* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrical Circuits Revision - School
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Printed circuit board wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
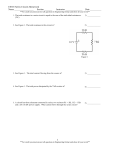
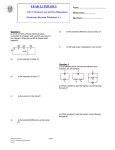
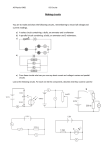
Electrical Circuits Revision P2 REVISION – CHAPTER 4 – Current Electricity Electrical Charges If you rub two electrically insulating materials are rubbed together, __________________ are rubbed off one material and deposited on the other. Objects that have opposite electric charges ______________ each other, if they have the same electric charge they___________. Electric Circuits Electric symbols I is the current in amperes, A Q is the charge in coulombs, C t is the time in seconds, s. Every component has an agreed circuit symbol. Make sure you can recognise and draw them! Resistance Current is measured with an ammeter. Where are ammeters placed in relation to the component? What is the unit of current? The potential difference(pd) across a component is measured with a voltmeter. These are always placed in parallel with the component. What is the unit of potential difference? V is ? W is ? Q is ? Don’t forget units! R is ? V is ? I is ? Don’t forget units! Ohm’s law: states that the current through a resistor at constant temperature is directly proportional to the potential difference across the resistor. KEY WORDS: Insulating Electron Attract Repel Resistance Series ASSESSMENT: P2 REVISION – CHAPTER 4 – Current Electricity Cont. Series Circuits Current-Potential Difference Graphs A current-potential difference graph for a resistor. How are the components connected in a series circuit? What happens if there is a break in the circuit? Is the current the same or different through each component? If you add together the potential difference what does it give you? The resistance of the individual components add up to give the total resistance of the circuit. A current-potential difference graph for a filament bulb, line is a curve so the current is not directly proportional to the __________________ ___________________. The current in a diode flows in one direction only, in the reverse direction the diode has a very high resistance so the current will be what? Parallel Circuits How are the components connected in a series circuit? What happens if there is a break in the circuit? Is the pd across each component the same or different? The bigger the resistance of a component, the ______________ the current through it. Use this equation to work out the current through a component in a parallel circuit. Thermistor: Resistance _______________ if its temperature increases. LDR: resistance decreases if the light intensity on it ___________. KEY WORDS: Diode Filament bulb Resistor Thermistor ASSESSMENT: