* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
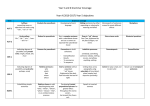
Download Year One English Curriculum
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Sanskrit grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Context-free grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Probabilistic context-free grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Junction Grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Construction grammar wikipedia , lookup
Year One English Curriculum Term 1 Term 2 Term 3 Fiction Non-fiction Poetry Stories in familiar settings Grammar: Writing, leaving spaces between words; using capital letters for the names of people, places, days of the week, etc Stories with repeating patterns Grammar: Writing, leaving spaces between words; beginning to punctuate sentences using a capital letter and a full stop, a question mark or exclamation mark; using grammatical terminology Stories with repeating patterns Grammar: Beginning to write in complete sentences; beginning to punctuate sentence Labels, lists and signs Grammar: Writing, leaving spaces between words; using capital letters for the names of people, places, days of the week, etc Information texts Grammar: Writing, leaving spaces between words; using capital letters for the names of people, places, days of the week, etc; using grammatical terminology Songs and repetitive poems Grammar: Writing, leaving spaces between words; using capital letters for the names of people, places, days of the week, etc Instructions Grammar: Beginning to write complete sentences; using capital letters at the start of a sentence and a full stop, exclamation mark or question mark at the end Poems about the senses Grammar: Beginning to punctuate sentences correctly; using capital letters for the start of lines in poems Traditional Tales Grammar: Using capital letters for proper names; using full stops and capitals to demarcate sentences Information texts Grammar: Writing leaving spaces between words; using capital letters proper nouns; punctuate questions with question marks and sentences with full stops and exclamation marks; using grammatical terminology Humorous Poems Grammar: Writing proper names using capital letters; using capital letters for the start of lines in a poem Fairy Stories and Traditional Tales Grammar: Joining words and joining clauses using ‘and’; leaving a space between words; using full stops and capital letters to demarcate sentences Letters Grammar: Beginning to write complete sentences; using capital letters at the start of a sentence and a full stop, exclamation or question mark at the end; identifying and distinguishing statements, questions and exclamations Information Texts Grammar: Writing leaving spaces between words; punctuating questions with question marks and sentences with full stops and exclamation marks; using grammatical terminology Poems about nature Grammar: Beginning to punctuate sentences correctly; using capital letters for the start of lines in poems Fantasy Grammar: Using capital letters for proper names; leaving space between words; using full stops and capitals to demarcate sentences Poems with Pattern and Rhyme Grammar: Writing, leaving spaces between words; using capital letters for the names of people, places, days of the week, etc Traditional Poems Grammar: Writing proper names using capital letters; using capital letters for the start of lines in a poem; punctuating sentences using full stops, question and exclamation marks Year Two English Curriculum Term 1 Term 2 Term 3 Fiction Non-fiction Stories in familiar settings Grammar: Learning how to use punctuation correctly, including capital letters, full stops, question or exclamation marks; learning how to use sentences with different forms: statement, question, exclamation, command Traditional Tales Grammar: Co-ordination: using conjunctions (and, or, but) to join simple sentences; learning how to use punctuation correctly, including capital letters, full stops, question or exclamation marks; learning how to use sentences with different forms: statement, question, exclamation, command. Traditional tales from a variety of cultures Grammar: Using conjunctions ‘and’, ‘or’, ‘but’ to join sentences; using ‘when’, ‘because’, ‘if’, ‘where’ etc. to create subordinate clauses; demarcating sentences using capital letters, full stops, question or exclamation marks Stories involving fantasy Grammar: Using adjectives to describe nouns; using conjunctions ‘and’, ‘or’, ‘but’ to join sentences; using conjunctions (when, if, because) to add subordinate clauses Postcards & Letters Grammar: Learning how to use punctuation correctly, including capital letters, full stops, question or exclamation marks; learning how to use sentences with different forms: statement, question, exclamation, command Information texts Grammar: Using expanded noun phrases to describe and specify, e.g. adjectives to describe nouns; learning how to use punctuation correctly, incl. capital letters, full stops, question or exclamation marks; learning how to use sentences with different forms: statement, question, exclamation, command Instructions Grammar: Demarcating sentences using capital letters, full stops, question or exclamation marks Songs and repetitive poems Grammar: Using expanded noun phrases to describe and specify, e.g. adjectives to describe nouns; using and understand grammar terminology Recounts Grammar: Learning how to use punctuation correctly, including capital letters, full stops, question or exclamation marks; using conjunctions ‘and’, ‘or’, ‘but’ to join sentences; using ‘when’, ‘because’, ‘if’, ‘where’ etc. to create subordinate clauses Information texts Grammar: Learning how to use past and present tense correctly including the progressive form; learning how to use familiar and new punctuation Recounts Grammar: Using subordination and co-ordination writing sentences with two main clauses or with subordinate clauses; punctuating questions with question marks and sentences with full stops and exclamation marks; using grammatical terminology Humorous poems Grammar: Using expanded noun phrases to describe and specify, e.g. adjectives to describe nouns; using and understand grammar terminology Quest and Adventure stories Grammar: Identifying and using sentences with different forms; using and distinguishing past and present tense; learning how to use familiar and new punctuation Stories by the same author Grammar: Using past tense consistently; using subordination and co-ordination writing sentences with two main clauses or with subordinate clauses; using expanded noun phrases; using familiar and new punctuation correctly Poetry Traditional poems for young children Grammar: Using expanded noun phrases to describe and specify, e.g. adjectives to describe nouns; using and understand grammar terminology The Senses Grammar: Using expanded noun phrases to describe and specify, e.g. adjectives to describe nouns; using and understand grammar terminology; using ‘when’, ‘if’, ‘that’, ‘because’ to create subordinate clauses Favourite poems Grammar: Using a variety of end of sentence punctuation; using capital letters for the start of lines in poems; beginning to use commas correctly Really looking! Poems about birds Grammar: Using expanded noun phrases in writing descriptions; using familiar and new punctuation correctly Year Three English Curriculum Term 1 Term 2 Term 3 Fiction Non-fiction Stories by the same author Grammar: Extending the range of sentences with more than one clause by using a wider range of conjunctions; using conjunctions, adverbs and prepositions to express time and cause; using and punctuating direct speech Stories from other cultures Grammar: Using grammatical terminology, specifically using and recognising adjectives, nouns and prepositional phrases; using prepositions to express time, place and cause Instructions and explanations Grammar: Using grammatical terminology specifically by beginning to recognise the concept of a verb and by choosing and using powerful verbs; understanding that writing can be first or third person; using and understanding grammatical terminology Information texts Grammar: Extending the range of sentences with more than one clause by using a wider range of conjunctions; using conjunctions, adverbs and prepositions to express time and cause; using grammatical terminology Letters Grammar: Using grammatical terminology specifically by beginning to recognise the concept of a verb and by choosing and using powerful verbs; using the perfect form of verbs Recounts Grammar: Using adverbs and adverbials (prepositional phrases which act as adverbs); creating complex sentences; using commas after or before phrases and clauses; using and punctuating direct speech Non-chronological reports Grammar: Extending the range of sentences with more than one clause: compound and complex sentences; using commas after or before phrases and clauses; using pronouns to avoid repetition or ambiguity and to add clarity and cohesion Persuasive writing Grammar: Using a wide range of connectives to extend sentences to include more than one clause; using conjunctions; using commas after or before phrases and clauses; using and punctuating direct speech Myths and legends Grammar: Using powerful verbs/ beginning to recognise the concept of a verb; understanding that writing can rd st be 3 or 1 person; using and punctuating direct speech Stories about imaginary worlds Grammar: Introducing the idea of tense in verbs; using pronouns for cohesion and to avoid repetition and ambiguity; using dialogue punctuation Adventure Stories Grammar: Extending sentences using adverbials and fronted adverbials; using commas to separate fronted adverbials; using and punctuating direct speech; using a wide range of connectives to create sentences with more than one clause Poetry Creating images Grammar: Using grammatical terminology specifically by using and recognising adjectives, nouns and adverbs; understanding and using adverbials and fronted adverbials; using and understanding grammatical terminology Humorous poems Grammar: Using grammatical terminology specifically by beginning to recognise the concept of a verb and by choosing and using powerful verbs; understanding and using adverbs, adverbials and fronted adverbials; using and understanding grammatical terminology Traditional poems Grammar: Introducing the idea of tense in verbs; using prepositions to express time or place; writing sentences with more than one clause using a wider range of connectives Performance poems Grammar: Using and recognising nouns, adjectives and adjectival phrases; using conjunctions to express time or cause; using possessive apostrophe with singular and plural nouns Traditional poems Essential books: Going to the Fair by Charles Causley The Puffin Book of Fantastic First Poems Grammar includes: Using adverbs and fronted adverbials; using commas after fronted adverbials; using grammatical terminology correctly and with confidence Fiction Plays and Dialogues Grammar: Understanding and using adverbs; using and punctuating direct speech; using powerful verbs; using and understanding grammatical terminology Non-fiction Non-chronological reports Grammar: Using the perfect form of verbs to mark relationships of time and cause; using commas after or before phrases and clauses; using pronouns to avoid repetition or ambiguity and to add clarity and cohesion Poetry Shape poems: Playing with form Grammar: Using possessive apostrophe with singular/plural nouns; extending the range of sentences with more than one clause; using a wide range of conjunctions Year Four English Curriculum Fiction Term 1 Poetry Fables Grammar: Recognising simple sentences; revise compound and complex sentences; using conjunctions to express time or cause; revise how to use dialogue punctuation Stories in Familiar Settings Grammar: Using and recognising nouns, adjectives and prepositional phrases; using adverbs; using adverbs and prepositions to express time and place Instructions and explanations Grammar: Using grammatical terminology specifically by beginning to recognise the concept of a verb and by choosing and using powerful verbs; choosing nouns and pronouns for clarity and to avoid repetition Information texts Grammar: Extending the range of sentences with more than one clause by using a wider range of conjunctions; using conjunctions, adverbs and prepositions to express time & cause; using grammatical terminology Creating images Grammar: Using grammatical terminology specifically by using and recognising adjectives, nouns and adverbs; understanding and using adverbials and fronted adverbials; using and understanding grammatical terminology Poetic form: Syllabic poems Grammar: Using grammatical terminology specifically by beginning to recognise the concept of a verb and by choosing and using powerful verbs; understanding and using adverbs, adverbials and fronted adverbials. Myths and Legends Recounts List Poems and Kennings Grammar Using powerful verbs and adjectives; using the present perfect rather than simple past tense; understand that rd st writing can be 3 or 1 person; using and punctuating direct speech; using apostrophes in possessives. Grammar Understand grammatical terms: verb, noun, adjective, adverb; using adverbs and adverbials (prepositional phrases which act as adverbs); using past tense; begin to understand the perfect form of verbs. Grammar Using grammatical categories: noun, adjective, verb, adverb and preposition; using prepositions to express time or place; writing sentences with more than one clause using a wider range of connectives. Fairy Stories and Playscripts Non-chronological reports Poems to Perform Grammar Using past tense and the perfect form of verbs; using pronouns for cohesion and to avoid repetition and ambiguity; using dialogue punctuation. Grammar Using present tense of verbs; extending range of sentences with more than one clause and using a wide range of conjunctions, including those expressing time, place and cause. Grammar Choosing and using pronouns appropriately for cohesion and to avoid repetition; using possessive apostrophe with singular and plural nouns. Adventure Stories Persuasive writing Traditional poems Grammar Extend sentences using adverbials and fronted adverbials; use commas to separate fronted adverbials; use and punctuate direct speech; use a wide range of connectives to create sentences with more than one clause. Grammar Use a wide range of connectives to extend sentences to include more than one clause; use conjunctions; use commas after or before phrases and clauses; use and punctuate direct speech. Grammar Use adverbs and fronted adverbials; use commas after fronted adverbials; use grammatical terminology correctly and with confidence. Term 2 Term 3 Non-fiction Fiction Plays and Dialogues Non-fiction Non-chronological reports Poetry Shape poems: Playing with form Grammar Grammar Grammar Understand and use adverbs; use and punctuate direct speech; use powerful verbs; use and understand grammatical terminology. Use the perfect form of verbs to mark relationships of time and cause; use commas after or before phrases and clauses; use pronouns to avoid repetition or ambiguity and to add clarity and cohesion. Use possessive apostrophe with singular/plural nouns; extend the range of sentences with more than one clause; use a wide range of conjunctions Year Five English Curriculum Term 1 Term 2 Fiction Non-fiction Classic fiction Grammar includes: Learning the grammar in Appendix 2 specifically using a range of conjunctions to create compound and complex sentences; using relative clauses; using commas correctly, including to clarify meaning, avoid ambiguity and to indicate parenthesis; using correct punctuation to indicate speech Biographies and autobiographies Grammar: Learning the grammar in Appendix 2 specifically using a range of conjunctions to create compound and complex sentences; using expanded noun phrases to convey complicated information concisely Recounts Grammar: Learning the grammar in Appendix 2 specifically using adverbials of time, space and number; using commas correctly, including to clarify meaning, avoid ambiguity and to indicate parenthesis; using expanded noun phrases to convey complicated information concisely Instructions and Explanations Grammar: Using brackets, dashes and commas to indicate parenthesis; using semi-colons, colons or dashes to mark boundaries between main causes; using colons to introduce lists; punctuating bullet points consistently Argument and debate Grammar: Dialogue, direct/indirect speech punctuation, reported speech; using of passive form to present information; using semi-colons and dashes to mark boundaries between independent clauses; using commas to clarify meaning Slam Poetry Grammar: Recognising vocabulary and structures appropriate for formal and written speech, and the differences between this and spoken speech, including the use of contractions; using correct punctuation to indicate speech Reports and Journalistic Writing Grammar: Dialogue, direct/indirect speech punctuation, reported speech; using of passive form to present information; using semi-colons and dashes to mark boundaries between independent clauses; using commas to clarify meaning Poetic Style Grammar: Dialogue, direct speech punctuation; using commas to clarify meaning; using and understanding grammatical terminology Genre fiction Grammar: Adverbials of time, place and number; using elaborated language of description, including expanded noun phrases, adjectives, adverbials and a variety of subordinate clauses, including relative clauses; using semi-colons to mark boundary between independent clauses. Drama (Shakespeare) Grammar: Using dialogue, differences between spoken and written speech, punctuating to indicate direct speech; formal and informal speech and writing, using subjunctive forms; using commas to clarify meaning Poetry Classic poems Grammar: Learning the grammar in Appendix 2 specifically using and choosing descriptive language; adjectives, adverbs and powerful nouns and verbs; using expanded noun phrases to convey complicated information concisely; using hyphens to avoid ambiguity Classic narrative and oral poetry Grammar: Using commas to clarify meaning; using elaborated language of description, including expanded noun phrases, adjectives, adverbial and a variety of subordinate clauses, including relative clauses. Fiction Term 3 Classic novels Grammar: Writing complex and compound sentences; using elaborated language of description, including expanded noun phrases, adjectives, adverbials and, particularly, relative clauses; using accurate sentence and speech punctuation Genre fiction-science fiction Grammar: Using dialogue, recognise differences between spoken and written speech; using speech punctuation to indicate direct speech; understanding and using modal verbs Non-fiction Poetry Persuasive writing Grammar: Understanding and using modal verbs in persuasive writing; using apostrophes correctly; using correct sentence punctuation Debate poetry and poetry that tells a story Grammar: Using elaborated descriptive language; using expanded noun phrases; using and understanding grammatical terminology Non-chronological Reports Grammar: Beginning to understand the use of active and passive verbs, especially the use of the passive form in reports; recognising and using a past participle; using semi-colons, colons and dashes appropriately in reports; using bullet points in reports Power of Imagery Grammar: Using fronted adverbials and non-finite verbs to start a sentence; using commas after fronted adverbials; using elaborated description, including adjectives and adverbs, and subordinate clauses Year Six English Curriculum (Starting Sept 2015) Term 1 Term 2 Fiction Non-fiction Poetry Historical Stories Grammar: Using a range of conjunctions to create compound and complex sentences; using relative clauses; using commas correctly, including to clarify meaning, avoid ambiguity and to indicate parenthesis; using correct punctuation to indicate speech Significant authors Grammar: Learning the grammar in Appendix 2 specifically using a range of conjunctions to create compound and complex sentences; using expanded noun phrases to convey complicated information concisely Stories with flashbacks Grammar: Adverbs, adverbials, including fronted adverbials; using commas after fronted adverbials and to clarify meaning; using relative clauses beginning with who, whom, which, where, when, whose, that or with an implied relative pronoun Recounts Grammar: Learning the grammar in Appendix 2 specifically using adverbials of time, space and number; using commas correctly, including to clarify meaning, avoid ambiguity and to indicate parenthesis; using past and present tense verbs appropriately and recognising the differences; using the perfect form of verbs Instructions and Explanations Grammar: Using brackets, dashes and commas to indicate parenthesis; using semi-colons, colons or dashes to mark boundaries between main clauses; using colons to introduce lists; punctuating bullet points consistently Persuasive writing Grammar: Recognising vocabulary and structures that are appropriate for formal speech and writing; using modal verbs in writing; using expanded noun phrases; using and understand the grammatical terminology Choral or performance poems Grammar: Recognising vocabulary and structures appropriate for formal and written speech, and the differences between this and spoken speech, including the use of contractions; recognising and using the subjunctive forms of the verb; recognising and using apostrophes correctly; using expanded noun phrases in own writing Narrative poems Grammar: Learning the grammar in Appendix 2 specifically using and choosing descriptive language; adjectives, adverbs and powerful nouns and verbs; using relative clauses correctly and appropriately; recognising and using the perfect form of verbs; identifying and using adverbials Free form poetry Grammar: Revising grammatical categories: noun, adjective, verb, adverb and preposition; using expanded noun phrases and adverbials; identifying and using relative clauses; using commas and semi-colons correctly Fiction Non-fiction Poetry Tales from other cultures Grammar: Using dialogue punctuation to indicate direct speech; recognising differences between spoken and written speech and between direct and indirect speech; formal and informal speech and writing, including the use of the subjunctive Report and Journalistic Writing Grammar: Understanding active and passive moods and when to use each one; recognising differences between direct and indirect speech, including punctuation; understand the grammatical differences between spoken and written speech, incl. contractions Classic poems Grammar: Using brackets, dashes or commas to indicate parenthesis; using semi-colons, colons or dashes to mark boundaries between independent clauses; using commas to clarify meaning; using expanded noun phrases to convey complicated information concisely; using and understanding grammatical terminology Classic novels Grammar Writing complex and compound sentences; use elaborated language of description, including expanded noun phrases, adjectives, adverbials and, particularly, relative clauses; use accurate sentence and speech punctuation Persuasive writing Grammar Understand and use modal verbs in persuasive writing; use apostrophes correctly; use correct sentence punctuation. Debate poetry and poetry that tells a story Grammar Use elaborated descriptive language; use expanded noun phrases; use and understand grammatical terminology. Genre fiction – science fiction Grammar Use dialogue, recognise differences between spoken and written speech; use speech punctuation to indicate direct speech; understand and use modal verbs. Non-chronological Reports Grammar Begin to understand the use of active and passive verbs, especially the use of the passive form in reports; recognise and use a past participle; use semi-colons, colons and dashes appropriately in reports; use bullet points in reports. Power of Imagery Grammar Use fronted adverbials and non-finite verbs to start a sentence; use commas after fronted adverbials; use elaborated description, including adjectives and adverbs, and subordinate clauses. Term 3