* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Regents Review
Tennessee in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Mississippi in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Border states (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom and the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Radical Republican wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
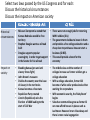
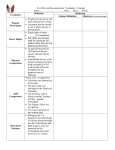
Regents Review US History & Government Tuesday 5/13 How did each of the following contribute to the Civil War? • Compromise of 1850 – California joined the Union as a free state – Popular Sovereignty would determine slavery in the Mexican Cession – Fugitive Slave Act would force slaves to return to the South • Uncle Tom’s Cabin (1852) – An emotional work of fiction that depicted the evils of slavery. It became a best seller in the North • Kansas Nebraska Act (1854) – Overturned the Missouri Compromise and allowed popular sovereignty in the Kansas Nebraska Territory. Led to ‘Bleeding Kansas.’ • Birth of the Republican Party (1854) – A sectional political party that arose in reaction to the Kansas-Nebraska Act. It opposed the spread of slavery to the territories. – “Free Soil, Free Labor, Free Men” How did each of the following contribute to the Civil War? • The Dred Scott Case (1857) – No person of African descent was a citizen – Missouri Compromise was unconstitutional – 5th Amendment protected slave owners • John Brown’s Raid at Harper’s Ferry (1859) – Brown planned to steal weapons and start a slave uprising. – He was captured and executed for leading a raid on an arsenal in West Virginia. – Brown was viewed as a martyr after his execution. • The Presidential Election of 1860 – The Democratic Party split (North vs. South) – Lincoln (Republican) was elected with 39% of the vote (He won NO southern states) Civil War Review What advantages and disadvantages did the North & South have entering the Civil War? Union Advantages Disadvantages • Larger Population • More Economic Resources • Stronger Political Leadership • Strong World Recognition • Strong Navy • Weaker Reason for Fighting • Weak Military Leadership • Lack of Knowledge of Land • Long Supply Lines • Few North/South Railroads Confederacy Advantages • Fighting on home soil • Strong Military Leadership • Strong Morale Disadvantages • Less Industry • Less Technology • Fewer Economic Resources • Fewer People Able to Fight • Weak Political Leadership • Weak Navy That Could Not Break Blockade Civil War Review • What were the ‘Border States’? • States that stayed loyal to the Union despite permitting slavery (Missouri, Kentucky, West Virginia, Maryland, Delaware • What happened to civil liberties during the Civil War? • Civil liberties were limited. Lincoln suspended habeas corpus and arrested southern sympathizes in Maryland • What was the significance of the Battle of Antietam and the Battle of Gettysburg? • After Antietam, Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation (ending slavery in areas of rebellion). This turned the war from a conflict over states’ rights to a war over slavery • Gettysburg was the turning point in the war. After this battle, the South’s defeat was inevitable • What was Total War? • The destruction of all food, supplies, and civilian morale in enemy territory, to force an end to the war • Gen. Sherman used total war in his ‘March to Sea’ from Atlanta to Savannah • How did the war impact the North and the South? • The war was an engine of economic growth in the North and ushered in the age of Industrialization. • In the South, the war was economically devastating. It took the region approx 100 years to fully recover. Reconstruction Review • How was Presidential Reconstruction different from Congressional (Radical) Reconstruction? • Presidential reconstruction was lenient on the South (Lincoln’s 10% Plan) • Congressional reconstruction was harsh on the South (Military Reconstruction) • Why was President Andrew Johnson impeached? • Formally he was accused of breaking the ‘Tenure of Office Act.’ However in reality, Northern Republicans hated Johnson (a Southern Democrat) and who had vetoed the Freedman’s Bureau • Who upheld Reconstruction in the South? • African-Americans; Carpetbaggers & Scalawags • How did the Reconstruction Amendments change the Constitution? • 13th Amendment – ended slavery • 14th Amendment – all people born in the US are citizens (equal protection clause) • 15th Amendment – granted all men the right to vote Reconstruction Review • Why did Reconstruction end in 1877? – The result of the President Election of 1877 was disputed – The Democrats and Republicans make a deal (Compromise of 1877): • The Republican candidate (Hayes) becomes president • The Democrats get the withdrawal of troops from southern states. • How did the Redeemers change the South? • Redeemers (often old Confederates) were elected to office in Southern states with the promise of restoring white supremacy through poll taxes, literacy tests, grandfather clauses, lynching & KKK attacks • What was the ‘New South’? • Some industrialization but mostly agricultural and very poor (sharecropping) • Segregation (Jim Crow laws) were made legal in Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) • How did Booker T. Washington and W.E.B. DuBois work to improve conditions for African-Americans • Washington: argued for economic betterment without directly challenging southern segregation (Tuskegee Institute) • Du Bois: demanded full social, economic and political equality immediately, especially for the ‘talented tenth’ (NAACP) 12 Significant Presidencies Washington Jefferson Jackson Polk • Set precedents (i.e. cabinet) • Hamilton’s Financial Plan • Whiskey Rebellion • Proclamation of Neutrality & Farewell Address • Revolution of 1800 • Favored limited government • Opposed Hamilton’s Financial Plan • Strict Construction • Louisiana Purchase • Vetoed Bank of US • Ignored Supreme Court (Worcester v. Georgia) • Supported Trail of Tears • Used the Spoils System • Popular Campaigning • Nominating Conventions • Manifest Destiny “54 40 or Fight” • Mexican American War • Gained Oregon Territory • Gained Mexican Cession 12 Significant Presidencies Lincoln T. Roosevelt Wilson F. Roosevelt • First Republican • Civil War to maintain the Union • Issued Emancipation Proclamation • Gettysburg Address • 10% Plan • Assassinated • Progressive • Square Deal • Trustbuster • Conservationist • Pure Food and Drug Act • Meat Inspection Act • Great White Fleet • Roosevelt Corollary • Progressive • Clayton Antitrust • Federal Reserve • Federal Trade Commission • Led the nation in WWI “War to end all wars” • 14 Points (League of Nations( • Failed to get Treaty of Versailles ratified • New Deal • Greatly expanded the Power of Federal government (Social Security, FDIC, SEC…) • Good Neighbor Policy • Led the US during World War II • Japanese-American Internment • Elected 4 times to the Presidency 12 Significant Presidencies Truman Johnson • Use of Atomic Bomb • Great Society (‘War to end WWII on Poverty’ • Containment programs Head Start, (Truman Doctrine, Food Stamps, Marshall Plan, NATO) Medicare….) • Korean War • Promoted Civil Rights • Fair Deal (Civil Rights Act & Voting Rights Act) • Gulf of Tonkin Resolution & Escalation in Vietnam Nixon • ‘Peace with Honor’ • Nixon Doctrine (Vietnamization) • Détente (improved relations with China & USSR) • Paris Peace Accords of 1973 • Southern Strategy • Watergate Reagan • Conservative on social issues • Believed in smaller government & lower taxes • Supply-side economics (Reaganomics) • Huge budget deficits • Arms control with USSR • Reagan Doctrine • Iran-Contra Scandal Select two laws passed by the US Congress and for each: Discuss the historical circumstances Discuss the impact on American society Kansas Nebraska Act GI Bill • Missouri Compromise stated that Historical Kansas-Nebraska would be free circumstances • • Impact on society • • • • • • • territory • Stephen Douglas wants a railroad built Douglas supports popular sovereignty in order to get support • in the Senate for his railroad Bleeding Kansas (pro and anti slavery forces fight) John Brown’s massacre Divides the country over the issue of slavery in the territories Kansas becomes a free state Republican Party created Lincoln (Republican) wins the Election of 1860 leading to the start of Civil War • • • • There were not enough jobs for returning WWII soldiers (GIs) The government decides to invest in them and provides a free college education and a cheap loan to purchase a house or start a business (GI Bill). This would provide a boost for the economy The middle class and the number of colleges increase as former soldiers get a college education With a college education, former GIS become of white collar professionals often working for corporations With economic security, the ‘Baby Boom’ begins Suburban communities grow as former GI can now afford houses in places such as Levittown. However inner cities decay and there is more racial segregation