* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download LB 144: Organismal Biology
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
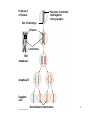
LB 144: Organismal Biology Class 8 02/04/2016 Learning objec<ves 1. Explain Mendel’s laws with rela<on to gamete forma<on and inheritance of traits. 2. Model and diagramma<cally explain how meiosis accounts for Mendel’s observa<ons. 3. Apply the principles of simple Mendelian inheritance to predict paLerns of inheritance. 2 How does alignment for chromosomes affect gamete formation? OR - In meiosis 1, the arrangement of homologous chromosomes on either side of the equatorial plane is random. - Alleles on different chromosomes separate independently - Principle of Independent Assortment Mendel’s Laws 1. Principle of Segregation - Diploid organisms have pairs of alleles - Individual alleles in the pair separate during meiosis - Meiosis I- separation of homologous chromosomes 2. Principle of Independent Assortment - Different pairs of alleles on different chromosomes separate independently of each other during meiosis. - Meiosis I- alignment of chromosomes 4 Viola/on of Independent Assortment: Linked Genes • genes that occur on the same chromosome • In the figure to the right, the SCA1, IDDM1, and EPM2A genes are linked because they all occur on Chromosome 6 5 Linked Genes Genes that occur on the same chromosome will not assort independently Independent assortment applies to whole chromosomes q q Q Q R R R R T T t F F f t f 6 Prophase I of meiosis Pair of homologs Nonsister chroma/ds held together during synapsis Does this mean genes on the same chromosome can never be separated? 7 Prophase I of meiosis Pair of homologs Nonsister chroma/ds held together during synapsis Chiasma Centromere TEM Anaphase I Anaphase II Daughter cells Recombinant chromosomes 8 Larger the distance between genes, more likely to have cross-over Gene 1 Gene 2 Crossing over is rare between genes that are close together Gene 2 Crossing over occurs frequently between genes that are far apart Gene 3 ? Pedigree = family tree with relatedness, sex and phenotype Many human gene/c disorders are known to be inherited as dominant or recessive traits controlled by 1 gene locus Autosomal Recessive Traits • Males and females are equally likely to be affected • Affected offspring often have unaffected parents • Trait often skips generations • Unaffected parents of affected offspring are heterozygous (carriers) • Affected offspring are homozygous Unaffected male Unaffected female Affected male Affected female