* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 9.5 Medieval Europe
Survey
Document related concepts
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
Medieval technology wikipedia , lookup
Medieval Inquisition wikipedia , lookup
Medievalism wikipedia , lookup
Wales in the Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
European science in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Migration Period wikipedia , lookup
Late Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Patrimonium Sancti Petri wikipedia , lookup
High Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 13th century wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 9th century wikipedia , lookup
History of Christianity during the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
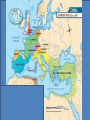
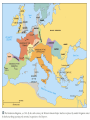
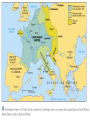
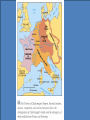
9.5 Medieval Europe 500-1500 CE The Big Picture 4th-5th centuries Roman Empire Allies with “Barbarians” To watch over regions In name of Rome 476 Western Roman Empire Falls 8th-9th centuries Invasion, instability, decentralization Vikings Magyars 5th-8th centuries “Dark Ages” Barbarian Kingdoms Mostly fail 9th century Charlemagne One Europe Holy Roman Empire 11th century Crusades 10th century fragmentation 12th-13th century “High Middle Ages” Frankish Rulers Merovingian • 400s CE Franks = strongest Germanic group • Clovis • 1st king of Franks • 1st accept Catholicism • 714 CE Charles Martel • Defeat Muslims at Tours • 752 CE Pepin le Bref • Quid pro quo: Pope’s blessing in exchange for helping Pope Frankish Rulers Charlemagne • 768 Charlemagne = king • Son of Pepin • Frankish Empire • Revival of Learning • “Carolingian Renaissance” • Pope crowns him new Roman Emperor, Rheims, 800 • Local officials help enforce • 814 Empire breaks up at death • 843 Treaty of Verdun • Divide empire; grandsons Vikings • Raiders from north • Settled throughout Europe • Disconnected trade • Instability • Weaken monarchs Invasions Medieval Life Feudal Relationships • 700s – military service linked to land ownership to support cavalry • Fief • Helps finance horses & equipment • Warriors, then counts and nobles • Noble class evolves to carry out government functions • Oath of loyalty • Vassal • homage • 900s – feudalism • peasants Feudalism • Political system • Social hierarchy • Obligations up and down • Rights and responsibilities • Three estates • Middle Ages as transformation of Roman world Medieval Life Nobility – The Second Estate • • • • Lord of the manor Rents Knights chivalry Medieval Life Manorialism • Lord’s wealth from peasant labor • Serfs • Economic system • Contrast to feudalism, which is a political system • Agricultural improvements boost productivity & ease threat of famine • System was low on freedom, high on stability/security Manorialism • • • • Economic system “Insular”; independent Social hierarchy Land = “wealth generator” – Wealth trickle-down • commons New technologies make life better… Medieval help desk... New Agriculture • Population growth • Climate change • Technology • Mills • Iron tools • Carruca • Iron plow • Horse collar • Horseshoe • 2-field to 3-field system Roman Catholic Church 100-500 CE The Church took over where Roman government left off, imitating its forms and authority and preserving much Roman culture. 500-750 CE 750-1500 CE 1347 Black Death 1053 Great Schism 1517 Reformation Medieval Church The First Estate • Church grows into shell of Roman Empire • Hierarchy • Pope, Cardinal, Bishop, Priest • Monasticism = the highest ideal of Christian life • 529 Benedictines founded • Periodic need for reform Medieval Church Monasticism • • • • • Preserve knowledge School Hospital Lodging Mid-1100s Benedictine Rule adopted by Gregory I Medieval Church Power • • • • • • • Heresy Blasphemy Orthodoxy Interdict Excommunication Lay investiture 1232 Inquisition Church Control Tools • • • • Interdict Excommunication Inquisition Control of information – The Sunday Pulpit • “Peace of God” • Indulgences • tax exempt Medieval Church Friars • • • • Reformers Towns Debaters! Francis of Assisi Medieval Church Jews • • • • • Increase in Church power led to worsening position of Jews Not citizens of European countries ‘til 19th century Anti-Semitism Blamed for crucifixion Stories… • Blood libel • Role in society • Money lending Controversy: Church Law • Churchmen were subject to Church (ecclesiastical) courts, not civil authorities. Controversy: King or Pope? • Could the Pope remove kings? • Did kings have to obey the Pope? Controversy: Lay Investiture • Who got to pick bishops? New Orders • Cistercians • Outside monastery • Hildegard of Bingen • chant • Franciscans • Dominicans RISE OF EUROPEAN MONARCHY Rise of European Monarchy England • 400s immigration / invasion Angles, Saxons, Jutes • 886 Alfred the Great • Defeats Danes • Revival of learning • 1066 William of Normandy “The Conqueror” • Norman French • Battle of Hastings • 300 years of blending French-Anglo-Saxon • 1215 King John and Magna Carta • Emerging middle class in later Middle Ages • “bourgeois” • Parliament invented Rise of European Monarchy France • 987 Hugh Capet • Seized French throne • 300 year dynasty • Centralized monarchy • 12th cen. Philip II • Double size of France • Weaken feudal lords • Estates-General evolves • French history is monarchy becoming more absolute Rise of European Monarchy Holy Roman Empire • • • • • Not holy, not Roman, not an empire Germany Weak, separate states/kingdoms Powerful feudal lords 962 Otto I crowned Holy Roman Emperor by pope in exchange for helping Pope John XII • Otto & successors claim right to help pick pope; popes claim right to depose kings