* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fixed Ratio (FR)
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Parent management training wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Psychophysics wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
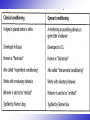
OPERANT CONDITIONING OPERANT CONDITIONING • Learning in which a certain action is reinforced or punished, resulting in corresponding increases or decreases in behavior. OPERANT CONDITIONING • Reinforcement: A stimulus or event that follows a response and increases the likelihood that the response will be repeated. • Punishment An unpleasant consequence occurs and decreases the frequency of behavior that produced it. OPERANT CONDITIONING Positive Reinforcement Making a behavior stronger by following the behavior with a pleasant stimulus. Example: a rat presses a lever and receives food. Negative Reinforcement Making a behavior stronger by taking away a negative stimulus. Example: a rat presses a lever and turns off the electric shock. PUNISHMENT + Positive punishment – The application of an aversive stimulus after a response. Example: You touch a hot plate; the painful consequence reduces the likelihood of you repeating that behavior. - Negative punishment - Results from the removal of a reinforcer. Example: Your parents take away your cell phone because you are not doing well in school. Limitations of Punishment • Punishment often only produces temporary changes • Punishment produces undesirable emotional side effects • Children who are physically punished learn to model or imitate aggressive acts and often become more aggressive in their interactions with others • Punishment NEVER teaches a new behavior Primary vs Secondary Reinforcers • Primary – Innate (unlearned) • Secondary – Conditioned (learned) Schedules of Reinforcement • Ratio schedules – Provide reward after a certain number of responses. • Interval schedules – Provide reward after a certain time interval. Fixed Ratio (FR) Variable Ratio (VR) Fixed Interval (FI) Variable Interval (VI) Schedules of Reinforcement Fixed Ratio (FR) Variable Ratio (VR) Fixed Interval (FI) Variable Interval (VI) Rewards appear after a certain set number of responses. e.g. factory workers getting paid after every 10 cases of product are completed Schedules of Reinforcement Fixed Ratio (FR) Variable Ratio (VR) Fixed Interval (FI) Variable Interval (VI) Rewards appear after a certain number of responses, but that number varies from trial to trial. e.g. slot machine payoffs Schedules of Reinforcement Fixed Ratio (FR) Variable Ratio (VR) Fixed Interval (FI) Variable Interval (VI) Rewards appear after a certain fixed amount of time, regardless of number of responses. e.g. weekly or monthly paychecks Schedules of Reinforcement Fixed Ratio (FR) Variable Ratio (VR) Fixed Interval (FI) Variable Interval (VI) Rewards appear after a certain amount of time, but that amount varies from trial to trial. e.g. random visits from the boss who delivers praise Shaping • A technique in which a new behavior is produced by reinforcing responses that are similar to the desired response. Chaining • Response chains – Learned reactions that follow one another in sequence, each reaction producing the signal for the next. Swimming has 3 major chains: – Arm stroking chain – Breathing chain – Kicking chain Aversive Control • Escape Conditioning – Training of an organism to remove or terminate an unpleasant stimulus. • Example: A child whines and gags when he eats his vegetables, so his mother removes them from his plate. • Avoidance Conditioning – Training of an organism to withdrawal from or prevent an unpleasant stimulus before it starts. • Example: A child complains that he does not like vegetables, so his father does not cook them for dinner. Classical vs. Operant Conditioning • Classical Conditioning – involves the association of two stimuli (UCS + CS) before the response or behavior. • Operant Conditioning – involves a reinforcing (reward) or punishing stimulus after a response or behavior.