* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is reinforcement?
Bullying and emotional intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Prosocial behavior wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral modernity wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Parent management training wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
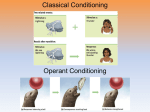
1. Why are children of abusive parents more likely to be aggressive? What causes this? 2. The fact that learning can occur without reinforcement is most clearly demonstrated in studies of _____________. AP Psych DMA • DMA • Turn in FRQ # 1 & 2 • Chap. 8 • Finish Pavlov • Skinner Homework: • Chap. 8 notes due Thursday, Oct. 27th • Chap. 8 test – Thursday, Oct. 27th • FRQ #3 due Monday, Oct. 24th Today’s Agenda Pavlov didn’t use a bell Step 1 Step 2 UCS (food) UCR (salivation) NS (metronome) +UCS (food) U CR (salivation) Step 3 Repeat step 2 several times Step 4 CS (metronome) CR (salivation) Why the heck do we care? Think about how we explain the following: • Phobias • Why you dislike certain foods • How advertising works • What arouses you sexually • The source of your emotions • Why you feel anxiety before a test Extinction… • When the pairing of NS and UCS no longer happens • eventually the CR goes away. What was the: • UCS • UCR • NS • CS • CR “Pavlov” & Powder What was the: • UCS – powder • UCR - drooling • NS - “Pavlov” • CS - “Pavlov” • CR- drooling “Pavlov” & Powder B. F. Skinner Superstitious Pigeon What is the behaviorist approach to Psychology? Discuss with a neighbor… Intro Video Clip Skinner believed that EVERYTHING psychological is essentially behavioral. This belief includes both.. • public, or external • private, or internal (events such as feelings and thoughts) Radical Behaviorist What are some behaviors that you were punished for as a child? In any given situation, your behavior is likely to be followed by consequences. • Some will make behavior more likely to be repeated in the future. Reinforced. • Some will tend to make the behavior less likely to be repeated in the future. Punished. In simple terms: What does it mean when something goes “extinct”? When a behavior has been reinforced in the past • and then the reinforcement is withdrawn • the likelihood of the behavior reoccurring will slowly decrease until the behavior is effectively suppressed. And of course, extinction • You use operant conditioning and positive reinforcement to train Fido to fetch. • You can quit reinforcing Fido’s habit of begging at the table by not reinforcing him with food • thus triggering extinction of the begging behavior. People are o.k. when this applies to Fido • Skinner maintained that all human behavior is created and maintained in precisely the same way. • It is just that the exact behaviors and consequences are not always so easy to identify. • According to Skinner - just because you can’t identify the reinforcer, doesn’t mean it’s not there. But, of course, apply it Fred and people get antsy. What are some superstitions? • Skinner believed that superstition occurs when people’s behavior is accidentally reinforced once • Twice • or even several times. • Skinner called this noncontingent reinforcement • A reward that is not contingent on any particular behavior. Which brings us to superstition • Skinner boxes • You saw one in the video clip • Skinner’s operant chamber (box) was used, but with an important distinction • the food pellet chamber was rigged to drop food at 15 second intervals • regardless of what the pigeon was doing at the time. • Each pigeon was placed in the cage for a few minutes each day and left alone. • After several days of conditioning in this way, two independent observers recorded the birds’ behavior. Pigeons & superstitions • None of the behaviors were observed in the pigeons before the experiment. Note: • One bird turned counterclockwise in the cage, making 2 turns before the reinforcement. • One repeatedly thrust its head into one of the upper corners of the cage. • One developed a tossing response as if placing it head beneath an invisible bar and lifting it repeatedly. (Bobbing motion.) • Two developed a pendulum motion of the head and body. Results • Skinner increased the time interval between reinforcements for one of the head bobbing birds • which actually increased the behaviors • the pigeon’s bob became a full on food dance. • Extinction did work on all of the birds, but the one above kept the hopping dance up for over 10,000 hops. Messing with the birds • Superstitions are resistant to extinction. • Expectations stay high that the behavior might work to produce the reinforcing consequences. So what does this tell us? Please take out a piece of paper… I need a volunteer… You will get wet Was Wheeler using classical conditioning (Pavlov) or operant conditioning (Skinner)? Please identify each of these for the squirt bottle experiment. • NS, UCS, UCR, CS and CR Please answer these questions on your paper… • What is reinforcement? • What is the difference between positive & negative reinforcement? Please give examples More questions to answer on your paper… What is reinforcement? • Any event that increases the frequency of a preceding action. What is the difference between positive & negative reinforcement? • Positive – strengthens a response by presenting a (typically) pleasurable stimulus. • Food, attention, approval, money… • Negative – strengthens a response by reducing or removing an averse stimulus. • Taking an Aspirin for a headache, smoking a cigarette to calm down, hitting the snooze button… Office Clip Clip • Identify the NS, UCS, UCR, CS and CR from The Office clip. On your paper, please answer Conditioning & Gaming… Clip