* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 10 – The Cold War
Survey
Document related concepts
Iron Curtain wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Domino theory wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Cuba–Soviet Union relations wikipedia , lookup
Eastern Bloc media and propaganda wikipedia , lookup
Operation Anadyr wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1953–1962) wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
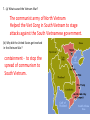
Monday April 11, 2016 6th & 7th Periods Hartsville Middle School 7th Grade Social Studies Lesson Plan Unit 10-The Cold War Ms. Judith Lambert Assessment Check for Understanding Questions Teacher will check for 80% class mastery of understanding throughout the period. Assessment & Report Card Grade Quiz & graded classwork will count 40% of final grade. Test grades will count 50% of final grade. Homework will count 10% of final grade. All grades will allow a score up to 100% based on percent correct. Feedback from all assessments will be used to determine necessary spiral review and/or reteaching. Opportunities will be provided for ALL students to master ALL content. Differentiation A variety of methods are incorporated to accommodate the needs of individual learners throughout the lesson such as: • discussion (whole group, partner, & team). • visuals (graphic organizers, charts, pictures, animations, videos, etc). • note-taking. • text features & text structures. • informational text strategies. • hands-on activities. • early finishers work. • IEPs & 504 Plans are followed. Grouping Students are grouped based on ELA PASS scores using Kagan Team Tools. Highs and mediums or mediums and lows are partnered (face and shoulder partners). NOTEBOOK Students are required to maintain a notebook (marble top). Students are directed to include in their notes the information on a slide if the slide has a note icon like the one to the left. The notes provided contain the important information students are responsible for knowing in order to meet the South Carolina Academic Standards for 7th Grade Social Studies and to be successful on quizzes and tests. READING RENAISSANCE 1ST Wri@ng-‐Chapters 1-‐3 2nd Wri@ng-‐Chapters 4-‐6 3rd Wri@ng-‐Chapters 7-‐9 4th Wri@ng-‐Chapters 10-‐11 • Get your reading materials and begin reading. • At the end of 3 chapters…. -‐Write a 3-‐5 sentence summary of the chapter. OR -‐Select & answer one of the ques9ons provided on the RR guidelines sheet on the inside front cover. BELLWORK-‐DAY 112 1. The peasants’ Storming of the Bas@lle was significant because it______________. A. was the first violent act of the American Revolu@on B. sparked the beginning of Robespierre’s Reign of Terror C. resulted in the repeal (taking back) of France’s unfair tax laws D. represented the beginning of revolu@on in France by destroying a symbol of the king’s 2. Freedom of the seas, the right of self-‐determina@on, limi@ng military buildups, and the League of Na@ons were all outlined in the post-‐World War I peace plan submi\ed by President Wilson. This plan is known as _______________. A. The Treaty of Versailles B. The Fourteen Points C. The Geneva Conven@on D. The stock market crash of 1929 BELLWORK QUIZ DAYS 108-‐114 Friday, APRIL 15, 2016 A G E N D A • Bellwork • Check Homework (Unit 10 Study Guide-‐ Sec. 2) • Game Review UNIT 10 TEST on Wednesday, April 13 Materials Needed Notebook Pencil Unit 10 Study Guide White board w/dry erase marker Remember, we are aiming for 80% to 100% in EVERYTHING that we do! UNIT 10 THE COLD WAR Unit 10 – The Cold War 7-‐5.1 Compare the poli@cal and economic ideologies of the United States and the Soviet Union during the Cold War. 7-‐5.2 Summarize the impact of the Truman Doctrine, the Marshall Plan, the North Atlan@c Treaty Organiza@on (NATO), the United Na@ons, and the Warsaw Pact on the course of the Cold War. 7-‐5.3 Explain the spread of communism in Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and La@n America. 7-‐5.4 Analyze the poli@cal and technological compe@@on between the Soviet Union and the United States for global influence. 7-‐5.5 Analyze the events that contributed to the collapse of the Soviet Union and other communist governments in Europe. NEW LEARNING FOCUS STATEMENT IDENTIFY IMPORTANT EVENTS AND FACTS ABOUT THE COLD WAR BETWEEN THE UNITED STATES AND THE SOVIET UNION CHECK YOUR ANSWERS Unit 10 Study Guide – Sec9on 1 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Cold War Berlin blockade Berlin airlie East Germany West Germany democracy communism NATO 9. Warsaw Pact 10. United Na@ons 11. Truman Doctrine 12. Marshall Plan 13. containment 14. domino theory 15. Iron Curtain 16. satellite state Unit 10 Study Guide – Sec@on 2 1. What happened to Germany and its capital city, Berlin, aeer World War II? German was divided into East Germany & West Germany. Berlin was divided into East Berlin & West Berlin. 2. What was the underlying cause of the Cold War? Different views about government. 3. What two na@ons competed to spread their form of government during the Cold War? Soviet Union & United States 4. Why did Joseph Stalin refuse to remove Soviet troops out of the eastern European na@ons bordering the Soviet Union aeer World War II? He made them satellite states to serve as a buffer zone between the Soviet Union and the democra@c na@ons of Europe. 5. How did NATO and the Warsaw Pact impact the con@nent of Europe? -‐divided Europe crea@ng the Iron Curtain. 6. (a) What caused the Korean Conflict? Communist North Korea invaded South Korea. (b) What was the role of the United Na@ons and the United States in the Korean Conflict? The United Na@ons sent troops under the command of the United States to defend South Korea. (c) How did the Korean Conflict end? An armis@ce was signed by both na@ons. They agreed to keep Korea divided at the 38th parallel (demilitarized zone). 7. (a) What caused the Vietnam War? The communist army of North Vietnam Helped the Viet Cong in South Vietnam to stage a\acks against the South Vietnamese government. (b) Why did the United States get involved in the Vietnam War? containment -‐ to stop the spread of communism to South Vietnam. 8. (a) What caused the Cuban Missile Crisis? The Soviet Union placed nuclear missiles in Cuba. (b) What ac@on did the United States take during the Cuban Missile Crisis? U.S. created anaval blockade of Cuba. (c) How did the Soviet Union respond to the ac@ons of the United States? The Soviet Union removed the missiles from Cuba. 9. What accomplishments did the United States make in the space race during the Cold War? • First to walk on the moon 10. What accomplishments did the Soviet Union make in the space race during the Cold War? Sent the first satellite into space & launched the first spacecrae with an astronaut. 11. (a) What is nuclear annihila@on? Complete destruc@on caused by radioac@ve explosion b) How did the threat of nuclear annihila@on impact the Cold War? It caused na@ons to compete in developing more advanced nuclear weapons. 12. What 4 major things led to the collapse of the Soviet Union and an end to the Cold War? 1. Resistance movements in communist na@ons 2. Policies of Mikhail Gorbachev 3. Policies of Ronald Reagan 4. Failure of communist economic system 13. What economic problems did the Soviet Union face in the 1980s and 1990s? Soviet Union had spent huge amounts of money on space and arms race. Low income & standard of living for its people. 14. How did the resistance movements in Eastern Europe contribute to the collapse of the Soviet Union? Costs to deal with resistance movements added to the economic problems facing the Soviet Union. 15. What policies did Mikail Gorbechev start that led to the collapse of the Soviet Union? Define each. perestroika-‐economic restructuring allowing private ownership & control of businesses glasnost-‐ “policy of openness” Allowed public par@cipa@on & individual rights. democra@za@on-‐allowed government elected by people 16. How did U.S. President Ronald Reagan contribute to the collapse of the Soviet Union? He par@cipated in talks with President Gorbachev to bring an end to the Cold War. GAME REVIEW The policy of the United States to stop the spread of communism was called A. an@-‐communism. B. the domino theory. C. separa@on movement. D. containment. Eastern European na@ons that were occupied by the Soviet Union at the end of World War II and used to serve as a buffer between the Soviet Union and the democra@c na@ons of Western Europe were called A. satellite states. B. border states. C. confederate states. D. imperialist states. Which best describes the underlying causes of the Cold War? A. Bi\er personal disputes between Stalin and Truman B. The remaining anger of enemies on the opposing sides of World War II C. Soviet anger at United States interven@on in Greece and Turkey D. Economic and poli@cal differences between the United States and the Soviet Union. The Truman Doctrine and the Marshall Plan represented a\empts by the United States to deal with the A. na@onal debt. B. spread of communism. C. president’s poli@cal opposi@on. D. arms race Which of the following took place as a response of the Soviet Union blockading West Berlin? A. crea@on of NATO. B. the Berlin airlie C. invasion of East Germany D. building of the Berlin Wall The idea that if one na@on fell to communism then its neighboring na@ons would fall to communism was believed by President Truman. What name was given to this idea? A. Bolshevik Revolu@on B. Democra@za@on C. Domino Theory D. Communist Manifesto The Warsaw Pact was created to A. stop Soviet aggression in Europe. B. provide economic aid to Jews aeer World War II. C. create a plan to reduce nuclear weapons in Europe aeer World War II. D. create a military alliance between the Soviet Union and communist na@ons of Eastern Europe. What interna@onal organiza@on was created aeer World War II to replace the League of Na@ons? A. United Na@ons B. European Union C. NATO D. SEATO The Marshall Plan was supposed to A. prevent Soviet involvement in Africa. B. provide money to help western European na@ons rebuild aeer World War II. C. make the Soviet Union stronger than western European na@ons. D. help build up the military of Asian countries aeer World War II. Why was NATO formed? A. to create a military alliance for democra@c na@ons in Western Europe B. to prevent the Soviet Union from invading China C. to work to prevent the reunifica@on of Germany D. because Greece and Turkey were figh@ng the Communists What name was given to the invisible poli@cal line that separated the communist na@ons of Eastern Europe and the democra@c na@ons of Western Europe? A. Berlin Wall B. Line of Demarca@on C. Iron Curtain D. Communist Border Which of the following was not true of the Korean Conflict during the Cold War? A. China invaded North Korea and South Korean joined in the fight to support China. B. Desiring to unite North and South Korea under a communist government, North Korea invaded South Korea. C. The United Na@ons sent troops into South Korea to drive the North Koreans out of South Korea. D. The United Na@ons placed the United States in command of the UN troops in Korea. The Vietnam War started because A. France wanted to colonize Vietnam. B. South Vietnam wanted to unite North and South Vietnam. C. China wanted to take control of Vietnam and establish a communist government there. D. the communist Viet Minh army of North Vietnam helped guerilla groups to a\ack the government of South Vietnam. The outcome, or final result, of the Korean War was A. atomic destruc@on of Chinese bases. B. victory for the United States. C. victory for North Korea. D. the signing of an armis@ce. Which of the following was not true of the Cuban Missile Crisis? A. The Soviet Union tried to secretly build nuclear missile bases in Cuba. B. U.S. President Kennedy ordered a naval blockade of Cuba to stop the shipping of Soviet missiles to Cuba. C. The Soviet Union threatened to a\ack the United States if the U.S. naval blockade was not removed. D. The Soviet Union removed all Soviet nuclear missiles from Cuba. What leader of the Soviet Union enacted reforms that led to the collapse of the Soviet Union? A. Leonid Brezhnev B. Nikita Khrushchev C. Mikhail Gorbachev D. Boris Yeltsin The Soviet policy of “openness” in speech was known as A. glasnost. B. perestroika. C. détente. D. democra@za@on. Aeer the United States withdrew from Vietnam, the country A. stayed divided at the 17th parallel. B. was taken over by democra@c South Vietnam. C. returned to French control. D. was reunited by communist North Vietnam. Which of the following is not a cause for the collapse of the Soviet Union? A. resistance movements in Eastern Europe because of economic problems B. Mikhail Gorbachev’s policies of perestroika and glasnost C. Ac@ons of U.S. President Ronald Reagan reduced tensions between U.S. and Soviet Union D. the takeover of the government of the Soviet Union by the Bolsheviks What does the map below show? A. Na@ons of eastern Europe that were forced to become a part of the Soviet Union aeer World War II. B. Na@ons of eastern Europe that came under the control of the Soviet Union aeer World War II. C. Na@ons of eastern Europe that gained their freedom from the Soviet Union aeer World War II. A. Na@ons of eastern Europe that formed the NATO alliance aeer World War II. Add up your points. Which partner has the most points? HOMEWORK STUDY FOR UNIT 10-‐COLD WAR TEST USE NOTES & STUDY GUIDE