* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth Science: Tectonic Plates Section 1-1
Survey
Document related concepts
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
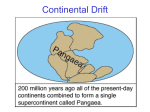
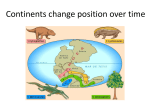
September 18, 2014 Earth Science: Tectonic Plates Section 1-1: Essential Questions 1) What does a geologist do? 2) How were scientist able to study the inside of the Earth since they were not able to explore it first hand? 3) Describe the differences between the lithosphere and asthenosphere. 4) What are the different characteristics of the Earth's crust? September 18, 2014 1) Geologist study the forces that make and shape Earth. They study the chemical and physical characteristics of rock. Map where rocks are found and describe landforms. And study how structures have been shaped (changed) by the environment. 2) Geologist studied seismic waves produced by earthquakes to learn about the Earth's interior. They discover there were 3 main sections crust, mantle, and core. Seismic waves travel at different speeds based on the density of the object they are traveling through. the more dense the material the faster. Solid rock is more dense than liquids. 3. Lithosphere primarily makes up the crust, both continental and oceanic. It is a hard rigid layer that makes up the surface of the Earth. Composed of tectonic plates. The Asthenosphere is the upper portion of the mantle that is hot flowing magma. It is responsible for the causing tectonic plates to move and for the crust to be recycled. 4. Continental crust is made of granite. Is less dense. Oceanic crust is made of basalt. Is more dense. Is under oceans. September 18, 2014 Section 1-2: Convection currents and the Mantle What is heat transfer and describe the three types. Give examples. How does density affect convection currents? What's the role of convection currents in recycling the Earth's crust? 1) Heat transfer is the movement of energy from a warmer object to a cooler object. There are 3 types: radiation, conduction, and convection. 2) Radiation transfer of energy through empty space. Heat source and object do not touch. Sun warming a pool. 3) Conduction heat transfer through direct contact. Heat source and object do touch. Child touching hot stove. 4) Convection heat transfer by the movement of heated fluid. fluids include liquids and gases. Caused by differences in temp and density. Density is a measure of how much mass is in an object. As an object's atoms move faster the atoms spread apart being heated. if they move slower they come together. being cooled. 5. Convection currents in our Earth. They occur in the asthenosphere. The heat comes from the Earth's core. it causes hot columns of mantle to rise slowly. the material spreads out on the crust and pushes cooler material out of the way. then the cooler material sinks (subducts) back into the asthenosphere. September 18, 2014 September 18, 2014 Section 3: Drifting continents 1) Why was Alfred Wegener's hypothesis rejected by the scientific community? 2) What evidence did Wegener have to support his hypothesis? 3) Describe the important scientific discovery Wegener made in 1910? 1) In 1910 Alfred Wegener made an observation about how the continents fit together like a jigsaw puzzle. He formed a hypothesis that all continents were once joined together into a massive landmass (Pangaea) and has since drifted apart. The idea of the continents slowly moving over Earth's surface is known as Continental Drift. 2) Geological structures like mountain ranges provided evidence of continental drift. Mountain ranges in Africa and South America and coal mines in Europe and North America line up. 3) Fossils have also provided evidence. A fossil is any trace of an ancient organism preserved in rock. Similar plant fossils have been found in Africa, South America, Australia, India, and Antarctica. 4) He also found tropical plant fossils on island in the Arctic and evidence of glaciers in rock that is in a more mild climate. 5) Even though he had all this evidence his theory still was not supported because he could not provide an explanation for the force that would push or pull the continents. In the 1960s new evidence about Earth's structure made scientist rethink Wegener's Theory. September 18, 2014 Section 1-4: Sea-Floor Spreading 1) Sonar was used in the mid 1900s to map the ocean's floor. By bouncing sound waves off underwater structures. Scientists found a mid-ocean ridge, which formed the longest mountain range in the world. 2) Ocean floor moves like a conveyor belt, carrying continents. The mid-ocean ridge is a crack along oceanic crust. Sea-floor spreading is caused by new molten rock comes out of the earth and cools and forces the old rock apart. 3) Evidence of sea-floor spreading. 1. pillow-like rocks: only fast cooling magma can form these types of rocks. 2. pattern of magnetized stripes: holds records of reversal in magnetic field. 3. rock samples: older rocks were further from the ridge and the younger rocks were closer to the ridge. 4. Ocean floors do not just keep spreading. Instead trenches are formed by part of the ocean floor sinking (subduction) due to its high density forming deep-ocean trenches. 5. Due to sea-floor spreading and subduction the oceans floor is being recycled. The Pacific Ocean is shrinking due to all the subduction zones and the Atlantic Ocean is getting larger due to the mid-ocean ridge. Essential Questions: 1: What causes sea-floor spreading? 2: What evidence supports the idea of divergent boundaries? 3: What process is keeping the Earth from getting bigger and bigger?