* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Food Studies Sample Questions
Survey
Document related concepts
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Protein phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
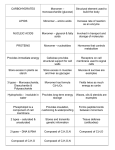
Structural unit of proteins. There are twenty common ones found in proteins. The process of converting simple nutrients (e.g. amino acids) into cellular/body components (e.g. proteins) -- an anabolic process (anabolism). amino acid assimilation Tough, fibrous protein with a high sulphur content Forms structures such as horns, nails, hair, feathers, etc. Food intake that contains the correct proportions of carbohydrate, fat, protein, minerals, vitamins, water and roughage. The quantities of each for an individual will depend on his/her sex, age and level of physical activity. keratin balanced diet Substances made inside organisms. Also known as biochemicals. There are four types found in food: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and vitamins. Composed of elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. General formula Cx(H2O)y. biomolecules carbohydrate The most abundant body protein, A main component of hair and forms the inelastic outer layer on arteries and veins. A five-carbon sugar found in the nucleotides of DNA. collagen deoxyribose A carbohydrate composed of two monosaccharide units joined together (e.g. sucrose = glucose + fructose = C12H22O11. Contains the elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, but in a different ratio to carbohydrates [very little oxygen]. It is solid at room temperature. disaccharide fat Food containing a large content of cellulose [plant cell walls], e.g. vegetables. Keeps the contents of the gut moving. Prevents constipation. A six-carbon single sugar, monosaccharide. Formed in plants during photosynthesis and is the end product of the digestion of carbohydrates. Most living organisms need it for respiration. fibre [roughage] glucose (C6H12O6) Fats are formed by attaching one of these molecules to three fatty acids. Animal storage polysaccharide found in muscles, liver and brain. glycerol glycogen A disaccharide reducing sugar, C12H22O11, found in milk and other dairy products. Fat or fat-like substance, composed of fatty acids and glycerol. Made of the elements carbon, hydrogen and oxygen Examples are oils, waxes and fat. lactose lipid A structure that is a combination of a lipid (fat) and protein, e.g. cell membrane is composed of it These are large molecules made up of many smaller organic molecules, e.g. carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. lipoprotein macromolecules Nutrients needed by plants in fairly large amounts for successful development, e.g. nitrogen, phosphorous, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulphur and iron. A disaccharide reducing sugar, C12H22O11, formed from the hydrolysis of starch. macronutrients maltose Elements required in very small amounts by organisms but essential for normal growth and development, e.g. for plants: boron, copper, zinc; for animals: most minerals and vitamins. Substance that contains some necessary ingredients for growth or energy for cellular metabolism and continuity. micronutrients / trace elements nutrient The process involved in the making and receiving or the absorption and utilisation of food (energy and materials) from the environment. A type of lipid that is liquid at room temperature. nutrition oil A carbohydrate composed of many sugar units. Compound with two or more amino acids linked together in sequence. A very small protein. Many of these form a polypeptide chain. polysaccharide peptide An essential organic catalyst of metabolism. Needed in small amounts, cannot be produced in the body. Some are water-soluble and some are fat-soluble. Compound composed of the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen [and sometimes sulphur]. Made by joining many amino acids together vitamin protein A polysaccharide made of repeated glucose molecules. Produced in photosynthesis It is found in bread, rice, and pasta. Smallest lipid consisting of three fatty acid and one glycerol molecule. starch triglyceride