* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Behaviorism - WordPress.com
Cross-cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Symbolic behavior wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Experimental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Social psychology wikipedia , lookup
Thin-slicing wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Organizational behavior wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
History of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Operant conditioning wikipedia , lookup
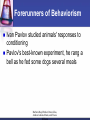
Behaviorism Stimulus-Response Conditioning through reinforcement Barbara Boyd-Parker, Dana Giles, Andrea Jenkins-Mann, and Tracee Behaviorism Any psychology that sees its mission as the explanation of behavior and stimuli and responses as its basic data (Kimble, 2000). Barbara Boyd-Parker, Dana Giles, Andrea Jenkins-Mann, and Tracee Behaviorism in an Academic Setting In an academic context, behaviorists substitute verbal behavior (e.g. responding appropriately to a question) for physical behavior. The behaviorist would interpret, for example, a student’s correct answer to a question as a sign of successful conditioning, and then continue to reinforce correct responses behaviorally by assigning good grades. Often, the form of conditioning used to achieve desirable verbal behavior is a lecture-based pedagogy (Boghossian, 2006). Barbara Boyd-Parker, Dana Giles, Andrea Jenkins-Mann, and Tracee Behaviorism views the student as an unreflective responder. In a behaviorist paradigm, the student is engaged in the educational process only in that she displays the appropriate verbal behavior (e.g. checking the correct box on a multiple choice test) (Boghossian, 2006). Barbara Boyd-Parker, Dana Giles, Andrea Jenkins-Mann, and Tracee Forerunners of Behaviorism John B. Watson, an American psychologist. Watson claimed that psychology was not concerned with the mind or with human consciousness Watson's work was based on the experiments of Ivan Pavlov Barbara Boyd-Parker, Dana Giles, Andrea Jenkins-Mann, and Tracee Forerunners of Behaviorism Ivan Pavlov studied animals' responses to conditioning Pavlov's best-known experiment, he rang a bell as he fed some dogs several meals Barbara Boyd-Parker, Dana Giles, Andrea Jenkins-Mann, and Tracee Behaviorism Today Behaviorism is associated today with the name of B.F. Skinner made his reputation by testing Watson's theories in the laboratory Skinner's studies led him to reject Watson's almost exclusive emphasis on reflexes and conditioning (Cohen, 1987). Barbara Boyd-Parker, Dana Giles, Andrea Jenkins-Mann, and Tracee Operant Conditioning Skinner developed the theory of "operant conditioning," the idea that we behave the way we do because this kind of behavior has had certain consequences in the past Skinner denied that the mind or feelings play any part in determining behavior. Instead, our experience of reinforcements determines our behavior (Cohen, 1987). Barbara Boyd-Parker, Dana Giles, Andrea Jenkins-Mann, and Tracee Presuppositions of Behaviorism Behaviorism is naturalistic Behaviorism teaches that man is nothing more than a machine that responds to conditioning. Behaviorism teaches that we are not responsible for our actions Behaviorism is manipulative (DeMar, 2007) Barbara Boyd-Parker, Dana Giles, Andrea Jenkins-Mann, and Tracee References Kimble, G. 2000. Behaviorism and Unity in Psychology. Current Directions in Psychological Science. 9(6). Boghossian, P. 2006. Behaviorism, Constructivism, and Socratic Pedagogy. Educational Philosophy and Theory. 38(6). Cohen, D. 1987. "Behaviorism," in The Oxford Companion to the Mind, Richard L. Gregory, ed. (New York: Oxford University Press. DeMar, G. (2007). Behaviorism. The Forerunner. Retrieved on April 1, 2008 from http://forerunner.com/forerunner/X0497_DeMar_-_Behaviorism.html. Barbara Boyd-Parker, Dana Giles, Andrea Jenkins-Mann, and Tracee