* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Structures - cloudfront.net
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
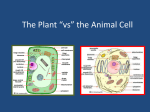
Cell Structures Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org CK-12 Foundation is a non-profit organization with a mission to reduce the cost of textbook materials for the K-12 market both in the U.S. and worldwide. Using an open-content, web-based collaborative model termed the FlexBook®, CK-12 intends to pioneer the generation and distribution of high-quality educational content that will serve both as core text as well as provide an adaptive environment for learning, powered through the FlexBook Platform®. Copyright © 2014 CK-12 Foundation, www.ck12.org The names “CK-12” and “CK12” and associated logos and the terms “FlexBook®” and “FlexBook Platform®” (collectively “CK-12 Marks”) are trademarks and service marks of CK-12 Foundation and are protected by federal, state, and international laws. Any form of reproduction of this book in any format or medium, in whole or in sections must include the referral attribution link http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (placed in a visible location) in addition to the following terms. Except as otherwise noted, all CK-12 Content (including CK-12 Curriculum Material) is made available to Users in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC 3.0) License (http://creativecommons.org/ licenses/by-nc/3.0/), as amended and updated by Creative Commons from time to time (the “CC License”), which is incorporated herein by this reference. Complete terms can be found at http://www.ck12.org/terms. Printed: October 1, 2014 www.ck12.org C HAPTER Chapter 1. Cell Structures 1 Cell Structures Lesson Quiz Name___________________ Class______________ Date________ Multiple Choice Circle the letter of the correct choice. 1. Functions of the cytoplasm include a. b. c. d. suspending cell organelles. providing a site for many of the biochemical reactions of the cell. pushing against the plasma membrane to help the cell keep its shape. all of the above. 2. The largest organelle in an eukaryotic cell is the a. b. c. d. endoplasmic reticulum. nucleus. mitochondria. cytoplasm. 3. The plasma membrane has the phospholipids’ a. b. c. d. hydrophilic tails on the interior and hydrophobic heads pointing outwards. hydrophilic heads on the interior and hydrophobic tails pointing outwards. hydrophobic tails on the interior and hydrophilic heads pointing outwards. hydrophobic heads on the interior and hydrophilic tails pointing outwards. 4. Functions of plastids include which of the following? a. b. c. d. Some plastids capture light energy from the sun and use it to make food. Some plastids store substances such as the monomers used to make proteins. Some plastids make and store other pigments. All of the above are characteristics of plastids. 5. Organization in which different cells are specialized for different functions, but each cell works alone, is characteristic of a. b. c. d. cell-level organization. tissue-level organization. organ-level organization. organ system-level organization. 6. Organelles specific to plant cells include which of the following? a. b. c. d. chloroplasts the cell wall peroxisomes centrioles 7. Which organelle helps make and transport proteins and lipids? a. the ribosome 1 www.ck12.org b. the endoplasmic reticulum c. the Golgi apparatus d. the vesicle 8. Which of the following statements about energy is true? a. b. c. d. Cells use energy from glucose to make ATP. Cells use energy from ATP to make glucose. Chloroplasts capture light energy from the sun and use it to make ATP. Glucose is made in the mitochondria. 9. Complete the following sentence: DNA “lives” in the ____________, proteins are made on the ____________, and the ____________ consists of everything inside the plasma membrane of the cell. a. b. c. d. nucleus, ribosomes, cytoskeleton mitochondria, ribosomes, cytoskeleton mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, central vacuole nucleus, ribosomes, cytoplasm 10. An organized structure composed of many cells, in which all of the cells live and work together, is characteristic of a. b. c. d. a single-celled organism. a biofilm. a colony. a multicellular organism. 11. Which organelle transfers the energy in glucose into molecules of ATP? a. b. c. d. the mitochondria the Golgi apparatus the endoplasmic reticulum the chloroplast 12. In a plant cell, DNA can be found in a. b. c. d. mitochondria. the nucleus. chloroplasts. all of the above. True or False Write true if the statement is true or false if the statement is false. _______ 13. The plasma membrane controls everything that enters and leaves the cell. _______ 14. Small, hydrophilic molecules cannot just flow into the cell, they need help to pass through the plasma membrane. _______ 15. The mitochondrion, where the cell’s energy is made, is often considered to be the cell’s control center. _______ 16. The nucleus is the largest organelle in a eukaryotic cell. _______ 17. All eukaryotic cells have chloroplasts. Fill in the Blanks Fill in the blank with the term that best completes the sentence. 18. The endoplasmic reticulum is an organelle that helps make and ____________ proteins and lipids. 19. The ____________ theory describes how small prokaryotic cells began to “live” inside larger cells. 20. The ____________ can make up as much as 90% of a plant cell’s volume. 2 www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Cell Structures 21. Chloroplasts that contain the green pigment ____________, which makes a plant green. 22. In some cells, a cell ____________ is outside the plasma membrane, 23. The two layers of phospholipids in the plasma membrane are called a phospholipid ____________. 24. ____________ are organelles where proteins are made. 25. A ____________ organism has different types of cells that are specialized for various functions. Short Answer Answer each question in the space provided. 26. Discuss the major differences between a plant cell and an animal cell. 27. List three organelles found in animal cells, and describe their functions. 3