* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BLM 2-30, Compare the Events of Meiosis and Mitosis Key Meiosis I
Survey
Document related concepts
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Kinetochore wikipedia , lookup
Spindle checkpoint wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
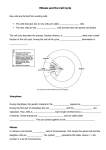
BLM 2-30, Compare the Events of Meiosis and Mitosis Key Meiosis I Mitosis Prophase I Prophase (early and late) nucleolus disappears nuclear membrane disappears spindle fibres form homologous chromosomes pair up and each attach to spindle fibres non-sister chromatids exchange genetic material (crossing over) nucleolus disappears nuclear membrane disappears spindle fibres form individual chromosomes attach to spindle fibres Metaphase I homologous chromosomes pair up at the equator Metaphase chromosomes form a single line at the equator Anaphase I spindle fibres contract and shorten homologous chromosomes attached to Anaphase spindle fibres contract and shorten the centromere pulls apart, and the sister centromeres separate and are pulled to opposite poles by the spindle fibres chromatids separate and are pulled to opposite poles by the spindle fibres Telophase I one chromosome from each homologous pair is Telophase one complete set of chromosomes is now at each at each pole of the cell the spindle fibres disappear the nucleolus appears within each nucleus the nuclear membrane forms pole of the cell the spindle fibres disappear the nucleolus appears within each nucleus the nuclear membrane forms Interkinesis cell divides in two (not genetically identical to parent cell) cell will grow and make proteins like interphase in mitosis no replication of DNA in this stage Cytokinesis cell divides in two (genetically identical to parent cell) cell will grow and make proteins like interphase in mitosis DNA will replicate later in interphase Meiosis II Mitosis Prophase II Prophase (early and late) nucleolus disappears nuclear membrane disappears spindle fibres form individual chromosomes attach to spindle fibres nucleolus disappears nuclear membrane disappears spindle fibres form individual chromosomes attach to spindle fibres Metaphase II X-shaped chromosomes form a single line at the equator Metaphase X-shaped chromosomes form a single line at the equator Anaphase II spindle fibres contract and shorten the centromere pulls apart and the sister chromatids separate and are pulled to opposite poles by the spindle Anaphase spindle fibres contract and shorten the centromere pulls apart, and the sister chromatids separate and are pulled to opposite poles by the spindle Telophase II Telophase half of a complete set of chromosomes is now at one complete set of chromosomes is now at each each pole of the cell (one chromosome for each pair) the spindle fibres disappear the nucleolus appears within each nucleus the nuclear membrane forms the spindle fibres disappear the nucleolus appears within each nucleus the nuclear membrane forms pole of the cell Cytokinesis cell divides in two (total four daughter cells not genetically identical to parent) cell will grow and make proteins like interphase in mitosis Cytokinesis cell divides in two (genetically identical to parent) cell will grow and make proteins like interphase in mitosis






![MITOSIS WORKSHEET - New Page 1 [bs079.k12.sd.us]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014668413_1-30813973b0cb9de17ced950a5cb16263-150x150.png)