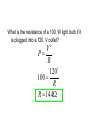* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Jeopardy
Survey
Document related concepts
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
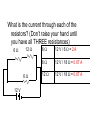
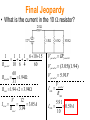
Jeopardy (CP) Subterm 2 Review Topics Covered: Waves Sound Electrostatics Circuits Magnetism A cork on the surface of a pond bobs up and down two times per second on ripples having a wavelength of 8.50 cm. What is the cork’s speed? 0.085m f 2Hz v f (2Hz)(0.085) v 0.17m / s If the speed of a wave stays the same, what happens to the frequency as the wavelength decreases? The frequency will INCREASE. V=f Mrs. Wright sings toward a cliff in the mountains and the sound is reflected directly back to her. She is standing 170 m from the natural wall. If her music is traveling through air at 340 m/s, how long will it take Mrs. Wright to hear her own echo? v 340m / s d 170m 2 340m t? d d 340m v t 1.0 sec t v 340m / s A rather noisy typewriter produces a sound intensity of 1 x 10-5 watts/m2. Find the decibel level of this machine. 105 w / m 2 7 10 log 12 10 log 110 2 10 w / m 70 dB During the Macy’s Thanksgiving Day Parade it is 5oC outside. A late parade watcher drives towards the parade at 15 m/s as the parade marches towards her, at 5 m/s. If one of the bands plays a note of 415 Hz, what frequency will she hear? (assume the speed of sound is 334 m/s at 5oC) vwave vobserver 33415 415 440Hz f ' f 3345 vwave vsource A 4.00 m long pipe is half way submerged in room temperature water where the speed of sound is 343m/s in the room. What is the fundamental frequency of the pipe? 1 = 4L L 4 v v 343m / s f 42.9Hz 4L 4(2.00m) • What do the electric field lines look like for the following charge: Two point charges of -1.0 nC and +2.0 nC are separated by a distance of 0.30 m. What is the electric force on each particle? (remember 1nC = 1x10-9 C) 9 9 9 kQ1Q2 (9 10 )(110 )(2 10 ) 7 F 2.0 10 N 2 2 d (0.3) An uncharged conductor is supported by an insulating stand. A positively charged rod is brought near the left end of the conductor. The you touch the right side of the conductor with your hand. The What is the charge of the conductor now? NEGATIVE An electric field of 2.0x104N/C is directed along the positive x-axis. What is the electric force on an electron in this field? (Qelectron = 1.6x10-19C) F QE (1.6 10 )(2.0 10 ) 3.2 10 N 19 4 Along the negative x-axis 15 What is the magnitude and direction of the electric field at a distance of 3.20 m from a –50.0 nC charge? kQ (9 10 )(50 10 ) E 2 43.9N /C 2 d (3.2) 9 9 Two point charges are 4 cm apart. They are moved to a new separation of 2 cm. By what factor does the resulting mutual force between them change? 1) ½ 2) 2 3) ¼ 4) 4 5) depends on the charges kQ1Q2 F d2 Charge A has 10 electric field lines coming out, Charge B has 20 lines coming out, and charge C has 30 lines coming in. Which pair of these charges will have the largest force between them if placed 1 cm apart? Charge A 10 lines Charge B 20 lines Charge C 30 lines • The leaves of a negative electroscope will stick out. What happens to the leaves when another negative rod is brought close to the scope, but does not touch it? More negatives - - - - - - - - are pushed into the leaves and the leaves stick out even further. What type of wire makes the best conductor? • Long or short • Thick or thin • Rubber or Aluminum When resistors are put in series, their overall resistance is a. Larger than that of any individual resistor b. The same as the resistance of one of the resistors c. Smaller than the resistance of any of the resistors A wire 5.0 m long and 3.0 mm in diameter has a resistance of 100 W. A 15 V potential difference is applied across the wire. What is the current in the wire? V IR V 15 I 0.15A R 100 What is the resistance of a 100. W light bulb if it is plugged into a 120. V outlet? V P R 2 120 100 R R 144W 2 Three resistors with resistance of 6 W, 12 W, and 24 W are connected in series. What is the total resistance of the circuit? Rtotal 612 24 42W • What is the same in a parallel circuit? Three resistors with resistance of 6.0 W, 12 W, and 24 W are connected in series with a 12V battery. What is the current through the 12 W resistor? The current is the same through all of them so the total resistance must be used. V IR 12 42I I 0.29A What is the current through each of the resistors? (Don’t raise your hand until you have all THREE resistances) 6W 12 W 6W 12 V 6W 12 V / 6 W = 2 A 6W 12 V / 18 W = 0.67 A 12 W 12 V / 18 W = 0.67 A • What is the direction of the force on the electron? . . . . . . . . . What does the magnetic field look like for a loop of wire with a clockwise current as shown? Into the board inside the loop, out of the board outside the loop X X X X An electron moves with a speed of 7.0 x 106 m/s along the +x axis. It enters a region where there is a magnetic field of 2.5 T, directed at an angle of 60 to the +x axis and lying in the xy plane. Calculate the magnetic force of the electron. F QvB sin (1.6 10 )(7 10 )(2.5)(sin 60 ) 19 F 2.4210 N 12 6 A proton is released such that its initial velocity is from right to left across this page. The proton's path, however, is deflected (by a force) in a direction toward the bottom edge of the page due to the presence of a uniform magnetic field. What is the direction of this field? A generator is created by moving a 0.300 m long wire in an external magnetic field of 5.50 T at a speed of 15.0 m/s. (a) What EMF is produced by the generator? (b) What effective emf if produced by the generator? (a) (b) EMF BLv sin (5.5T )(0.30m)(15m / s ) 24.75 24.8V Veff 0.707Vmax 0.707(24.75) 17.5V Final Jeopardy • What is the current in the 10 W resistor? 1 Rparallel 1 1 1 6 10 15 10 6 4 60 60 Rparallel 1.94W 31 Rtotal 1.94 2 3.94W V 12 I total 3.05A Rtotal 3.94 Vparallel IRparallel Vparallel (3.05)(1.94) Vparallel 5.91V Vparallel I10W R10W I10W 5.91 0.59A 10