* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 12: The Circulatory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
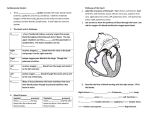
Chapter 12: The Circulatory System 1. A) B) C) D) Ans: The myocardium is the major portion of the heart. largely cardiac muscle tissue. endocardium. the major portion of the heart and largely cardiac muscle tissue. D 2. A) B) Ans: Which are the strongest pumping chambers? atria ventricles B 3. A) B) C) D) Ans: What is the function of the valves? to push blood to prevent backflow to stimulate the heart to give support to the heart B figure 12.1 4. Which letter in figure 12.1 points to the aorta? Ans: e 5. Which letter in figure 12.1 points to the pulmonary artery? Ans: d 6. Which letter in figure 12.1 points to the right atrium? Ans: c Page 92 7. Which letter in figure 12.1 points to the left ventricle? Ans: b 8. Which letter in figure 12.1 points to the inferior vena cava? Ans: a 9. A) B) C) D) Ans: The aorta receives blood from lungs. carries blood toward the body tissues. receives blood from the body tissues. carries blood to the heart. B 10. A) B) C) D) Ans: The left atrium receives blood from lungs. carries blood toward the body tissues. receives blood from the body tissues. carries blood to the heart. A 11. A) B) C) D) Ans: The pulmonary vein receives blood from lungs. carries blood toward the body tissues. receives blood from the body tissues. carries blood to the heart. D 12. A) B) C) D) Ans: The right atrium receives blood from lungs. carries blood toward the body tissues. receives blood from the body tissues. carries blood to the heart. C 13. A) B) C) D) Ans: Which vessels would have a high oxygen content? aorta pulmonary vein pulmonary artery aorta and pulmonary vein D Page 93 14. Which of the following represents the correct sequence when tracing the path of blood from the superior vena cava to the lungs? A) left atrium, pulmonary semilunar valve, left ventricle, mitral valve, pulmonary artery B) right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary semilunar valve, pulmonary artery C) tricuspid valve, right atrium, aortic semilunar valve, right ventricle, pulmonary vein D) pulmonary semilunar valve, right atrium, mitral valve, right ventricle, pulmonary vein Ans: B 15. A) B) C) D) Ans: Which chambers contract simultaneously? two atria right atrium and right ventricle all chambers contract simultaneously all chambers contract separately A 16. A) B) C) Ans: Systole refers to relaxation. contraction. stimulation. B 17. A) B) C) D) Ans: The heart sounds are due to the valves closing. heart contraction. heart relaxing. blood flowing. A 18. A) B) C) D) Ans: What initiates the heartbeat? nerves AV node SA node brain C 19. A) B) C) D) Ans: In an ECG, the QRS complex represents depolarization of the atria. depolarization of the ventricles. repolarization of the atria. repolarization of the ventricles. B Page 94 20. A) B) C) D) Ans: A correct sequence in the conduction system is Purkinje fibers, AV bundle, bundle branches. AV node, SA node, Purkinje fibers. SA node, AV node, AV bundle, bundle branches. AV node, bundle branches, SA node, Purkinje fibers. C 21. A) B) C) Ans: __________ carry blood to the heart. Veins Arteries. Capillaries. A 22. A) B) C) Ans: __________ handle tissue exchange. Veins Arteries. Capillaries. C 23. A) B) C) Ans: __________ are thick walled. Veins Arteries. Capillaries. B 24. A) B) C) D) Ans: Phlebitis and hemorrhoids are conditions involving arteries. capillaries. veins. all of these. C 25. A) B) C) Ans: The systemic circuit involves the body. lungs. body and lungs. A 26. A) B) C) D) Ans: Which is the correct sequence when blood flows from the heart to the kidney? right ventricle, vena cava, renal vein left ventricle, aorta, renal artery left atrium, aorta, renal artery right ventricle, aorta, renal vein B Page 95 figure 12.2 27. Which letter in figure 12.2 points to the hepatic portal vein? Ans: a 28. Which letter in figure 12.2 points to the carotid artery? Ans: b 29. Which letter in figure 12.2 points to the descending aorta? Ans: c 30. A) B) C) Ans: The celiac artery goes to the head. stomach. leg. B 31. A) B) C) Ans: The brachiocephalic artery goes to the head. stomach. leg. A Page 96 32. A) B) C) Ans: The iliac artery goes to the head. stomach. leg. C 33. A) B) C) D) Ans: The hepatic portal vein goes from the liver to vena cava. small intestine to the liver. kidney to vena cava. intestine to kidney. B 34. A) B) C) D) Ans: What is blood pressure directly dependent on? cardiac output peripheral resistance autonomic nervous system cardiac output and peripheral resistance D 35. A) B) C) Ans: What accounts for blood flow in the arteries? blood pressure skeletal muscle contraction blood pressure and skeletal muscle contraction A 36. A) B) C) D) Ans: Where is blood pressure the greatest? arteries arterioles capillaries all are the same A 37. A) B) C) Ans: Why is it important that blood move very slowly through the capillaries? to allow for molecular exchange between the blood and the tissues to allow for normal heart functioning blood moves very quickly through the capillaries A 38. A) B) C) D) Ans: Which of these is a correct sequence when tracing the path of blood in the fetal heart? right atrium, foramen ovale, left atrium left ventricle, pulmonary arteries, lungs the umbilical arteries, ductus venosus, right atrium placental artery, ductus arteriosus, right atrium A Page 97 39. A) B) C) D) Ans: Which artery is usually used to determine blood pressure? aorta brachial artery renal artery coronary artery B 40. A) B) C) D) Ans: How is the heart muscle nourished? by blood in the left ventricle by the coronary artery by the cardiac vein by the carotid artery B 41. Trace the path of the blood from the right atrium to the lungs and then to the left ventricle. Ans: Right atrium, right ventricle, pulmonary trunk, pulmonary arteries, capillary beds surrounding the alveoli of the lungs, pulmonary veins, left atrium, left ventricle. 42. Trace the path of the blood from the heart to the kidneys and then back to the heart. Ans: Left ventricle, aorta, renal artery, renal arterioles, renal capillaries, renal venules, renal vein, inferior vena cava, right atrium. 43. How does the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone mechanism affect blood pressure? Ans: This mechanism increases blood pressure via arteriole constriction, and also leads to an increase in blood volume as a result of absorption of sodium and water. 44. How does the parasympathetic nervous system regulate blood pressure? Ans: The sympathetic nervous system influences peripheral resistance and therefore helps to regulate blood pressure. Arterioles constrict as a result of nerve impulses carried by the nerves of the sympathetic nervous system. This increases blood pressure. 45. Describe a myocardial infarction. Ans: A myocardial infarction, or heart attack, is generally the result of a thromboembolism (clot) which forms in a coronary artery that has been narrowed by plaque accumulation. The portion of the heart supplied by that particular coronary artery dies. 46. What is arteriosclerosis and why does it increase the risk of heart attack? Ans: Arteriosclerosis is also called hardening of the arteries and results from the accumulation of plaque that decreases the diameter of the artery. The plaque accumulation also causes the deterioration of the vessel's smooth muscle and elastic fibers, and the formation of calcium deposits. All of this causes rigidity of the vessel wall. Arteriosclerosis increases the risk of heart disease because the narrow, rigid vessel is more likely to become blocked by a thromboembolism. Page 98 47. List and describe the four fetal circulatory structures. Ans: See text. 48. Explain how cardiac output and peripheral resistance influence blood pressure. Ans: If either the cardiac output or the peripheral resistance increase, the blood pressure will increase. If either the cardiac output or the peripheral resistance decrease, the blood pressure will decrease. 49. Explain how the factors that increase the risk of coronary heart disease that are listed in the text actually function to increase that risk. Ans: See text. 50. Why is the heart referred to as a double pump? Ans: The right side of the heart functions to pump blood to the lungs while the left side of the heart functions to pump blood to the body tissues. 51. Differentiate between cardiac output and stroke volume. Ans: Stroke volume equals the volume of blood pumped out of a ventricle during one contraction. Cardiac output equals the volume of blood pumped by one ventricle in one minute. 52. List the three waves of an ECG and explain what physiological activity each wave represents. Ans: P wave—Accompanies atrial depolarization. QRS complex—Accompanies ventricular depolarization. T wave—Accompanies ventricular repolarization. 53. Describe the causes, characteristics, and symptoms of congestive heart failure. Ans: Congestive heart failure occurs when the left side of the heart fails to pump blood at a rate that is sufficient to meet the body's needs. This can occur as a result of a heart attack that damaged the left side of the heart or as a result of heart valve failure. Congestive heart failure leads to an accumulation of fluid in the lungs (pulmonary congestion and edema) which causes shortness of breath and fatigue. 54. A) B) C) D) Ans: When is the first sound of the hearbeat produced? beginning of atrial systole beginning of atrial diastole beginning of ventricular systole beginning of ventricular diastole C Page 99 55. A) B) C) D) Ans: When is the second sound of the heartbeat produced? beginning of atrial systole beginning of atrial diastole beginning of ventricular systole beginning of ventricular diastol D 56. A) B) C) Ans: Which layer of an artery wall is primarily smooth muscle tissue? tunica externa tunica interna tunica media C 57. A) B) C) D) Ans: Which organ secretes renin? lungs kidneys heart liver B Page 100