* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease wikipedia , lookup
Psychological trauma wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Learning disability wikipedia , lookup
Retrograde amnesia wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Externalizing disorders wikipedia , lookup
Intellectual disability wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Memory disorder wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
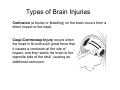
D.A.R.T. Alaska A Collaborative Approach to Addressing Violence and Abuse of People with Disabilities Presenter: Leslie Myers, MS, CRC, CDVC Domestic Violence Specialist and Counselor 600 W Virginia Street Milwaukee, WI 53204 (414) 226-8381 (V/Relay) (414) 291-7520 (V/TTY) [email protected] www.independencefirst.org DISABILITY 101 US Disability Demographics 300,000,000 250,000,000 Total Population 200,000,000 150,000,000 Disability status (population 5 years and over) 100,000,000 50,000,000 0 257,167,527 49,746,248 Alaska Disability Demographics 600,000 500,000 400,000 300,000 200,000 100,000 0 585,263 Alaska Population 88,000 Persons with Disabilities Brain, Cognitive and Developmental Disabilities There are a variety of disabilities that affect the brain, including: Alzheimer's Disease, a progressive disability that gradually destroys a person's memory and ability to learn and carry out daily activities such as talking, eating, and going to the bathroom. Stroke, also known as cerebrovascular accident (CVA),is an acute neurological injury in which the blood supply to a part of the brain is interrupted. Huntington's Disease (Huntington's chorea) is a progressive, degenerative disease that causes certain nerve cells in the brain to waste away, resulting in uncontrolled movements, emotional disturbances and mental deterioration. Epilepsy is a brain disorder in which, the normal pattern of neuronal activity becomes disturbed, causing strange sensations, emotions, and behavior or sometimes convulsions, muscle spasms, and loss of consciousness. Parkinson's Disease causes tremors, stiffness of the limbs and trunk, slowness of movement and impaired balance and coordination, making it difficult to walk, talk, or complete other simple tasks. ALS (Lou Gehrig's Disease) is a rapidly progressive neurological disease, that is always fatal. It attacks the nerve cells (neurons) responsible for controlling voluntary muscles, causing the loss of the ability to move arms, legs and body. Multiple Sclerosis is an unpredictable disease of the central nervous system, that can range from relatively benign to somewhat disabling to devastating, as communication between the brain and other parts of the body is disrupted. Cerebral Palsy is caused by abnormalities in parts of the brain that control muscle movements and appears in infancy or early childhood and permanently affects body movement and muscle coordination. Muscular Dystrophy are a group of more than 30 diseases characterized by progressive weakness and degeneration of the skeletal muscles that control movement. Some of these disabilities impact the person’s cognitive ability while others do not. The concept of cognitive disabilities is extremely broad, and not always well-defined. In general a person with a cognitive disability has greater difficulty with one or more types of mental tasks than the average person. Some of the main categories of functional cognitive disabilities include deficits or difficulties with: • Memory • Problem-solving • Attention • Reading, linguistic, and verbal comprehension • Math comprehension • Visual comprehension The head is a primary target in domestic violence. The effect of this battering can results in a cumulative brain injury. We can expect to find numerous symptoms of multiple brain injuries in women escaping from an abusive relationship. Besides an actual injury to the brain, alterations in the brain can be caused by shock and trauma of witnessing violence, for both women and children. Domestic Violence and Head Injuries Types of Brain Injuries Diffuse Axonal Injury- occurs when the head is shook or rotated causing the brain structures to tear. This disrupts the brain’s regular communication and chemical processes and produces temporary or permanent brain damage, coma, or death. Concussion occurs when the brain receives trauma from an impact or a sudden momentum or movement change. A person may or may not experience a brief loss of consciousness. A concussion can cause diffuse axonal type injury resulting in permanent or temporary damage. Types of Brain Injuries Contusion (a bruise or bleeding) on the brain occurs from a direct impact to the head. Coup-Contrecoup Injury occurs when the head is hit with such great force that it causes a contusion at the site of impact, and then slams the brain to the opposite side of the skull, causing an additional contusion. Types of Brain Injuries Second Impact Syndrome-("recurrent traumatic brain injury“) occurs when a person sustains a second traumatic brain injury before the symptoms of the first traumatic brain injury have healed, causing brain swelling and widespread damage. Penetration Injury- occurs when a bullet, knife or other sharp object forces hair, skin, bone and fragments from the object into the brain. Shaken Baby Syndrome occurs when a baby or young child is aggressively shaken, causing the brain to be injured. Developmental Disability The definition of a developmental disability is “a chronic disability from a mental and/or physical impairment that manifests before the person reaches age 22. The disability continues indefinitely and results in substantial functional limitations in three or more areas of major life activity”. Major life activities include: • capacity for independent living • economic self-sufficiency • learning • mobility • receptive and expressive language • self-care • self-direction Mental Retardation Mental Retardation manifests before age 18 and is characterized by significantly sub average intellectual functioning, concurrent with related limitations in two or more of the following applicable adaptive skill areas: •Communication •Self-care •Home living •Social skills •Community use •Self-direction •Health and safety •Functional academics •Leisure •Work Classification Additional Developmental Disabilities 1) Pervasive Developmental Disabilities (Autism, Asperger’s, etc. 2) Learning Disabilities (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, Dyslexia) 3) Cerebral Palsy 4) Fetal Alcohol Syndrome 5) Down’s Syndrome 6) Spina Bifida Physical Disabilities Physical disabilities include orthopedic, neuromuscular, cardiovascular and pulmonary disorders. Physical Disabilities can be: Congenital/Hereditary: A congenital/hereditary disability is a disability that have been their since birth or developed later due to genetic problems, problems with muscle cells or injury during birth. Acquired: An acquired disability is one that occurs as a result of a road or industrial accidents, crime, infections such as polio or diseases and disorders such as stroke or cancer Orthopedic Disabilities 9A congenital anomaly (e.g., scoliosis, Spina Bifida) 9Disease, (e.g., Muscular Dystrophy, Arthritis) 9Trauma or accident (e.g., amputation) Orthopedic Disabilities or Musculoskeletal Disabilities are disabilities related to the musculoskeletal system; the bones, joints and muscles. These disabilities can be the result of: Neurological Disabilities Neurological disabilities involve the nervous system affecting the ability to move, use or control certain parts of the body. Such impairments can be the result of: A congenital anomaly (e.g., Cerebral Palsy) Disease (e.g., poliomyelitis, carpal tunnel syndrome) Trauma or accident (e.g., spinal cord injury, head trauma). Violence and Physical Disabilities Physical Disabilities can occur as a result of violence, some of these may be temporary, i. e. broken bones. Other injuries may result in permanent disabilities like spinal cord injury from the battery or from gun shots or amputations from an injury. Mental Illness Does it look something like this? When you hear the words “mental illness” or “psychiatric disability”…what image comes to your mind? What is Mental Illness? Mental illness is an illness that affects or is manifested in a person's brain. It may impact the way a person thinks, behaves and interacts with other people. The term "mental illness" encompasses numerous psychiatric disorders and just like illnesses that affect other parts of the body, they can vary in severity. Many people suffering from mental illness may not look as though they are ill or that something is wrong, while others may appear to be confused, agitated, or withdrawn. Stigma of Mental Illness In our society mental illness carries a substantial stigma. People with mental illnesses are blamed for bringing on their own illnesses or seen as victims of bad fate, religious and moral transgression, or witchcraft. This stigma keeps families and individuals from acknowledging that a family member is ill. Some may hide or overprotect the person with a mental illness, which keeps them from receiving potentially effective care. Others may reject the person from the family. When these attitudes are magnified to a whole society it leads to underfunding of mental health services and inadequate care. The Experience of Mental Illness People with psychiatric disabilities are the only Americans who can have their freedom taken away and be institutionalized or incarcerated without being convicted of a crime and with minimal or no respect for their due process rights. They are the only Americans who can routinely be forced to submit to medical treatments against their will. When people with psychiatric disabilities die in facilities that are supposed to serve and protect them, their deaths are rarely investigated, and even when they are, criminal charges are rarely filed. Degradation Neglect Overcrowding Extermination People with mental illnesses were the first victims to be exterminated in Nazi Germany. In 1939 German psychiatric hospitals held between 300,000 and 320,00 patients. Only 40,000 were still alive after the war. In 1941, the Hadamar psychiatric institution celebrated the cremation of its ten thousandth "mental patient." Death Between 1950 and 1964, more people died in United States federal, state and county 'mental institutions' than the number of Americans killed in the Revolutionary War, the War of 1812, the Mexican War, the Civil War, the SpanishAmerican War, World War I, World War II, the Korean War, Vietnam, and the Persian Gulf War……………………. Combined! Prevalence of Mental Illness Domestic Violence and Mental Illness There are many psychological effects of domestic violence: ¾ 60% of battered women report depression ¾ Battered women are at greater risk for suicide attempts, with 25% of suicide attempts by Caucasian women and 50% of suicide attempts by African American women preceded by abuse. ¾ Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) is another common effect and it is characterized by symptoms such as flashbacks, intrusive imagery, nightmares, anxiety, emotional numbing, insomnia, hypervigilance, and avoidance of traumatic triggers. Psychiatric Disabilities Anxiety disorders involve excessive apprehension, worry, and fear. Includes generalized anxiety disorder, phobias, panic disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder. Mood disorders, also called affective disorders, create disturbances in a person’s emotional life, includes depression, mania and bipolar disorder. Psychiatric Disabilities Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders cause a person to lose contact with reality and may include delusions and hallucinations, disorganized thinking and speech, bizarre behavior, and social withdrawal. Personality disorders are mental illnesses in which one’s personality results in personal distress or a significant impairment in social or work functioning. Psychiatric Disabilities Cognitive disorders, such as delirium and dementia, involve a significant loss of mental functioning. Dissociative disorders involve disturbances in a person’s consciousness, memories, identity, and perception of the environment. Includes amnesia, dissociative identity disorder, depersonalization disorder, and dissociative fugue. Somatoform disorders are characterized by the presence of physical symptoms that cannot be explained by a medical condition or another mental illness. Includes conversion disorder and hypochondriasis. Psychiatric Disabilities Factitious disorders, people intentionally produce or fake physical or psychological symptoms in order to receive medical attention and care. For example Munchausen Syndrome. Substance-related disorders result from the abuse of drugs, side effects of medications, or exposure to toxic substances. Includes alcoholism and other forms of drug dependence, like caffeine, nicotine, cocaine, heroin, amphetamines, hallucinogens and sedatives. Psychiatric Disabilities Eating disorders are conditions in which an individual experiences severe disturbances in eating behaviors. Includes anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa. Impulse-control disorders cause an inability to control an impulse to engage in harmful behaviors, such as explosive anger, stealing (kleptomania), setting fires (pyromania), gambling or pulling out their own hair (trichotillomania). Sensory and Communication Disabilities Low Vision There are two general classifications of low vision: Partially sighted visual acuity that with conventional prescription lenses is still between 20/70 and 20/200 Legal blindness visual acuity that cannot be corrected to better than 20/200 with conventional lenses and/or the patient has a restricted field of vision less than 20 degrees wide, 90% of people who are legally blind have some remaining vision. Normal Vision 20/20 Vision Glaucoma Cataract Diabetic Retinopathy Vision Macular Degeneration Myopia (nearsightedness) Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) Hearing Loss and Deafness Conductive hearing loss is caused by the failure of the three tiny bones inside the middle ear to pass along sound waves to the inner ear or the failure of the eardrum to vibrate in response to sound waves. Sensorineural hearing loss results from malfunction of inner ear structures (i.e., cochlea) due to disease, trauma or some other disruptive event targeting the cochlear nerve. Mixed hearing loss is a combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. Central auditory dysfunction results from damage or dysfunction at the level of the 8th cranial nerve, auditory brain stem, or cerebral cortex. Prelingual hearing loss is present before speech develops. Postlingual hearing loss occurs after the development of normal speech. Causes of hearing loss and deafness include: 9 Hereditary, in most cases, hereditary deafness is caused by malformations of the inner ear. 9 Genetics, includes osteogenesis imperfecta and multiple lentigines syndrome. 9 Prenatal exposure to disease, including rubella (German measles), influenza and mumps. 9 Noise 9 Trauma 9 Diseases, like meningitis, mumps, cytomegalovirus and chicken pox. 9 Meniere's disease 9 Exposure to certain chemicals. 9 Age Deaf vs. deaf Deaf with a lowercase-d is generally understood to mean a physical loss of hearing. This use of the word “deaf” refers to the millions of people who suffer some degree of hearing loss due to age. Despite this loss of hearing, whether it is a mild reduction or a complete loss, these individuals are not members of the Deaf Community. Capital-d Deaf is a term that is applied to those individuals who lose their hearing at a young age. These individuals grow up NOT in the hearing world, but as members of the Deaf Community. Linguistically, the Deaf are a separate community from the hearing world. The Deaf Community's primary language is American Sign Language. This distinction may seem minor, but it underlies the foundation of Deaf Culture. The Deaf Community has its own social structures, art, clubs and organizations, values and cultural history. Speech Disabilities Fluency disorder: an interruption in the flow or rhythm of speech characterized by hesitations, repetitions or prolongations of nouns, syllables, words or phrases. Articulation disorder: difficulties with the way sounds are formed and strung together, characterized by substituting one sound for another (wabbit for rabbit), omitting a sound (han for hand) and distorting a sound (shlip for sip). Voice disorder: characterized by inappropriate pitch (too high, too low never changing or interrupted by breaks; quality (harsh, hoarse, breathy or nasal); loudness, resonance, and duration. Speech Disabilities Aphasia the loss of speech and language abilities generally resulting from stroke. Apraxia of speech, is a speech disorder in which a person has trouble saying what he or she wants to say correctly and consistently. Delayed language characterized by a marked slowness in the development of language skills necessary for expressing and understanding thoughts and ideas.