* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Magnetic Field - World of Teaching
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
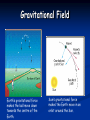
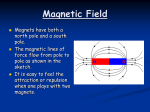
Magnetic Field Magnets have both a north pole and a south pole. The magnetic lines of force flow from pole to pole as shown in the sketch. It is easy to feel the attraction or repulsion when one plays with two magnets. Electromagnetism A magnetic field is produced when an electric current flows through a coil of wire. This is the basis of the electromagnet. We can make an electromagnet stronger by doing these things: wrapping the coil around an iron core adding more turns to the coil increasing the current flowing through the coil. A Simple Electromagnet: Using electromagnets Many objects around you contain electromagnets. They are found in electric motors and loudspeakers. Very large and powerful electromagnets are used as lifting magnets in scrap yards to pick up, then drop, old cars and other scrap iron and steel. They are better than magnets because the magnetism can be turned off and on. Electromagnet animation http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ks3bitesi ze/science/physics/magnetism_4.shtml Electric bells Electric bells like the ones used in most schools also contain an electromagnet. When the current flows through the circuit, the electromagnet makes a magnetic field. The electromagnet attracts the springy metal arm. The arm hits the gong, which makes a sound and the circuit is broken. The electromagnet is turned off and the springy metal arm moves back. The circuit is complete again. Animation of electric bell http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/ks3bitesize/ science/physics/magnetism_5.shtml Gravitational Fields All objects have a force that attracts them towards each other. This is called gravity. Even you attract other objects to you because of gravity. But you have too little mass for the force to be very strong. Gravity only becomes noticeable when there is a really massive object like a moon, planet or star. Gravitational Field The Earth has more mass than the Moon, so the gravitational force is greater on the Earth than it is on the Moon. The Earth's gravitational force pulls objects towards the centre of the Earth. "Down" is towards the centre of the Earth, wherever you are on the planet Gravitational Field Earth’s gravitational force makes the ball move down towards the centre of the Earth. Sun’s gravitational force makes the Earth move in an orbit around the Sun. Electric Fields An electric field shows us how electric charges behave around each other. See what elec field looks like: http://www.colorado.edu/physics/2000/ waves_particles/wavpart3.html Electric Fields Positive and negative charges attract each other. What do two positive charges do to each other? Electric Fields Lightning discharges an excess of positive and negative charge within clouds, between clouds, or between clouds and the ground. Extension: Physics textbook: Read p78-79 – Gravity Try questions 4 & 5 on p81. Read p139/140 and try questions. This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.