* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 6 Power Point Notes
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Canada wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
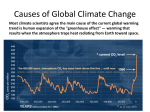
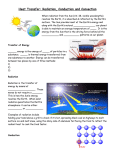
Unit 6: Atmosphere Notes Chapter 17: Climate I. 17.1: Climate and Its Cause: a. Introduction: i. Although almost anything can happen with the weather, climate is more predictable ii. Climate then is the long-term average of weather iii. Good climate is why we choose to vacation in Hawaii in February, even though the weather is not guaranteed to be good. b. What is Climate? i. The __________________ of weather in that location over a period of time, usually for at least 30 days ii. A location’s climate can be described by its: 1. Air temperature, humidity, wind speed, and direction 2. The type, quantity, and frequency of precipitation iii. Climate can change, but only over a long periods of time iv. The climate of a region depends on its position relative to many things c. Latitude: i. The ________________ factor influencing the climate of a region – because different latitudes receive different amounts of solar radiation 1. The _____________________ receives the most solar radiation 2. The polar region receives the least solar radiation d. Atmospheric Circulation Cells: i. The position of a region relative to the circulation cells and wind belts has a great effect on climate e. The ITCZ (Intertropical Convergence Zone): i. The ____________ pressure area near the equator in the boundary between the two Hadley Cells f. Cell Boundary: i. Hadley Cell and Ferrell Cell Boundary: 1. At this location the air is ___________________________, and shrinking air warms and causes evaporation ii. Ferrell Cell and Polar Cell Boundary: 1. The meeting of the two different air masses causes the polar jet stream, which is known for its stormy weather g. Prevailing Winds: i. The bases of the Hadley, Ferrell, and Polar Cells ii. Bring _____________________ from the locations they come from h. Continental Position: i. When a particular location is near an ocean or large lake, the body of water plays and extremely important role in affecting the region’s climate 1. __________________________ climate is strongly influenced by the nearby seas a. Temperature vary a relatively small amount seasonally and daily 2. __________________________ climate – more extreme a. With greater temperature differences between day and night and between summer and winter i. Ocean Currents: i. The temperature of the water offshore influences the temperature of a coastal location, particularly if the winds came off the sea. II. ii. Coastal _______________________ also brings cold, deep water up to the ocean surface off of California which contributes to the cool coastal temperatures. j. Altitude and Mountain Ranges: i. Air pressure and air temperature ___________________ with altitude ii. The closer molecules are packed together, the more likely they are to collide 1. Collisions between molecules give off heat, which warm the air iii. Mountain ranges have two effects on the climate of the surrounding region: 1. ___________________________ effect – which brings warm dry climate to the leeward side of a mountain range 2. Separation of the coastal region from the rest of the continent. 17.3: Climate Change: a. Introduction: i. For the past two centuries, climate has be relatively stable ii. People placed their farms and cities in location that were in a favorable climate without thinking that the climate could change iii. But climate has changed throughout Earth’s history, and a stable climate is not the norm 1. _________________________ has allowed the expansion of agriculture and the development of towns and cities b. Short-Term Climate Change: i. Are common – the largest and most important of these is the oscillation between El Nino and La Nina conditions. ii. The cycle is called the ______________ (El Nino Southern Oscillation) 1. The ENSO drives changes in climate that are felt around the world about every two to seven year iii. In a normal year, the ________________ winds blow across the Pacific Ocean near the equator from east to west (towards Asia) iv. In an El Nino year, when water temperatures reaches about 820F, the trade winds weaken or reverse direction and blow east (towards South America) 1. Upwelling stops v. By altering atmospheric and oceanic circulation, El Nino events change global climate patterns 1. Some regions receive more than average rainfall, including the west coast of North and South America, the southern US and Western Europe 2. Drought occurs in other parts of S. America, the western Pacific, southern and northern Africa, and southern Europe vi. An El Nino cycle last one to two years – sometimes circulation patterns bounce back quickly and extremely – this is called a ____________________________ vii. In a La Nina year, as in a normal year, trade winds move from east to west and warm water piles up in the western Pacific Ocean 1. Ocean temperatures along coastal S. America are _____________________ than normal (instead of warmer like in El Nino) 2. Cold waters reach farther into the western Pacific than normal c. Causes of Long-term Climate Change: i. Many processes can cause climate to change. These include changes: 1. In the amount of energy, the Sun produces over years 2. In the __________________________ of the continent’s over millions of years 3. In the tilt of Earth’s axis and orbit over thousands of years 4. That are sudden and dramatic because of random catastrophic events, such as a large asteroid impact. d. e. f. g. h. 5. In greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, caused naturally or by human activities Causes of Long-Term Climate Change: i. Solar Radiation: 1. The amount of energy the Sun radiates is variable ii. Plate Tectonics: 1. Can alter climate 2. Over millions of years as seas open and close, ocean currents may distribute heat differently 3. When the continents separate, heat is more evenly distributed 4. Triggers volcanic eruptions, which release dust and CO2 into the atmosphere Milankovitch Cycle: i. Scientist attribute a series of ice ages to variation in the Earth’s position relative to the Sun 1. The shape of the Earth’s orbit changes slightly as it goes around the Sun 2. The planet wobbles on its axis of rotation 3. The planet’s tilt on its axis varies between 22.10 and 24.50 a. Seasons are caused by the tilt of Earth’s axis of rotation Changes in Atmospheric Greenhouse Gas Levels i. A ___________________________ in greenhouse gas levels decreases global temperature and an increase raises air temperature ii. Natural processes add and remove ___________________ from the atmosphere: 1. Add CO2 a. Volcanic eruptions and decay or burning of organic matter 2. Remove CO2: a. Absorption by plant and animal tissue iii. When ______________________ are turned into fossil fuels the CO2 in the tissue is stored with them. iv. So CO2 is removed from the atmosphere v. Fossil fuels use has skyrocketed in the past few decades – this has released CO2 in the atmosphere vi. Burning tropical rainforests, to clear land for ___________________________, also increases atmospheric CO2 vii. CO2 is the most important greenhouse gas that human activities affect because it is so ____________________________. 1. Methane 2. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) – human-made chemicals 3. Tropospheric Ozone – from vehicle exhaust Global Warming: i. With more greenhouse gases trapping heat, average global temperatures are rising (aka GLOBAL WARMING) Temperatures are Rising: i. The rate of increase has been more rapid in the past century, and has risen even faster since 1990 1. The nine warmest years or record have all occurred since 1998, and 10 of the 11 warmest years have occurred since 2001 ii. Annual variations aside, the average global temperature has increased 1. The US has long been the largest emitter of greenhouse gases 2. China’s rapid economic growth, its emissions surpassed those of the US in 2008 i. j. 3. The average US citizen produces far more greenhouse gases than the average Chinese person Future Warming: i. In the developed nations it will depend on technological advances or lifestyle changes that ___________________________ emissions 1. In the developing nations, it will depend on how much their lifestyles improve and how these improvements are made ii. Computer models are used to predict the effects of ______________________________ gas increase on climate for the planet as a whole and also for specific regions 1. If nothing is done to control greenhouse gas emissions and they continue to increase at current rates, the surface temperature of the Earth can be expected to ____________________________ iii. Whatever the temperature increase, it will not be uniform around the globe 1. The North Pole has been affected more than the South Pole 2. BUT the temperatures are still increasing in Antarctica iv. The timing of events for species is changing v. Glaciers are melting and vegetation zones are moving uphill vi. As greenhouse gases _____________________________, changes will be more extreme vii. Oceans will become slightly more acidic (making it hard for coral reefs to grow) viii. Decreased snowpack, shrinking glaciers, and the earlier arrival of spring will lessen the amount of water available in some regions of the world ix. Weather will become more extreme with heat waves and droughts x. Although scientists do not all agree, hurricanes are likely to become more severe and possibly more frequent xi. Sea level is expected to _________________ Food for Thought? i. Are the increase in global temperatures natural? ii. In other words, can natural variations in temperature account for the increase in temperature that we see? iii. _____________________ Changes in the Sun’s radiance, El Nino and La Nina cycles, natural changes in greenhouse gas, and other atmospheric gases cannot account for the increases in temperature that has already happened in the past decades!