* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 24 Plant Hormones and Tropisms
Survey
Document related concepts
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Arabidopsis thaliana wikipedia , lookup
Cultivated plant taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Hydroponics wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
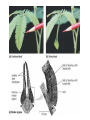
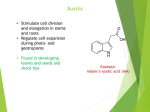
Chapter 24 Plant Hormones and Tropisms Hormone Substance produced in one part of an organsim that affects another part of that same organism. Target Cell Portion of an organism affected by a hormone Plant Hormone • Chemical substance • Controls plant’s: • patterns of growth & development • responses to environmental conditions • Produced in apical meristem Auxins • Transported downward to rest of plant • Stimulate cell elongation Auxins The above diagram shows how auxin production in a plant causes it to grow toward sunlight. • Light hits one side of stem Auxin and Phototropism • Higher concentration of auxins develops in shaded part of the stem • Change in concentration stimulates cells in the dark side to elongate • Result: stem bends away from the shaded side and toward the light How does auxin affect plant growth in the presence of gravity? • Built up on the lower sides of roots and stems but slows growth • Result: roots grow downward How does auxin affect plant height or width? • As a stem grows in length, it produces lateral buds • Lateral bud gives rise to side branches on the side of stem • Growth at lateral buds is inhibited by auxin, which is on the stem’s tip • The closer a lateral bud is to stem’s tip, the more it is inhibited (apical dominance) cytokinins • Produced in growing roots and developing fruits & seeds • Stimulate cell division and growth of lateral buds • Cause dormant seeds to sprout • Delays aging of leaves As a result of cytokinin the top carrot is 2x bigger than the other. • Inhibit elongation and cause cells to grow thicker How do gibberellins affect plant growth? • Produce increase in size in stem and fruit • Responsible for rapid early growth in many plants Notice the difference in sizes of the fruit bunches and plants How does ethylene gas affect plants and how is it used on a fruit? • Trees suffer leaf loss • Ethylene stimulates fruits to ripen • Use to treat fruit picked before ripening to ripen them when being handled for shipment Homeostasis • Plant hormones have opposing effect! – Auxins (made in meristem – stimulate root growth) VS. Cytokinins (made in roots/fruits – stimulate leaf/tip growth) – Gibberelins (growth of stems and fruit) VS. Absicisic Acid (halt growth until conditions improve) Tropism response of a plant to an environmental stimulus Phototropism tendency for plants to grow towards light Thigmotropism response of plants to touch Gravitropism tendency of a plant to grow in a direction in response to force of gravity Tradescantia- A plant that shows growth response to gravity upward when young and downward when older. Notice how the trunk of the tree to the right grows up away from gravity. What Is Photoperiodism? Photoperiodism is the response of plants to periods of light and darkness. Plants such as chrysanthemums and poinsettias flower when days are short. Long Day Plants Plants such as spinach and irises flower when days are long. • It is a plant pigment that is held responsible for photoperiodism. • Absorbs red light • Activates a number of signaling pathways within plant cells