* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Answer Key
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Matter wave wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
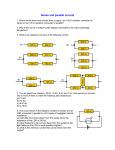
Honors Physics Review Problems Multiple Choice 1. 2 positive charges are placed near each other. What is the direction of the force exerted by one charge on the other? a. towards each other b. up c. away from each other d. down 2. A long straight wire is carrying current running to the right across the page. What is the direction of the magnetic field above that wire? a. to the right b. to the left c. into the page d. out of the page 3. A magnetic field is directed up the page. A wire carrying current to the left is placed in the field. What is the direction of the force on that wire? a. to the right b. to the left c. into the page d. out of the page 4. The unit of magnetic field is a. Volts c. Ohms b. Tesla d. Farads 5. The velocity selector balances the forces between a. electric fields and gravity b. magnetic fields and gravity c. electric and magnetic fields d. electric and magnetic fields and gravity 6. A loop of wire is located in a region of magnetic field pointed into the page. If I increase the strength of the field, in which direction does the current flow? a. clockwise b. counterclockwise c. neither d. depends on the strength of the field 7. Which of the following statements regarding current is true? a. it flows from the positive side of the battery b. it measures how much charge is moved per second c. it refers to the movement of positive charges d. all of the above 8. Which of the following laws describes the relationship between the voltage and current in a resistor? a. Coulomb’s Law b. Kirchhoff’s Law c. Ohm’s Law d. Faraday’s Law 9. If you double the resistance in a circuit while keeping the voltage the same, what happens to the power dissipated in that circuit? a. doubles b. halves c. quaduples d. quarters 10. Objects that are in parallel will have the same a. current b. resistance c. voltage d. capacitance 11. A wave that describes particle motion perpendicular to the wave motion is a a. mechanical wave b. longitudinal wave c. sound wave d. transverse wave 12. If you double the frequency of a wave while keeping the speed the same, what happens to the wavelength? a. doubles b. halves c. quadruples d. quarters 13. The property when 2 waves combine and ADD together is known as a. reflection b. constructive interference c. destructive interference d. standing waves 14. The property of waves that occurs because different frequencies of a wave travel at slightly different speeds in a medium is known as a. refraction b. diffraction c. dispersion d. polarization 15. The fundamental wavelength is always ______ the wavelengths of the higher harmonics a. the same as b. longer than c. shorter than d. unable to tell from given information 16. When 2 objects are moving towards each other while one emits a sound, the resulting frequency of the sound heard by the other object is a. higher b. the same c. lower d. depends on how far apart they are 17. The speed of light can be best thought of as a. a constant b. a universal speed limit c. a really big number d. all of the above 18. The quantization of energy in quantum mechanics is most connected to what? a. conservation of energy b. special relativity c. standing waves d. black holes 19. Which statement is true regarding general relativity? a. It is a theory of gravity b. It includes special relativity c. It was confirmed by an experiment involving a solar eclipse in 1919. d. all of the above 20. Which recent discovery in cosmology has caused us to believe the universe will continue to expand forever? a. dark matter b. cosmic microwave background c. dark energy d. the big bang Short Answer Examples Electrostatics q1 = 2C q2 = -4 C r = 3 cm 1. What is the magnitude and direction of the electric force between the 2 charges? 2. What is the value of the electric field 20 cm away from a 9nC point chart? Magnetism 3. What is the magnitude and direction magnetic field 4 cm to the right from a long, straight wire carrying a current of 10 Amps up the page? 4. What is the magnitude and direction of the force on a proton moving at 10,000 m/s up the page at that point 4 cm away? 5. What is the current necessary to produce a 0.05 T magnetic field in the middle of a solenoid that has 1000 turns/length. Circuits 6. What is the equivalent resistance of 3 resistors in parallel, each with R = 15 ? 7. If those resistors were connected to a 25 V battery, what would be the current running through each resistor? 8. What would be the power dissipated by each resistor? Waves 9. What is the fundamental frequency of a string fixed at both ends with a length of 1.2 meters and a wave speed of 240 m/s? What would be the frequencies of the next 2 harmonics? 10. What is the wavelength of sound (v = 343 m/s) with a frequency of 20,000 Hz. What would be the wavelength of light (c = 3 x 108 m/s) with the same frequency. Drawing Problems Examples 1. Draw the electric field lines for the charge configuration given in the 1st section of this review. 2. Draw the magnetic field lines for a long, straight wire. 3. Draw a circuit containing 2 sets of 2 resistors in parallel that are in series with each other. In other words, 2 resistors are in parallel and another 2 resistors are in parallel and those 2 sets are in series with each other. 4. Draw the lowest three harmonics of a pipe that is open at one end and closed at the other. For each, indicate what fraction of the wavelength fits in each pipe. Medium Problem Examples 1. For the circuit described in the drawing problems section (2 sets of parallel resistors in series), assume that the 1st set of resistors in parallel have a resistance of 3 and 6 respectively. Assume the other 2 resistors have 9 and 18 and they are all connected to a 24 V battery. a. What is the equivalent resistance of the circuit? b. What is the total current leaving the battery? c. What is the current going through the 18 resistor? d. If each resistor were a light bulb, rank them in order of brightness. 2. A guitar player is interested in learning more about his guitar. The lowest note (played by strumming the open bottom string) is an E with a frequency of 82.4 Hz. a. If you assume the length of the string is 65 cm, what will be the wavelength of the fundamental harmonic that will fit on that string. b. Given that wavelength and the above frequency, what is the wave speed on that string? c. You can play an E that is an octave higher (has twice the frequency) on the bottom string. Where should you place your finger in order to do this? Explain why. d. The top string is also an E with a frequency exactly 4 times larger than the bottom one (2 octaves higher). What is the wave speed on that string? Why is it different than the bottom one? 3. Possible modern physics discussions: question will come from one of these topics Describe the basic underpinnings and results of special relativity and quantum mechanics Describe the fundamental particle and forces of the standard model Describe the role of gravity in understanding various topics: apples falling, planets orbiting, warped spacetime, black holes, universe expanding, etc. Describe Albert Einstein’s role in the progression of modern physics in the early parts of the 20th century. Which topics did he most contribute to and what were those contributions? Answer Key Multiple Choice: 1. C 2. D 3. C 4. B 5. C 6. B 7. D 8. C 9. B 10. C 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. D B B C B 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Short Answer 1. 80 N towards each other 2. 405 N/C 3. 0.0001 T into the page 4. 1.6 x 10-19 N towards the wire (to the left) 5. I = 39.8 A 6. 5 7. 5/3 = 1.67 A 8. 41.67 W 9. 100 Hz, 200 Hz and 300 Hz 10. sound = 0.0175 m; light = 15,000 m Medium Problems 1. a. 8 b. I = 3 A c. I = 1 A d. 9, 18 3, 6 (order of which resistors for their brightness) 2. a. b. c. d. 1.3 m v = 107 m/s right in the middle 4 times bigger = 428 m/s A D C D C









![2014 Honors Physics B Final Review[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002207112_1-ab66bbfc816602918dd68cb75979954d-150x150.png)