* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Heart chambers and valves
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
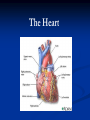
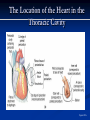
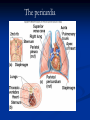
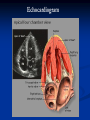
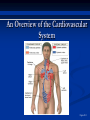
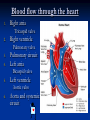
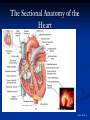
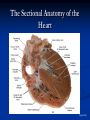
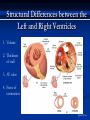
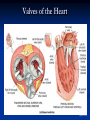
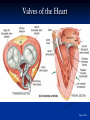
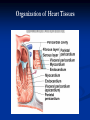
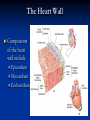
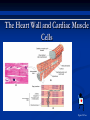
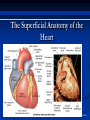
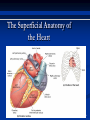
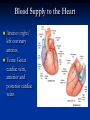
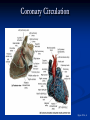
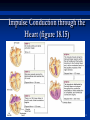
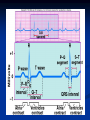
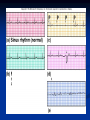
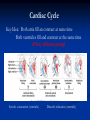
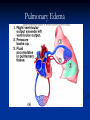
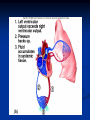
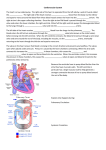
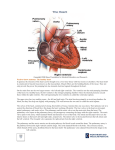
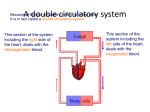
The Heart The Location of the Heart in the Thoracic Cavity Figure 20.2c The pericardia Echocardiogram The cardiovascular system is divided into two circuits Pulmonary circuit blood to and from the lungs System circuit blood to and from the rest of the body Vessels carry the blood through the circuits Arteries carry blood away from the heart Veins carry blood to the heart Capillaries permit exchange An Overview of the Cardiovascular System Figure 20.1 Compare (what is the same) and Contrast (what is different) Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits 1. Oxygenated Deoxygenated 2. Pressure 3. Arteries Veins 4. Color Internal Anatomy and Organization Atria Ventricles Thick walled chambers separated from the atria by AV valves Chordae tendineae Thin walled chambers that receive blood from the vena cavae Tendinous fibers attached to the AV valves Papillary muscle and trabeculae carneae Muscular projections on the inner wall of ventricles Blood flow through the heart 1. Right atria Tricuspid valve 2. Right ventricle Pulmonary valve 3. 4. Pulmonary circuit Left atria Bicuspid valve 5. Left ventricle Aortic valve 6. Aorta and systemic circuit The Sectional Anatomy of the Heart Animation: Diagrammatic Frontal Section through the Heart Figure 20.6a, b The Sectional Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20.6c Heart chambers and valves Structure and Function Question: Why does the human heart have four chambers? Heart chambers and valves Structural Differences in heart chambers The left side of the heart is more muscular than the right side Functions of valves AV valves prevent backflow of blood from the ventricles to the atria Semilunar valves prevent backflow into the ventricles from the pulmonary trunk and aorta Leaky valves???? Structural Differences between the Left and Right Ventricles 1. Volume 2. Thickness of wall 3. AV valve 4. Force of contraction Figure 20.7a-c Valves of the Heart Figure 20.8a Valves of the Heart Figure 20.8b Organization of Heart Tissues The Heart Wall Components of the heart wall include Epicardium Myocardium Endocardium Quiz Yourself- pg 453 in lab manual The Heart Wall and Cardiac Muscle Cells Figure 20.5a-c Superficial Anatomy of the Heart The heart consists of four chambers Two atria and two ventricles Major blood vessels of the heart include Inferior and superior vena cavae Aorta and pulmonary trunk The Superficial Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20.3a The Superficial Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20.3b, c Blood Supply to the Heart Arteries: right/ left coronary arteries, Veins: Great cardiac vein, anterior and posterior cardiac veins Coronary Circulation Figure 20.9c, d By Pass Surgery- Video Complete Activity 2, 3, 4 Lab 30 The Conducting System The conducting system includes: Sinoatrial (SA) node Atrioventricular (AV) node Conducting cells Atrial conducting cells are found in internodal pathways Ventricular conducting cells consist of the AV bundle, bundle branches, and Purkinje fibers Impulse Conduction through the heart SA node begins the action potential Stimulus spreads to the AV node Impulse is delayed at AV node Impulse then travels through ventricular conducting cells Then distributed by Purkinje fibers Impulse Conduction through the Heart (figure 18.15) Figure 20.13 Cardiac Cycle Key Idea: Both atria fill an contract at same time Both ventricles fill and contract at the same time A Very efficient pump! Systole- contraction (ventricle) Diastole: relaxation (ventricle) Pulmonary Edema Regulation of Stroke Volume More stretch = more forceful contraction Think about rubber bands! High volume of venous return causes more stretching of myocytes Factors that increase venous return: 1. slow heart rate (why?) 2. exercise (why) Regulation of Heart Rate Normal heart rate is _____________? Tachycardia and bradycardia…… Medulla Oblongata (Brain stem) Sympathetic Parasympathetic Cardiaccelatory Cardioinhibitory Center (vagus nerve) center SA/AV node SA/AV node Regulation of Heart Rate Sympathetic nervous system- speeds up heart rate epinephrine (adrenaline) , norepinephrine Stress and exercise, high level of calcium Parasympathetic nervous system- slows heart rate beta blockers, morphine- block epinephrine binding sites calcium channel blockers Alcohol- decreases activity of the vagus nerve- and the caridoaccelratory center in the brain stem.