* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduccon to PLATE TECTONICS
Survey
Document related concepts
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Van Allen radiation belt wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
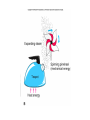
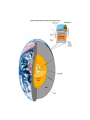
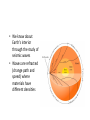
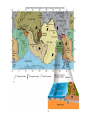
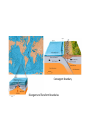
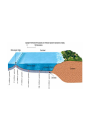
Introduc)onto PLATETECTONICS part1:Earth’sStructureandFounda)ons AlessandroGrippo,Ph.D. Earthissubjecttochange • Earthchangesin)me • Earthchangesinspace • Energyforchangecomes(asheat)from: – anexternalsource(theSun) – aninternalsource(radioac)vedecayinEarth’s coreandmantle) • HeatfromtheSun:weathering&erosion – atmosphericandoceaniccircula)on,watercycle, erosion,“smoothing”ofoutersurface • Heatfromradioac)vity:platetectonics – buildingofoceans,mountains,con)nents; volcanoesandearthquakes,“roughing”ofthe outersurface Heatvs.Temperature • Heat – energytransferfromabodytoanotherduetoa differenceintemperature • Temperature – ameasureoftheaveragekine)cenergyofthe moleculesthatmakeupasubstance Heatcantravel(transfer)inthreedifferentways: conduc)on,radia)on,convec)on HowDoesHeatTravel? • Radia)on – Heatenergyisfeltfromahotobjectatadistance (aroundafire,baskinginthesun,etc.) • Conduc)on – Heatenergyisfeltbytouchingahotobject(ahotpan, hotwater,etc.) • Convec)on – Heatenergyistransferredinbulkmo)onorflowofa fluidmass(alavalamp,theasthenosphere,etc.) Earth’sInterior • Layersbasedonchemicalcomposi)on(layersaremadeofdifferent rocks),frominsideoutward: – Core – Mantle – Crust • OceanicCrust • Con)nentalCrust • Layersbasedonphysicalbehavior(independentlyfromwhatthey aremadeof,rocksbehaveindifferentways),frominsideoutward: – – – – InnerandOuterCore Mesosphere Asthenosphere Lithosphere • Composi)onalLayers – Crust(~3-70kmthick) • VerythinouterrockyshellofEarth – Con)nentalcrust-thickerandlessdense – Oceaniccrust-thinnerandmoredense – Mantle(~2900kmthick) • Hotsolidthatflowsslowlyover)me;Fe-,Mg-,Si-richminerals – Core(~3400kmradius) • Outercore-metallicliquid; • mostlyiron • Innercore-metallicsolid;mostlyiron HowdoweknowaboutEarth’slayers? • Notbydrilling:wedonothavethetechnology toreachthecoreorthemantle) – deepestwellisabout11km(11,000mor~7mi) – thicknessofthecrust: • oceaniccrust:around5km–cannotdrillbecausewe alsohave5kmofoceanaboveit • con)nentalcrust:upto80km–toothicktodrill – wehaveneverseenthemantleorthecore • Weknowabout Earth’sinterior throughthestudyof seismicwaves • Wavesarerefracted (changepathand speed)where materialshave differentdensi)es • P(primary)andS(secondary)waves – PwavesarefasterthanSwaves – Swavesdonottravelthroughliquids – Swavesdonotreachpastthe“shadowzone” – Swavesarestopped(reflected)atthemantle/core boundary • Thisimpliesthattheoutercoreisliquid – ThepakernofPandSwavesrefrac)ontellsus wherethesechangesoccur • Earth’scoreismadeofIron(Fe)andNickel(Ni) • Theinnercoreissolidwhiletheoutercoreis liquid • MetalslikeFearekepttogetherbyachemical bondcalledmetallicbond • Inmetallicbonds,electronsarefreetoroam • Whenelectronsroam,theycreatean electricalcurrent • Inablockofironthesecurrentscanceleach otherout • Iftheoutercoreisliquid,andEarthrotates arounditsaxis,theironisinmo)on • Iftheironisinmo)on,itwillcreatean electricalcurrent • Anyelectricalcurrentwouldalsocreatea magne)cfield Earth’sMagne)cField • thespinningofEarth: – causesametallicliquid outercoretomove – createsanelectrical field – thatgeneratesEarth’s magne)cfield • Earth’sMagne)cField: – protectsus(life)fromdamagingsolarradia)on – canberecordedincertainrocks,par)cularlythose formingatthebokomoftheocean – itsproper)eschangefromplacetoplaceonEarth, andcanbeiden)fied – itisveryusefulingeologicalstudies • MechanicalLayers – Lithosphere(~100kmthick) • Rigid/brikleoutershellof Earth • Composedofbothcrust anduppermostmantle • MakesupEarth’stectonic “plates” – Asthenosphere • Plas)c(capableofflow) zoneonwhichthe lithosphere“floats” PLATETECTONICS • ThesurfaceofEarthisbrokendowninaseries ofLITHOSPHERICPLATES,thatmovearound passively,draggedbyCONVECTIONINTHE ASTHENOSPHERE • Therearesevenmajorplates(NorthAmerica, SouthAmerica,Pacific,Eurasia,Africa, Antarc)ca,India-Australia)andavarietyof smallerones • Con6nentalDri8Hypothesis – Originallyproposedinearly20thcenturytoexplainthe“fitof con)nents”,commonrocktypesandfossilsacrossoceanbasins,etc. – Insufficientevidencefoundfordrivingmechanism;hypothesisini)ally rejected • PlateTectonicsTheory – Originallyproposedinthelate1960s – Includednewunderstandingoftheseafloorandexplana)onofdriving force – Describeslithosphereasbeingbrokenintoplatesthatareinmo)on – Explainsoriginandloca)onsofsuchthingsasvolcanoes,faultzones andmountainbelts • Divergentboundaries – Platesmoveapart – Magmarises,coolsandformsnewlithosphere – Typicallyexpressedasmid-oceanicridges • Transformboundaries – Platesslidepastoneanother – Faultzonesandearthquakesmarkboundary – SanAndreasfaultinCalifornia • Convergentboundaries – Platesmovetowardeachother – Mountainbeltsandvolcanoescommon – Oceanicplatesmaysinkintomantlealongasubduc6onzone,typically markedbyadeepoceantrench ConvergentBoundary DivergentandTransformBoundaries PlateTectonics endofpart1