* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Practice Packet: Magnetism and Electromagnetic Induction Name
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
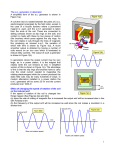
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
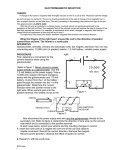
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Practice Packet: Magnetism and Electromagnetic Induction Name ________________________ Answer the following questions using Chapters 19 and 20 of your book and your notes. Magnetic Field 1) What is the source of magnetism? 2) What are the two types of fields surrounding a moving electron? 3) What is a magnetic domain? 4) Why are iron atoms so strongly affected by magnetic fields? 5) If an unmagnetized piece of iron is attracted to one pole of a magnet, will it be repelled by the opposite pole? Why or why not? 6) How would you determine if an iron bar is magnetized without using another magnet? 7) When a small magnet is repeatedly dropped it becomes demagnetized. Explain what happens to the domains in the magnet. 8) What is the minimum number of poles for a magnet? 9) Sketch the magnet field lines around a bar magnet. Make sure you label the north and south pole. 10) Which of the compass needle orientations in the figure below correctly describe the magnet’s field at the point? 11) Which magnets would attract one another? a) N S N b) S N N S S 12) The north pole of a magnet is attracted to the geographic north pole of the Earth, yet like poles repel. Explain. 13) Which way would the North Pole of a compass needle point if you were at the magnetic South Pole? Magnetism from Electricity 14) If a compass is placed near a wire carrying current, which way does the compass needle deflect? 15) Explain the right hand rule. 16) What TWO factors does the strength of the magnetic field of a solenoid depend on? 17) If a solenoid was suspended by a string so that is could rotate freely, could it be used as a compass when it carried a direct current? Why or why not? 18) Why does a piece of iron in a current carrying loop increase the magnetic field strength? 19) In what direction relative to the magnetic field does a charged particle move in order to experience the maximum magnetic force? 20) Why does the picture on a TV screen become distorted when a magnet is brought near the screen? 21) Since a magnetic force acts on a moving charged particle, why does it make sense that a magnetic force also acts on a current carrying wire? Electromagnetic Induction 22) Explain electromagnetic induction. 23) A circular loop made of flexible wire is located in a magnetic field. How would you move the loop of wire in relation to the magnetic field to induce a potential difference? 24) What does a potential difference induce in the wire loop? 25) Explain how the relative motion between a closed circuit and a magnet induces a current. 26) According to Faraday’s Law, what two things does the induced voltage in a coil of wire depend upon? 27) Why is it difficult to push a magnet into a coil of wire? 28) If a magnet is place inside a stationary coil of wire, is there an induced current in the coil of wire when the magnet is stationary? Why or why not? 29) In terms of energy, what is the basic similarity between a generator and an electric motor? 30) What is the basic difference between a generator and an electric motor? Transformers 31) Why is electrical energy transmitted at high voltages and low current? 32) What are the parts of the simplest AC transformer? 33) Why does a transformer require alternating current? 34) What exactly does a transformer transfer? 35) If a transformer is efficient enough can it step up energy? Why or Why not. 36) In a step up transformer there are more turns on the ________________ coil and the voltage will ___________________ and current will _________________ in the secondary coil. 37) In a step down transformer there are more turns on the ________________ coil and the voltage will ___________________ and current will _________________ in the secondary coil. 38) If 10 volts of alternating current is inputted across a primary coil of a transformer, how much voltage is induced in the secondary coil if the secondary coil has 5 times the number of turns? 39) A transformer has 50 turns in its primary coil and 250 turns in its secondary coil. If 12 volts of alternating current is connected to the primary coil, how many volts are available at the secondary coil? 40) What is the current in a 10 ohm device that is connected to the secondary coil above? 41) What is the power supplied to the primary coil above? 42) A model electric train requires 6 volts to operate. If the primary coil of its transformer has 240 turns, how many turns should the secondary coil have it the primary is connected to a 120 volt household circuit?