* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Happy Tuesday! Pull out a ½ sheet of paper or share a whole with
Survey
Document related concepts
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Phanerozoic wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Marine geology of the Cape Peninsula and False Bay wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
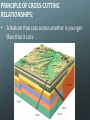
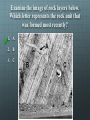
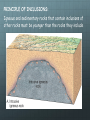
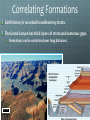
Happy Tuesday! Pull out a ½ sheet of paper or share a whole with your neighbor. Weekly Schedule Today Quiz # 2 Relative Dating Age of the Earth Geotimeline Act Thursday Radiometric Dating Geologic dating methods lab WORK WITH A CLASSMATE TO PUT THIS LIST OF EVENTS IN CHRONOLOGICAL ORDER: • MOTHER’S BIRTH • GRANDFATHER MEETS GRANDMOTHER • MOTHER MEETS FATHER • MY HIGH SCHOOL GRADUATION • MY GRANDFATHER’S BIRTH (THERE ARE CERTAIN CONDITIONS THAT MUST BE TRUE FOR A SEQUENTIAL EVENT TO OCCUR) LIKEWISE THERE ARE A SET OF PRINCIPLES THAT GOVERN THE DEPOSITION OF ROCK ON EARTH Geologic Time Relative ages—based upon order of formation Qualitative method developed hundreds of years ago. Permit determination of older vs. younger relationships. Numerical ages—actual number of years since an event Quantitative method developed recently. PRINCIPLE OF UNIFORMITARIANISM: “The present is key to the past.” -James Hutton • Processes seen today are the same as those of the past. PRINCIPLE OF SUPERPOSITION: • Younger sedimentary rocks overlie older rocks Examine the image of rock layers below. Which letter represents the layer that was formed earliest? 1. A 2. B 3. C 4. D Image courtesy of USGS PRINCIPLE OF ORIGINAL HORIZONTALITY: Sedimentary rocks are deposited relatively horizontal Folds and tilting must postdate deposition Examine the image of rock layers below. Tilting must have occurred 1. After A was deposited 2. Between the deposition of E and A 3. before B was deposited. 4. between deposition of layers C and E. PRINCIPLE OF LATERAL CONTINUITY • Sedimentary rocks accumulate in continuous sheets These layers once spanned the canyon at one time Examine the image of rock layers below. Which statement is most accurate in regard to rocks located at A and B? 1. A is older than B 2. B is older than A 3. A and B are the same age PRINCIPLE OF CROSS-CUTTING RELATIONSHIPS: • A feature that cuts across another is younger than that it cuts Dike = an igneous intrusion that cuts across preexisting rock Is the dike older or younger than the surrounding rock? Examine the image of rock layers below. Which letter represents the rock unit that was formed most recently? 1. A 2. B 3. C PRINCIPLE OF INCLUSIONS: Igneous and sedimentary rocks that contain inclusions of other rocks must be younger than the rocks they include The embedded rocks (inclusions) in the sedimentary layers are: A. metamorphic. B. older than the sedimentary layers. C. younger than the sedimentary layers. D. the same age as the layers. The Principle of Fossil Succession Fossils are often preserved in sedimentary rocks. Fossils are time markers useful for relative age-dating. Fossils speak of past depositional environments. Specific fossils are only found within a limited time range. Unconformities • Gaps in the rock record are called unconformities. • EROSION OR NONDEPOSITION • An angular unconformity happens when tilted or folded rock is covered by younger, horizontal rock. Examine the image of rock layers below. An angular unconformity is present between layers ___ and ___. 1. A and E 2. B and D 3. C and F 4. F and D Correlating Formations Earth history is recorded in sedimentary strata. The Grand Canyon has thick layers of strata and numerous gaps. Formations can be correlated over long distances. Fig. 10.6a Geologic Time The geologic time scale—a “calendar” of Earth history. • Originally created using relative dates • Specific dates using radiometric dating • Subdivides geologic history into units: Eons, eras, periods, and epochs based on changes in life forms Precambrian Time The Precambrian ranges from 4.5 billion years ago to ~543 million years ago. • ~90% of Earth’s history • Considerable volcanic activity • Meteorite bombardment • Cyanobacteria • Soft-bodied organisms • Primitive atmosphere and ocean • Beginnings of lithospheric plate formation and movement The Paleozoic Era Spans ~300 million years. Six periods: Periods are marked by changes in: • In life forms, tectonics, and changes in sea level—rise and fall of sea level. The Mesozoic Era Mesozoic era spans ~180 million years from 248 Ma to 65 Ma Often called the “age of reptiles” -first true terrestrial animals • • • • Dinosaurs dominated. One group of reptiles led to the birds. Many reptile groups, along with many other animal groups, become extinct at the close of the Mesozoic. Possible Hypotheses for Extinction: — Impact from large asteroid or comet. — Extensive volcanism. The Cenozoic Era Cenozoic—a smaller fraction of geologic time than the Paleozoic or Mesozoic • 65 million years ago to the present • Often called the “age of mammals” • Pangaea’s breakup complete • • • One-third of the land covered by ice Marine mammals and large land animals evolved Humans evolved