* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science 8
Survey
Document related concepts
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
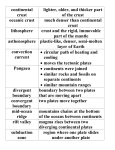
Science 8 Study Guide Chapter 7 Name _______________________________________ Date _____________ A. Match each of the following with the correct definition or description. ____1. The crust and upper mantle make up this layer of the earth A. Continental Drift ____2. The place where plates move together B. Pangaea ____3. This is the name for the place where one plate is forced under another. C. Convergent Boundary ____4. Alfred Wegener believed that these were all once joined together. D. Mid-Ocean Ridge ____5. This name comes from two words that mean, “all land.” E. Asthenosphere ____6. An underwater mountain chain F. Subduction Zone ____7. The Earth’s thick, plastic like layer G. Lithosphere ____8. The main points of evidence for this are fossils, rocks, and climate. H. Continents B. Choose the best answer to complete each section. ____1. At what rate do scientists say the Earth’s plates move? a. 1cm to 12 cm a century b. 1cm to 12 cm a decade c. 1cm to 12 cm a year ____2. Why does seafloor spreading occur? a. Because earthquakes break apart the ocean floor b. Because molten material beneath the Earth’s crust rises to the surface c. Because new material is being added to the Asthenosphere ____3. What is the hypothesis called that says the continents have slowly moved to their current locations? a. Continental slope b. Continental drift c. Magnetic reversal ____4. What do plates of the lithosphere float on? a. The crust b. The core c. The Asthenosphere ____5. Where are the youngest rocks on the ocean floor located? a. At mid-ocean ridges b. Near Asia c. Near continents ____6. The presence of the same ______________on several continents supports the hypotheses of continental drift. a. Fossils b. Rocks c. Both a and b ____7. What is the name of a place where plates move apart? a. Stable boundaries b. Transform boundaries c. Divergent boundaries ____8. Before the continental drift, what was the name given by scientists for the single super continent? a. Glomar b. Pangaea c. Wegener ____9. What mountains were formed by the collision of the Indo-Australian Plate and the Eurasian Plate? a. Appalachian b. Rocky c. Himalayan ____10. The matching of ________ on different continents are evidence of continental drift. a. Weather patterns b. Wind systems c. Rock structures ____11. What forms where two oceanic plates collide? a. A subduction zone b. A hot spot c. A rift valley ____12. Which of the following is an example of a transform boundary? a. The Appalachian Mountains b. The Mid-Atlantic Ridge c. The San Andreas Fault ____13. What type of currents might drive plate motion? a. Vertical b. Convection c. Horizontal ____14. What are formed when two continental plates collide? a. Mountain ranges b. Strike-slip faults c. Rift valleys ____15. What is the Great Rift Valley in Africa an example of? a. A Transform boundary b. A convergent boundary c. A divergent boundary C. Write a description of the following. 1. Describe how a mid-ocean ridge is made.















![jeopardy_platetectonics[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008388988_1-c1f7a56df21131a376d1ab2c8c0b8111-150x150.png)



