* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
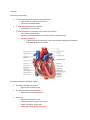
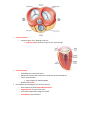
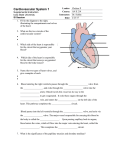
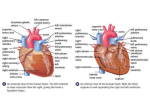
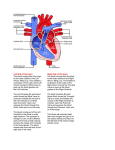
Cardiac Anatomy and Blood Flow Lecture KEY 2/10/16 Cardiovascular system can be referred to as a double pump Function The myocardium also known as the heart o Delivers oxygen and nutrients needed by cells o Transports hormones to help regulate body function o Delivers antibodies and inflammatory cells needed for protection o Removes waste from tissues Cardiovascular System Circuit Cardiovascular System Circuit is a closed circuit. o Material does not leave system o Lymphatic System circuit is an OPEN circuit Pulmonary circuit (right side) o Carries blood to the lungs for gas exchange Systemic circuit (left side) o Supplies blood to all organs of the body Structure and Position Location and Position Medial to both lungs o Felines and Canines lies at level between 3rd and 7th ribs o Horses and ruminant animals lies at level between 2nd and 6th ribs Right behind the sternum, Just in front of the thoracic vertebrae Base of the heart is where major vessels enter o Widest portion o Faces cranially o Tipped dorsally to the right Apex is the pointed tip o Faces generally caudal direction o Tipped ventrally to the left Structure Three layers of the heart 1st layer endocardium lining of the inside of the heart o Very smooth to create very little friction o Continues into blood vessels nd 2 layer Myocardium varies in thickness o Left ventricle is the thickest rd 3 layer Epicardium is also known as the visceral pericardium o Peri- prefix meaning around o Visceral pericardium doubles onto itself to create an additional layer o Parietal pericardium Creates lubricant to prevent the visceral pericardium and parietal pericardium from rubbing during contractions Four Major Chambers and Major Vessels Two Upper Chambers called atria o Right Atrium and Left Atrium Two lower chambers called ventricles o Right Ventricle and Left Ventricle Vena Cava o Bring blood toward the heart o Cranial Vena Cava (superior vena cava) o Upper neck region, upper limbs o Caudal Vena Cava (inferior vena cava) Trunk and lower limbs Pulmonary Trunk o Branches to left and right pulmonary artery Aorta o Aortic Arch runs from the left ventricle around the heart Branches three arches to supple “top” of the body with oxygenated blood left subclavian artery Left common artery brachiocephalic trunk All VEINS carry blood TOWARD the heart All ARTERIES carry blood AWAY from the heart The interatrial septum o Separates the right atrium from the left atrium The interventricular septum o Separates the right and left ventricles Valves Purpose of valves o provide one directional flow o When ventricles are relaxed the AV valves open, blood flows into both the right and left ventricles o When ventricles contract the blood is forced two directions, the valves act like parachutes holding the blood into the correct area right atrioventricular valve (RAV) o Separates the right atrium from the right ventricle o Also known as the tricuspid valve o Left atrioventricular valve (LAV) o Separates the left atrium from the left ventricle o Also known as the bicuspid valve or Mitral valve Pulmonary Semilunar valve o Located in the right ventricle o Separates the right ventricle from the pulmonary artery Aortic Semilunar valve o Located in the left ventricle o Separates the left ventricle to the aorta chordae tendinae o prevents valves from “blowing inside out” papillary muscle contracts to pull on the “heart strings” Coronary Vessels o Provided heart muscle with blood o Blood never touches the actual heart muscle due to the endocardium o “Best” blood available Most oxygen rich blood available o Breaks off the Aorta Heart Attacks are blockages of the coronary arteries o Heart attacks are called myocardial infarctions o Angina pectoris is a pain in the chest o If the heart is deprived of oxygen it will die o Anastomoses blood “detours”