* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 3 Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
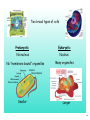
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
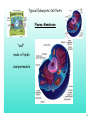
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
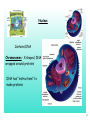
Transcript
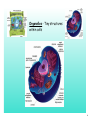
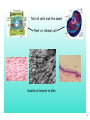
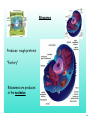
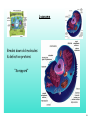
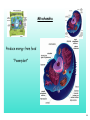
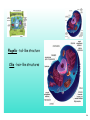
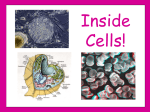
Chapter 3 Cells and Their Structures Section 1 - Intro to Cells 1 Cells Smallest unit of living thing Macromolecules build cells 2 We can see cells using a But, if we use an electron microscope we can see MUCH more! 3 Organelles - Tiny structures within cells 4 5 6 Cell Theory 3 parts... 7 Levels of organization 8 Not all cells look the same! Plant vs. Animal cell muscle vs neuron vs skin 9 1 A group of similar cells working together is called a(n) A Tissue B Organ C Organ System D Organism 10 2 Tiny structures that make up cells are called A Organs B Nucleus C Organelles D Sub-units 11 3 Which type of microscope allowed us to see organelles inside of cells? A Light Microscope B Electron Microscope C Sonic Microscope D Telescope 12 Section 2 Cell Structures 13 Two broad types of cells Prokaryotic Eukaryotic No nucleus Nucleus No "membrane bound" organelles Smaller Many organelles Larger 14 Typical Eukaryotic Cell Parts Plasma Membrane "wall" made of lipids semipermeable 15 Cytosol water + other molecules cytosol + organelles = cytoplasm 16 Nucleus Contains DNA Chromosomes - X shaped, DNA wrapped around proteins DNA has "instructions" to make proteins 17 Ribosomes Produces rough proteins "Factory" Ribosomes are produces in the nucleolus 18 Endoplasmic Reticulum Rough ER vs Smooth ER Proteins Lipids Transports products "Highway" 19 Golgi apparatus Finishes proteins "Refinery" Ships them to destination in vesicles "Post Office" 20 Lysosome Breaks down old molecules & defective proteins "Scrapyard" 21 Mitochondria Produce energy from food "Powerplant" 22 Cytoskeleton Gives shape and strength to cell 23 Flagella - tail-like structure Cilia - hair-like structures 24 4 The "brain" of the cell is the A Endoplasmic Reticulum B Ribosomes C Nucleus D Plasma Membrane 25 5 Which organelle produces proteins? (is like a factory) A Endoplasmic Reticulum B Ribosomes C Nucleus D Plasma Membrane 26 Special Plant Organelles Cell Wall Strength & Protection 27 Vacuole Stores water and nutrients 28 Chloroplast Location of photosynthesis 29 6 Which structure does a plant cell have that an animal cell does not? A Mitochondria B Plasma Membrane C Golgi apparatus D Cell Wall 30 7 Which organelle in a plant cell is the location of photosynthesis? A Chloroplast B Mitochondria C Vacuole D Cell Wall 31