* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells and Basketball
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
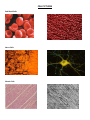
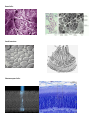
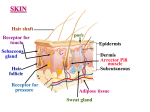
Name: ____________________________________________ Date: _____________________ Period: ____________ Cells and Basketball? When you shoot a basketball many parts of your body work together to help you make the shot! These different parts are made up of different tissues and cells. Each type of cell is specialized to perform its job in shooting a basketball. Cells can be specialized in their shape and the organelles that they have within them. Organelles are small parts of a cell that perform certain jobs with in the cell. For example one organelle, mitochondria, is often called the powerhouse of the cell because it produces energy for the cell to do its work. The mitochondria is where cellular respiration takes place. Organelles are like the organs of your body. The organs in your body perform a certain job to help keep you alive. Like your heart beats and pumps blood around your entire body. Look at the pictures of the cells that are provided. Use these pictures and slides to answer the questions below. You will have to think hard and look closely at the pictures to answer the questions so have fun! Red Blood Cells: Red blood cells (also called erythrocytes) are shaped like slightly indented, flattened disks. RBCs contain the iron-rich protein hemoglobin. Blood gets its bright red color when hemoglobin picks up oxygen in the lungs. The main function of the RBC is to transport and provide oxygen to the cells of the body. As the blood travels through the body, the hemoglobin releases oxygen to the tissues. The body contains more RBCs than any other type of cell. 1. What role would the red blood cells play in shooting the ball? 2. When you look at the EM of the red blood cells how did you think its structure will help it perform its function? Nerve Cells: Cells of the nervous system, called nerve cells or neurons, are specialized to carry "messages" through an electrochemical process. The human brain has approximately 100 billion neurons. The cell bodies of neurons have two or more dendrites and a single axon. They receive a signal from the brain (CNS) and conduct the signal to contract to the muscles. In the nerve cell all the organelles are found in the cell body. There are many mitochondria. The mitochondria produce ATP to meet the energy needs for the highly active cell. 1. What do you think is the role of the nerve cell in the process of shooting a basketball? 2. What unique characteristics of a motor neuron’s shape? How do these characteristics help the motor neuron to perform its job? 3. Why do you think that there are so many dendrites, all the branches on the cell body of the neuron? Muscle Cells: In the process of shooting a basketball the skeletal muscles main function is to produce skeletal movement. Bones are connected to muscles by tendons. As the individual muscles contract they pull on the tendons and they move the bones. Thee contractions of muscle are created by interactions of protein filaments. The muscle cells contain lots of mitochondria to provide the ATP for the muscle contractions. 1. What is the role of the muscle cell in the process of shooting a basketball? 2. Look at the images of the muscle cells. What do you notice about its structure? Now look at the images of the red blood cells. Do you see similar structures in the red blood cells? Give reasons to support your ideas. 3. How are the muscle cells and the nerve cells related to each other in the process of shooting a basketball? Bone Cells: Bones are made of two types of bone tissue: compact and spongy bone. Compact bone surrounds the spongy bone and gives bone its strength. Compact bone is made of repeating parts of living bone cells called osteoctyes. Spongy bone is in the inner part of the bone and contains many spaces. 1. What role would the bones play in the process of shooting a basketball? 2. What do you think the compact structure of bone provides? Small Intestine Cells: 90% of nutrient absorption occurs in the small intestines. The small intestines have a mucosa that lines it. This mucosa forms a series of fingerlike projections into the lumen. The cells of the small intestines pull the molecules, vitamins and nutrients from the digested food into the blood. 1. What role do you think the small intestines play in the process of shooting a basketball? 2. Describe the structures that are visible in the small intestine cells? What do you think these structures do? Photoreceptors Cells: There are two types of photoreceptor cells: rods and cones. 1. What would be the role of the eyes in the process of shooting a basketball? 2. As you look at the two types of photoreceptor cells how are they different? How are they similar? CELL PICTURES Red Blood Cells: Nerve Cells: Muscle Cells: Bone Cells: Small Intestine: Photoreceptor Cells: