* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PRACTICE CELL TOUR TEST STANDARD NAME
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
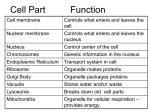
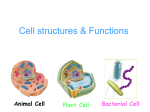
PRACTICE CELL TOUR TEST STANDARD NAME ____________________ Period _______ Date _________ Match the letters on the universal cell below to the terms listed below. “Burns sugar” A Universal Cell B Contains digestive enzymes C D E F N G M H I Harnesses sun’s energy L J Breaks K down H2O2 _____ 1. Smooth E.R. _____ 8. Cell wall _____ 2. Peroxisome _____ 9. Nucleolus _____ 3. Lysosome _____ 10. Vesicles _____ 4. Mitochondria _____ 11. Golgi body 15. List three structures not found in plant cells. a. __________________ b. __________________ c. __________________ _____ 5. Ribosomes _____ 12. Rough E.R. _____ 6. Central vacuole _____ 13 Plasma membrane 16. List three structures not found in animal cells. _____ 7. Chloroplasts _____ 14. Nucleus a. __________________ b. __________________ c. __________________ 1 PRACTICE CELL TOUR TEST STANDARD NAME ____________________ Period _______ Date _________ Match the letter of the function listed on the right to the structures on the left. _____ 17. Cell wall _____ 18. Central vacuole _____ 19. Chloroplasts _____ 20. Golgi body _____ 21. Vesicles _____ 22. Mitochondria _____ 23. Nucleus _____ 24. Plasma membrane _____ 25. Ribosomes _____ 26. Rough E.R. _____ 27. Smooth E.R. _____ 28. Plasmodesmata _____ 29. Nucleolus a. regulates traffic of chemicals between the cell and and its surroundings. b. organelle where cellular respiration occurs and most ATP is generated c. ribosome studded membrane; continuous with the nuclear envelope; synthesis of secretory proteins. d. a tiny membranous sac in a cell’s cytoplasm carrying molecules produced by the cell. e. photosynthetic organelle; converts light energy to chemical energy stored in sugar molecules. f. outer layer that maintains cell’s shape; made of cellulose, other polysaccharides, and protein. g. enveloped by a double membrane, contains nucleoli and chromatin. h. channels through cell walls that connect the cytoplasm of adjacent cells. i. small nonmembranous organelles that make proteins; free in cytoplasm, bound to rough E.R. j. a series of flattened sacs that modifies, sorts, packages and ships products from the ER. k. prominent organelle in older plant cells; stores water and dissolved minerals (sap). l. a network of channels that synthesizes lipids and steroids; detoxifies drugs and poisons. m. site within the nucleus where ribosomes are formed. 30. Is the cell on page 1 a prokaryote or eukaryote? Explain: 31. What structures are depicted in the micrograph shown to the right? 32. What might be carried in the round blobs? 2 Key NAME ____________________ Period _______ Date _________ PRACTICE CELL TOUR TEST STANDARD Universal Cell B A Contains digestive enzymes C D E F N G M H I L J Breaks K down H2O2 _____ F 1. Smooth E.R. _____ N 8. Cell wall _____ K 2. Peroxisome _____ C 9. Nucleolus 15. List three structures not found in plant cells. Centrioles a. __________________ _____ A 3. Lysosome _____ H 10. Vesicles Lysosomes b. __________________ _____ B 4. Mitochondria _____ G 11. Golgi body Flagella c. __________________ _____ J 5. Ribosomes _____ E 12. Rough E.R. _____ L 6. Central vacuole _____ M 13 Plasma membrane 16. List three structures not found in animal cells. _____ 7. Chloroplasts I _____ D 14. Nucleus Chloroplasts a. __________________ Cell wall b. __________________ Central vacuole c. __________________ Plasmodermata 3 Key NAME ____________________ Period _______ Date _________ PRACTICE CELL TOUR TEST STANDARD Match the letter of the function listed on the right to the structures on the left. _____ F 17. Cell wall _____ K 18. Central vacuole _____ E 19. Chloroplasts J _____ 20. Golgi body _____ D 21. Vesicles _____ B 22. Mitochondria _____ G 23. Nucleus A 24. Plasma membrane _____ I 25. Ribosomes _____ C 26. Rough E.R. _____ L 27. Smooth E.R. _____ H 28. Plasmodesmata _____ M 29. Nucleolus _____ a. regulates traffic of chemicals between the cell and and its surroundings. b. organelle where cellular respiration occurs and most ATP is generated c. ribosome studded membrane; continuous with the nuclear envelope; synthesis of secretory proteins. d. a tiny membranous sacs in a cell’s cytoplasm carrying molecules produced by the cell. e. photosynthetic organelle; converts light energy to chemical energy stored in sugar molecules. f. thick outer layer that maintains a plant cell’s shape; made of cellulose, other polysaccharides, and protein. g. enveloped by a double membrane, contains nucleoli and chromatin. h. channels through plant cell walls that connect the cytoplasm of adjacent cells. i. small nonmembranous organelles that make proteins; free in cytoplasm, bound to rough E.R. j. a series of flattened sacs that modifies, sorts, packages and ships products from the ER. k. prominent organelle in older plant cells; stores water and dissolved minerals (sap). l. a network of channels that synthesizes lipids and steroids; detoxifies drugs and poisons. m. s ite within the nucleus where ribosomes are formed. 30. Is the cell on page 1 a prokaryote or eukaryote? Explain: The cell is a eukaryote since it contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. 32. What structures are depicted in the micrograph shown to the right? The flat pancake-like structure is a Golgi body. The round blobs are vesicles. Key 32. What might be carried in the round blobs? Proteins, digestive enzymes, antibodies, lipids, hormones, water, salts, sugars, wastes, etc. 4