* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 2 Revision List Topic Key Questions Key Words Plant and
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
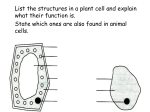
Unit 2 Revision List Topic ➔ Key Questions Key Words Plant and animal cells ➔ What do the different parts of the cell do? ➔ Can you identify them from a photograph? ➔ Can you identify them from a diagram? ➔ How are plant cells different from animal cells? ➔ Can you tell the difference between the cell wall and cell membrane? Cell wall, chloroplast, vacuole, cytoplasm, ribosome, mitochondria, cell membrane, nucleus Bacterial and yeast cells ➔ What are the parts of a bacterial cell? ➔ What are the parts of a yeast cell? ➔ How are bacterial cells different from eukaryotic (plant, animal and yeast cells?) Cell wall, cell membrane, flagellum, slime capsule, plasmid, loop of DNA Specialised cells ➔ What is a specialised cell? ➔ Can you identify how cells are specialised from diagrams? ➔ Can you explain how the following cells are specialised? ◆ red blood cells ◆ nerve cells ◆ muscle cells ◆ sperm cells ◆ ciliated cells ◆ palisade cells ◆ root hair cells ◆ xylem ◆ phloem Differentiated, structure, function, haemoglobin, shape, tail, mitochondria, chloroplasts, hairs, waft, sugars, water, Diffusion ➔ What is diffusion? ➔ What substances diffuse into and out of the cell? ➔ What factors affect the rate of diffusion? Movement, molecules, concentration gradient, passive, temperature, surface area, diffusion distance Organisation of cells ➔ What is a group of similar cells doing a similar job called? ➔ What is a group of tissues working together called? ➔ What is a group of organs working Tissue, organ, organ system together called? Process of photosynthesis ➔ What is the equation for photosynthesis? ➔ Where does photosynthesis happen? ➔ What chemical absorbs the light for photosynthesis? ➔ How are leaves adapted for efficient photosynthesis? Carbon dioxide, water, glucose, oxygen, light energy, chlorophyll, chloroplast, stomata, roots, thin, broad, surface area Uses of glucose in a plant ➔ What can glucose be converted to after it has been made? ➔ What can glucose be used for? ➔ Why is glucose stored as starch? Starch, insoluble, respiration, energy, fats, proteins, Limiting factors ➔ What is a limiting factor? ➔ What three factors can limit the rate of photosynthesis? ➔ Sketch a limiting factor graph. ➔ How do you know what the limiting factor is on each section of the graph? ➔ How is this information useful to farmers? Rate of photosynthesis, temperature, light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, levels out, increasing, profits, rate of growth, costs, all factors at optimum Abiotic factors ➔ List as many abiotic factors as you can. ➔ Why do these abiotic factors control what organisms can live in a certain area? Temperature, water availability, soil type, altitude, habitat, adaptations Random sampling with quadrats ➔ What is a sample? ➔ What is a quadrat? ➔ How can we make our sample accurate? ➔ How can we make our sample reliable? ➔ How can we make our sample fair? Population, proportion, grid, random, remove bias, large sample size, representative Sampling along a transect ➔ What is a transect? ➔ When would you use a transect rather than randomly placed quadrats? Line, change due to an abiotic factor Amino acids and proteins ➔ Why are proteins important? ➔ What are proteins made of? ➔ What makes one protein different from another protein? Enzymes, structures, amino acids, shape, order of amino acids, folding, bonds What is an enzyme? ➔ What is an enzyme? ➔ What is a substrate? ➔ Why is shape so important in an enzyme? ➔ Why are enzymes called specific? Biological catalyst, active site, lock and key, substrate fits into active site, only one substrate fits What factors control the rate of an enzyme reaction ➔ How do high and low temperatures affect an enzyme controlled reaction? ➔ How does a change in pH affect the rate of an enzyme controlled reaction? ➔ How does a change in the amount of enzyme or substrate affect the rate of an enzyme controlled reaction? Denature, reduce kinetic energy, collisions, change shape of active site, breaking bonds, optimum Digestive enzymes ➔ Why does food need to be digested? ➔ Where are digestive enzymes made? ➔ What do protease, amylase and lipase digest? ➔ Why does protease work in the stomach but lipase does not? Absorption, blood, small intestine, pancreas, salivary glands, amylase, protease, carbohydrase, lipase, stomach, pH, denature Bile ➔ What is bile? ➔ Where is it produced and stored? ➔ How does bile speed up the digestion of fats? Alkali, neutralise, emulsify, large droplets to small droplets, surface area, lipase, liver, gall bladder Use of enzymes in industry ➔ How are enzymes used in biological washing powders? ➔ How are enzymes used in low temperatures washing powders? ➔ How are enzymes used in producing baby food? In making sugar syrup? In making sweeteners? ➔ What are the advantages and disadvantages of using enzymes in industry? Digest stains, low optimum temperature, isomerase, carbohydrase, protease, low temperature and pressure, reusable, remove from final product, narrow range of temps/pH, biodegradable, initial cost What is respiration? ➔ Why do living things need energy? ➔ How is energy stored in the body? ➔ How is energy released from these stores? Movement, heat, growth, fats, respiration, glycogen Aerobic respiration and exercise ➔ What is the equation for aerobic respiration? ➔ Where does aerobic respiration take place? ➔ Why do heart and breathing rate glucose, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water, energy, mitochondria, blood carries glucose and oxygen, more exercise requires more need to increase if the rate of aerobic respiration is to increase? energy, meet increased energy demand Anaerobic respiration and exercise ➔ What is anaerobic respiration? ➔ When is it used by the body? ➔ What are the products of anaerobic respiration? ➔ Why is aerobic respiration favoured over anaerobic respiration? No oxygen, extra energy when aerobic respiration occurring at maximum rate, lactic acid, small amount of energy Lactic acid and oxygen debt ➔ What problems can lactic acid cause if it builds up in muscles? ➔ What is an oxygen debt? ➔ Why do we continue to breathe heavily after exercise has finished? Muscle fatigue, low pH, denature enzymes, break down lactic acid, require oxygen, blood delivers oxygen DNA, genes and chromosomes ➔ ➔ ➔ ➔ ➔ What is DNA? What is a gene? What is a chromosome? What is an allele? Where do our chromosomes come from? ➔ How does a gene code for a protein? ➔ Which chromosomes control sex inheritance? ➔ What is the probability of a child being male/female? Chemical carrying a code, section of DNA coding for a characteristic, string of genes, inherited in pairs, parents, three bases code for one amino acid, X and Y, version of a gene Mitosis ➔ What is mitosis? ➔ Where is mitosis used in the body? ➔ What are the daughter cells of mitosis like? ➔ What happens during the process of mitosis? cell division, growth, repair, replace, clones, genetically identical, two daughter cells, one division, DNA copied, chromosomes to equator, split copied chromosomes Meiosis ➔ What is meiosis? ➔ Where is meiosis used in the body? ➔ What are the daughter cells of meiosis like? ➔ How is meiosis different from mitosis? ➔ How many alleles of each gene does a gamete contain? cell division, gametes, half chromosome number, two divisions, genetically different, variation, one allele, one copy of each chromosome Stem cells ➔ What is a stem cell? ➔ How are scientists currently using stem cells in their research? ➔ What ethical issues surround the use Undifferentiated, grow new cells/organs, use of embryos destroys them, cure diseases, of embryonic stem cells in research? Embryo screening ➔ What is embryo screening? IVF, alleles present, reduce ➔ Why do some families choose to have incidence of genetic disease, their embryos screened? destroy unwanted embryos. ➔ What ethical issues surround the use of embryo screening? Dominant and recessive alleles ➔ What are dominant and recessive alleles? ➔ How can punnett squares be used to calculate the probability of offspring inheriting different conditions? ➔ What do you need include in your analysis of a punnett square? One copy, two copies, versions of a gene, probability, phenotype Mendel ➔ Who was Gregor Mendel? ➔ How did he collect evidence on how different characteristics are inherited? ➔ What conclusions did he draw? ➔ Why were Mendel’s findings not considered important during his lifetime? Pea plants, hereditary units, parents, dominant, recessive, genes, DNA, discoveries, Genetic disorders ➔ What causes a genetic disorder? ➔ What is cystic fibrosis? ➔ Is CF caused by a dominant or recessive allele? ➔ What is a carrier of CF? ➔ What is polydactyly? ➔ Is polydactyly caused by a dominant or recessive allele? ➔ Why can’t a person be a carrier of polydactyly? Mutation, recessive, dominant, mucus, digits, heterozygous, Genetic fingerprinting ➔ What is a genetic fingerprint? ➔ What are genetic fingerprints used for? ➔ How are genetic fingerprints interpreted? Individual, paternity tests, crime scenes, banding pattern, comparison, Fossils ➔ What is a fossil? ➔ List four ways that a fossil can be formed. ➔ How are fossils formed by the mold and cast process? ➔ Why are fossils useful for scientists? Preserved remains, amber, ice, tar, mold and cast, sediment, compression, groundwater, minerals, rock, evidence, rare, discovered ➔ Why is the fossil record incomplete? Extinction ➔ What does the term ‘extinct’ mean? ➔ What can cause an organism to become extinct? ➔ Why are scientists trying to conserve living organisms and prevent them from becoming extinct? Living example, natural disaster, habitat, disease, predator, environmental change, competition, rate of extinction Speciation ➔ ➔ ➔ ➔ What is a species? What is speciation? What is natural selection? Can you apply your knowledge of natural selection to explain how different species have evolved? Fertile offspring, mutation, adapted, survive, reproduce, allele, common,