* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download View PDF
Survey
Document related concepts
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
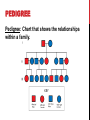
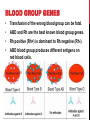
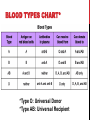
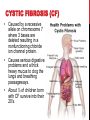
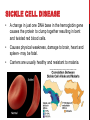
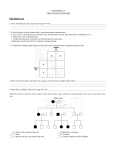
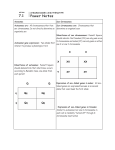
14-1: HUMAN HEREDITY HUMAN CHROMOSOMES Karyotype: set of photographs of chromosomes grouped in order and in pairs. SEX CHROMOSOMES* Sex Chromosomes: 2 chromosomes that determine an individual’s sex on the 23rd pair of chromosomes. Females– XX on 23rd pair Males– XY on 23rd pair AUTOSOMES Autosomes: chromosomes that are not sex chromosomes (everything except for pair #23). POST-IT-NOTE CHECK 1. How many total pairs of chromosomes do humans have? 2. Which pairs are autosomes? 3. Which pair(s) is/are sex chromosomes? PEDIGREE Pedigree: Chart that shows the relationships within a family. BLOOD GROUP GENES • Transfusion of the wrong blood group can be fatal. • ABO and Rh are the best known blood group genes. • Rh positive (Rh+) is dominant to Rh negative (Rh-). • ABO blood group produces different antigens on red blood cells. BLOOD TYPES CHART* *Type O: Universal Donor *Type AB: Universal Recipient THINK-PAIR-SHARE SCENARIO Imagine Person A is rushed to the ER because they have just been in a major car accident. They are losing a lot of blood in a short amount of time and you have to decide what to do next as the only doctor in the ER. Issues • Person A has type AB blood. • There are no more available blood bags for a blood transfusion. • There are plenty of nurses, technicians on staff etc. How are you going to keep this person alive? RECESSIVE ALLELES A normal, functioning gene is often revealed only when abnormal/nonfunctioning allele affects the phenotype. PKU: recessive allele on chromosome 12 causes severe mental retardation and inability to break down phenylalanine (found in milk and other foods). Tay-Sachs: recessive allele that results in the breakdown of the nervous system. DOMINANT ALLELES A dominant allele for a genetic disorder will be expressed in the phenotype. Achondroplasia: form of dwarfism Huntington’s Disease: causes loss of muscle control & mental function in middle age until death. CODOMINANT ALLELES Sickle cell disease is caused by a codominant allele and found in 1 in 500 African Americans. T-Boz From TLC has sickle cell disease Codominance in Panda Bears CYSTIC FIBROSIS (CF) • • • Caused by a recessive allele on chromosome 7 where 3 bases are deleted resulting in a nonfunctioning chloride ion channel protein. Causes serious digestive problems and a thick heavy mucus to clog the lungs and breathing passageways. About ½ of children born with CF survive into their 20’s. SICKLE CELL DISEASE • A change in just one DNA base in the hemoglobin gene causes the protein to clump together resulting in bent and twisted red blood cells. • Causes physical weakness, damage to brain, heart and spleen- may be fatal. • Carriers are usually healthy and resistant to malaria. CHECKING FOR UNDERSTANDING 1. What is the difference between autosomes and sex chromosomes? 2. List 1 disease associated to each: dominant, recessive and codominant alleles (3 total). 3. In terms of blood type groups, why is it possible for Type O people to donate blood to any blood type group? (HINT: Think about antigens/ antibodies)