* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate-Tectonics A review
Survey
Document related concepts
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Terra Australis wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
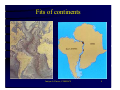
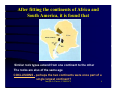
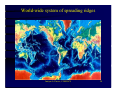
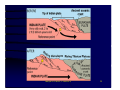
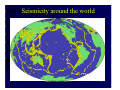
Plate-Tectonics A review Imtiyaz A. Parvez C-MMACS, Bangalore Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 1 The Theory of Continental Drift Alfred Wegener (1912) proposed:• A larger super-continent PANGEA split into smaller fragements about 200-300 million years ago. These then drifted apart to form the present arrangement of continents • He had no satisfactory mechanism to offer, but appealed to a less-dense continent “floating” and “drifting” over a more dense oceanic crust (Like icebergs in the ocean). Most Scientists were highly skeptical and the idea was NOT widely accepted. Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 2 This is what Wegener thought Pangea looked like 200-300 million years ago. Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 3 Fits of continents Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 4 Various attempts to fit Africa and South America Shoreline fit (not great) 200 m. fit (better) Work done by Carey in 1958 Continental Slope 2000 m (best) Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 5 After fitting the continents of Africa and South America, it is found that Similar rock types extend from one continent to the other The rocks are also of the same age COCLUSIONS - perhaps the two continents were once part of a single largest continent? Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 6 Similar rock types extend across continents Rocks in the Appalachians of North America and the Caledonides of Britain and Norway are very similar and are also similar in age When we fit Europe and North America together, we find that the Appalachians and Caledonides form a single mountain chain. Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 7 Distribution of Mesosausarus Mesosaurus was a small reptile that lived about 250 million years ago. Fossils of Mesosaurus are found in both South America and Africa (green shaded areas) Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 8 Distribution of other Reptiles and Plants Similar fossils (reptils and plants) are found on the different continents. How could they have crossed the oceans? CONCLUSION- they did not, the continents were part of the same landmass about 200-300 million years ago Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 9 This is how Wegener thought the continents moved over the last 200 million years:- Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 10 Arguments Favoring Continental Drift • Fits of continents • Apparent discrepancy in inferred latitudes of ancient rocks • Rocks of same age and similar characteristics on different continents • Distribution of similar plants and animals on different continents (how did they cross the ocean) WEGENERS CONCLUSIONS: The continents have drifted over the past 300 million years to their present positions! (not a very popular idea at the time!!!) Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 11 Plate Tectonics • The theory that describes the earth as being composed of giant solid plates that move relative to each other over the molten rock of the earth’s core. PLATE TECTONICS = CONTINENTAL DRIFT + SEA-FLOOR SPREADING + SUBDUCTION Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 12 Theory of Plate Tectonics The theory of plate tectonics was a revolution in the earth sciences that explained most of the major geological features of the earth’s crust in a single comprehensive theory IT EXPLAINED •The history of continents and ocean basins. •Location of earthquake zones. •Location of mountain ranges and mountain building. •The location and origin of volcanoes. Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 13 There are three basic types of plate margins:- 1. SPREADING 2. CONVERGING 3. TRANSFORM Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 14 SPREADING - plates move apart at ocean ridges or split continents apart Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 15 CONVERGING- Oceanic-continental convergence Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 16 CONVERGING- Oceanic-Oceanic convergence Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 17 CONVERGING- Continentalcontinental convergence Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 18 Transform- Plates slide horizontally past each other Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 19 World-wide system of spreading ridges Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 20 Three basic converging boundaries Ocean - Continent Collision Ocean - Ocean Collision Continent - Continent Collision Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 21 Ocean - Ocean Collision Examples Japan Aleutian Islands Indonesia Tonga - Fiji An oceanic plate is subducted beneath another oceanic plate, resulting in the formation of an oceanic trench and island arc (Japan) Earthquakes along the subducted slab The sea behind the arc is Black-Arc Basin Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 22 Ocean - Continent Collision Dense oceanic crust is subducted beneath lighter Continental crust, resulting in the formation of an oceanic trench and a linear volcanic mountain range. Melting occurs both in the downgoing slab and in the crust producing large diversity of volcanic rocks. Also Earthquakes along Bebioff Zone. Examples- Cascades and Andes Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 23 Continent - Continent Collision Examples Himalayas European Alps Mountain Chains Earthquakes No Volcanoes Initiated as oceanic - continent subduction. Continental crust on the subducted plate is too light to be subducted. Consequently it crashes into the other continental crust, Squeezing and folding the sediments between them to produce a high mountain range. Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 24 India collided into Eurasia Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 25 Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 26 History of the earth - Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 27 Tectonic Plates Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 28 Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 29 Journey of the India Landmass (Indian Plate) before its collision with Asia (Eurasian Plate) about 40 to 50 million years ago Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 30 Seismicity around the world Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 31 Imtiyaz A. Parvez, C-MMACS 32