* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Solid Earth
Survey
Document related concepts
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
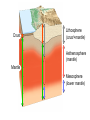
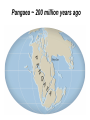
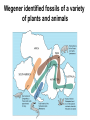
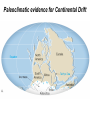
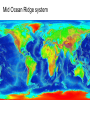
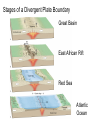
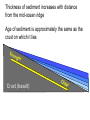
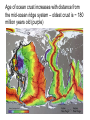
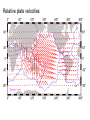
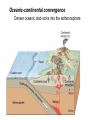
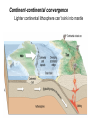
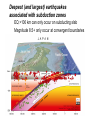
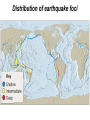
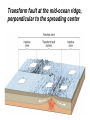
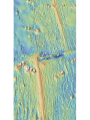
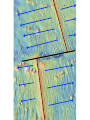
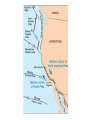
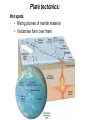
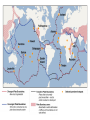
The Solid Earth Crust Lithosphere (crust+mantle) Asthenosphere (mantle) Mantle Mesosphere (lower mantle) Post-glacial rebound in Scandinavia: about 9 cm/100years Solid, lower density lithosphere floats atop plastic, denser asthenosphere lithosphere asthenosphere Pangaea ~ 200 million years ago Movement of continents from late Paleozoic to the present Wegener identified fossils of a variety of plants and animals Paleoclimatic evidence for Continental Drift Paleoclimatic evidence for Continental Drift Mid Ocean Ridge system Sea-floor spreading Stages of a Divergent Plate Boundary Great Basin East African Rift Red Sea Atlantic Ocean Magnetic reversals occur at random intervals in Earth’s history… The last reversal occurred ~ 730,000 years ago Rekyjanes Ridge, North Atlantic: stripes represent magnetic anomalies – Note symmetry Development of magnetic stripes As new crust cools it locks in the prevailing magnetic field orientation Thickness of sediment increases with distance from the mid-ocean ridge Age of sediment is approximately the same as the crust on which it lies You nge r Crust (basalt) Olde r Age of ocean crust increases with distance from the mid-ocean ridge system – oldest crust is ~ 180 million years old (purple) Relative plate velocities Convergent plate boundaries (destructive margins) Oceanic-oceanic convergence Two oceanic slabs converge and one descends beneath the other Oceanic-continental convergence Denser oceanic slab sinks into the asthenosphere Continent-continental convergence Lighter continental lithosphere can’t sink into mantle Continent-continental convergence Lighter continental lithosphere can’t sink into mantle Collision produces folded mountains Deepest (and largest) earthquakes associated with subduction zones EQ >100 km can only occur on subducting slab Magnitude 8.5+ only occur at convergent boundaries Distribution of earthquake foci Transform fault at the mid-ocean ridge, perpendicular to the spreading center Plate tectonics: Hot spots • Rising plumes of mantle material • Volcanoes form over them Guyots extinct islands, eroded flat by wave action Volcanic islands (Active) (Inactive) Atoll – Guyot formed in tropical regions, fringed by growing coral reefs as they erode and sink Increasing time Maldive islands in the Indian Ocean