* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 7th Grade Weather and Climate Vocabulary Terms Weather
Survey
Document related concepts
Water vapor wikipedia , lookup
Lockheed WC-130 wikipedia , lookup
Severe weather wikipedia , lookup
Satellite temperature measurements wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric circulation wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric model wikipedia , lookup
Climate change wikipedia , lookup
Automated airport weather station wikipedia , lookup
Weather Prediction Center wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Precipitation wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Weather lore wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Surface weather analysis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
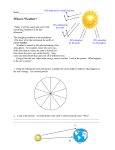
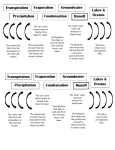
7th Grade Weather and Climate Vocabulary Terms 1) Weather - the state of the atmosphere with respect to wind, temperature, cloudiness, moisture, pressure, etc. 2) Radiation – transfer of heat energy through empty space. 3) Absorption - a taking in or reception of a substance. 4) Convection Currents - movement of fluid caused by cool, dense fluid sinking and warm, less dense fluid rising. 5) Meteorology - the science dealing with the atmosphere and its phenomena, including weather and climate. 6) Atmosphere – mixture of gases that surrounds the Earth. 7) Forecast - to predict a future condition or occurrence; to forecast a heavy snowfall. 8) Climate – general conditions of temperature and precipitation for an area over a long period of time. 9) Air pressure – measure of the force of air pressing down on the Earth’s surface. 10) Water Cycle - continuous movement of water from the oceans and freshwater sources to the air and land and finally back to the oceans; also called the hydrologic cycle 11) Fronts – boundary that forms when two air masses with different properties meet. 12) Humidity – the amount, or percentage, of water vapor in the air. 13) Temperature - a measure of the warmth or coldness. 14) Precipitation - process by which water returns to the Earth in the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail; third step of the water cycle