* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STATE of MATTER
Survey
Document related concepts
Surface tension wikipedia , lookup
Superfluid helium-4 wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Sessile drop technique wikipedia , lookup
X-ray crystallography wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor wikipedia , lookup
Supercritical fluid wikipedia , lookup
Self-assembled monolayer wikipedia , lookup
Crystal structure wikipedia , lookup
Glass transition wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
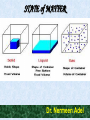
STATE of MATTER Dr. Nermeen Adel SOLID, LIQUID and GAS are the most common states of matter on Earth. Gases • Gas molecules have enough KINETIC ENERGY so that the effect of intermolecular forces is small. • A gas has NO DEFINITE shape or volume, but occupies the entire container in which it is confined • A Supercritical Fluid has the physical properties of a gas, but its high density confers solvent (liquid) properties i.e. supercritical carbon dioxide (solvents). Gases assume the volume and shape of the container. Gases are the most compressible state of matter Liquids • A liquid is a nearly incompressible FLUID that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. • Intermolecular forces are important, but the molecules have enough energy to move relative to each other and the structure is mobile. Liquids The highest temperature (at constant pressure)at which a given liquid (water) can exist is CRITICAL TEMPERATURE Solids • Their particles (ions, atoms or molecules) are PACKED CLOSELY together. The forces between them are STRONG enough so that they cannot move freely but can only vibrate. • A solid has a stable, definite shape, and a definite volume. • Solids can be changed into liquids by melting, and liquids can be transformed into solids by freezing. They can also change directly into gases through the process of sublimation. Solids Types of SOLIDS • CRYSTALLINE • AMORPHOUS Crystalline solid FORCES BETWEEN SOLID ATOMS IONIC BOND A crystal of sodium chloride (common salt) is made up of ionic sodium and chlorine COVALENT BOND In diamond or silicon, the atoms share electrons . ORGANIC COMPOUNDS, are held with Van der Waals forces resulting from the polarization of the electronic charge cloud on each molecule. Characterization of Crystalline Materials BY: • X-ray diffraction • Melting points • Polymorphs Amorphous solid It refers to materials with NO particular structure (lack of form). The atoms or molecules of amorphous materials are arranged in the SAME manner as they are in a liquid. They have increased mobility due to greater intermolecular distances. We can say that an amorphous system is actually fluid but appears to be a solid Properties of Amorphous Solid *** The molecules are closely packed & chemically bonded. *** Any material can be prepared as an amorphous solid. All amorphous materials have crystalline counterparts. *** Crystalline form will generally be more stable than the amorphous one, as the crystalline solid is at chemical equilibrium, whereas the amorphous form is not. Polymorphs • The molecules arrange themselves in two or more different ways in the crystal. They are arranged either differently in the crystal lattice or there may be differences in the orientation of the molecules at the lattice sites. • The polymorphs have different Physical and Chemical properties; i.e. different chemical reactivity, different melting points, solubilities. • Formation of polymorph by a drug depends on the conditions of crystallization; i.e. , the solvent used, the rate of crystallization and the temperature. Polymorphism problems in pharmaceutical preparations • It may be difficult to inject in suspension form or to formulate as tablets. • Change between polymorphic forms during storage can cause changes in crystal size in suspensions and their eventual caking. • Crystal growth in creams as a result of phase transformation can cause the cream to become gritty. Cont. • Changes in polymorphic forms of vehicles such as theobroma oil (cocoa butter), used to make suppositories, could produce supp. with different and unacceptable melting characteristics. COCOA BUTTER COCOA BUTTER is single glyceride, used as suppository base, it melts (34 oC – 36 oC). It has 4 polymorphic forms: • meta stable gamma form melting at 18 oC • alpha form melting at 22 oC, • beta prime form melting at 28 oC • stable beta form melting at 34.5 oC Proper Method of Preparation COCOA BUTTER • Melt cocoa butter at the lowest possible temperature, about 33oC. • Pour when sufficiently fluid; SO the crystal nuclei of the stable beta form are not lost. • When the mass is chilled in the mold, a stable suppository, consisting of beta crystals, which melt at 34.5oC, is produced. Liquid crystals (LCs) • It is state of matter that have properties between those of a conventional liquid and those of a solid crystal. • Liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way like a solid. • Liquid crystals can be divided into Thermotropic Lyotropic and Metallotropic phases. Liquid crystals (LCs) Thermotropic It exhibits a Phase Transition into the liquid crystal phase as Temperature is changed. (organic) Lyotropic It exhibits Phase Transition as a function of both Temperature and Concentration of the liquid crystal molecules in a Solvent (typically water). (organic) Metallotropic Their liquid crystal Transition depends not only on Temperature and Concentration, but also on the inorganic-organic composition ratio. (inorganic & organic) Applications of liquid crystals • In birefringence, the light passing through a material is divided into two components with different velocities and hence different refractive indices. Describes how • Some liquid crystals show consistent color light propagate changes with temperature, so they are used through medium to detect areas of elevated temperature under the skin that may be due to a disease process. • Liquid crystals are sensitive to electric fields, a property of advantage in developing display systems. (LCD) Ionic bond : attraction between complete positive and negative charge Van der Waals forces : attraction between partial positive and partial negative charge So, it is weaker than the ionic bond