable, disturbing, and atypical MUDA • A mnemonic device used to remember the four attributes of a psychological disorder – Maladaptive – Unjustifiable – Disturbing – Atypical Maladaptive • An exaggeration of normal, acceptable behaviors • Destructive to oneself or others Unjustifiable • A behavior which does not have a rational basis Disturbing • A behavior which is troublesome to other people Atypical • A behavior so different from other people’s behavior that it violates a norm • Norms vary from culture to culture Understanding Disorders Early Views of Mental Illness • In ancient times, mental illness was usually explained through a supernatural model; the person was possessed or a sinner • During the Middle Ages treatment methods were inhumane and cruel Philippe Pinel (1745-1826) • French physician who worked to reform the treatment of people with mental disorders • Encouraged more humane treatment Understanding Disorders: The Medical Model The Medical Model • Diseases have physical causes that can be diagnosed, treated, and in most cases, cured. • Psychological disorders can be diagnosed based on their symptoms and treated or cured through therapy. • Psychological disorders are similar to a physical illness. Understanding Disorders: The Bio-Psycho-Social Model Bio-Psycho-Social Model • Perspective of mental illness which assumes that biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors combine and interact to produce psychological disorders Bio-Psycho-Social Perspective Classifying Disorders DSM-V • Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders – Fifth Edition • A guidebook for clinicians for diagnosis • Provides a common language to label mental disorders • Recently revised by the American Psychiatric Association – See the Changes made in this new addition • Lists and describes symptoms for 250 specific psychological disorders • Has changed significantly since the first edition Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-V) • Describes specific symptoms and diagnostic guidelines for psychological disorders – Clinical Presentation (What are the symptoms?) – Etiology (What causes the disorder?) – Developmental Stage (How does this look in kids? Adults?) – Functional Impairment (What will happen short-term & long-term?) Labeling Stigmas • Studies show a clear bias against people diagnosed with mental disorders. • Rosenhan Study – “normal” people pretended to hear voices and checked into a mental health facility then acted normally. Their normal actions taken to be abnormal once they were labeled schizophrenic. Gender Differences for Disorders Prevalence of Mental Disorders Worldwide Americans with disorders Are People with a Mental Illness as Violent as the Media Portrays Them? • People with mental disorders are often depicted on TV as helpless victims or evil villains who are unpredictable, dangerous, and violent. • One study indicated that, overall, former mental patients did not have a higher rate of violence than a matched comparison group. • People with severe mental disorders who are experiencing bizarre delusional ideas and hallucinated voices do have a slightly higher level of violent and illegal behavior than do “normal” people.