* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 4 Mr. Knox GA Studies
Survey
Document related concepts
Commemoration of the American Civil War on postage stamps wikipedia , lookup
Georgia in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Union (American Civil War) wikipedia , lookup
Hampton Roads Conference wikipedia , lookup
Opposition to the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
United States presidential election, 1860 wikipedia , lookup
Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Military history of African Americans in the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Issues of the American Civil War wikipedia , lookup
Fifteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Carpetbagger wikipedia , lookup
Reconstruction era wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
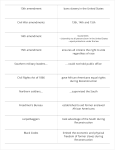
Unit 4 Mr. Knox GA Studies GPS SS8H6 The student will analyze the impact of the Civil War and Reconstruction on Georgia. c. Analyze the impact of Reconstruction on Georgia and other southern states, emphasizing Freedmen's Bureau; sharecropping and tenant farming; Reconstruction plans; 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments to the constitution; Henry McNeal Turner and black legislators; and the Ku Klux Klan. Essential Questions 1. How did Reconstruction efforts and policies impact Georgia and other southern states? (H6c) 2. How do sharecropping and tenant farming differ? (H6c) 3. How did the KKK intimidate people in the South? 4. How did the Republicans and the Freedmen’s Bureau affect African Americans? 5. How did resentment after the Civil War affect society? 6. How did the passage of the 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments to the Constitution affect all Americans, particularly African Americans? (H6c) End of the Civil War On April 9, 1865, General Robert E. Lee surrendered to General Ulysses S. Grant at Appomattox Courthouse, VA. After 4 years the bloody war was finally over. About 25,000 of the 125,000 GA soldiers who fought for the Confederacy died during the war. Reconstruction • Once the War was over, the Federal Government had to decide what to do with the states that seceded. • The process of rebuilding the South was known as Reconstruction. • Lincoln wanted to rebuild the south rather than punish them. He felt that all Americans had suffered enough. • Lincoln’s Reconstruction plan was known as the “10 percent plan” Reconstruction – Lincoln’s Plan Lincoln’s 10 Percent plan had 2 steps: 1. All southerners, except for high-ranking Confederate civil and military leaders, would be pardoned after taking an oath of allegiance to the US. 2. When 10 percent of the voters in each state had taken the oath of loyalty, the state would be permitted to form a legal government and rejoin the Union. Reconstruction • Lincoln never got to see the South rebuilt because he was assassinated by John Wilkes Booth on April 14, 1865. • Andrew Johnson succeeded Lincoln and became the USA’s 17th president and now had the task of rebuilding the nation.. • President Johnson was a southern Democrat who was loyal to the Union during the war. He favored a form of reconstruction that was less harsh on the South but did little to guarantee the rights of slaves. Reconstruction • President Johnson was opposed by the Radical Republicans. • Radical Republicans favored a more radical form of Reconstruction: – Felt that the south should be punished for starting the war. – Believed a majority of the states’ voting population should have to swear allegiance to the US before being readmitted to the Union. – Felt that the civil rights of slaves should be protected. – Also thought Congress, not the President should be in charge of Reconstruction. Reconstruction Johnson’s plan similar to Lincoln’s: His plan expanded groups of southerners not granted a general pardon. Those who owned property worth more than $20,000 or held high civil or military positions had to apply directly to the president for a pardon. Reconstruction Conflict over reconstruction grew so much that Johnson was impeached. Impeach – bringing formal charges against a government official in hopes of removing them from office. Johnson was saved by one vote from being removed from office. What other president in the US’s history has been impeached? Reconstruction Pressure from the Radical Republicans forced Johnson to add more requirements for the South: Southern states had to approve the 13th amendment. Southern states had to nullify their ordinances of secession. Southern states had to promise not to repay individuals and institutions that helped finance the Confederacy. The Freedman’s Bureau • Created by Congress in 1865 to help freed slaves. • Was the first federal relief agency in history. • The Freedman’s Bureau Provided: – – – – • Clothing Medical Attention Food Education It set up over 4,000 primary schools, 64 industrial schools, and 74 teacher training institutions. • Ended in 1869 because of lack of support, but helped many slaves in GA transfer to freedom. 13th, 14th, & 15th Amendments Amendment 13 1. Neither slavery nor involuntary servitude, except as a punishment for crime whereof the party shall have been duly convicted, shall exist within the United States, or any place subject to their jurisdiction. 2. Congress shall have power to enforce this article by appropriate legislation. 13th, 14th, & 15th Amendments Amendment 14 1. All persons born or naturalized in the United States, and subject to the jurisdiction thereof, are citizens of the United States and of the State wherein they reside. No State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States; nor shall any State deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws. 13th, 14th, & 15th Amendments Amendment 15 – 1. The right of citizens of the United States to vote shall not be denied or abridged by the United States or by any State on account of race, color, or previous condition of servitude. 2. The Congress shall have power to enforce this article by appropriate legislation. 13th, 14th, & 15th Amendments • Radical Republicans in Congress passed major legislation to help African-Americans after the war. – Prior to Lincoln’s death, the 13th Amendment was added to the US Constitution ending slavery. – 1868 – the 14th Amendment was ratified granting citizenship to African Americans. – 1870 – the 15th Amendment guaranteed that no citizen could be denied the right to vote by either the Federal Government or a State because of the color of their skin or because they use to be a slave. Sharecropping & Tenant Farming African Americans had to adjust to life after slavery. Former slaves had no money, no land, and no property. Many turned to sharecropping and tenant farming in order to make a living. Sharecropping vs. Tenant Farming • • • Sharecroppers agreed to farm a portion of a white landowner’s land in return for housing and a share of the crop. Some landowners were dishonest and cheated the sharecroppers. As a result of cheating, sharecropping became almost like slavery. Sharecropping A family rented a portion of land and owned the crops they grew. Tenants were less at the mercy of landowners. Tenant farmers also may have owned equipment and animals and also purchased their own seed and fertilizer. Tenant Farming Georgia’s Reconstruction Government After the war, the Federal Government took over GA’s government and appointed a provisional governor. 1866 – GA abolished slavery. 1867 – GA ratified the 13th Amendment. The US Army governed GA for a while (martial law) until Washington set up a new GA State Government. Georgia’s Reconstruction Government • Scalawags met in 1867 to adopt a new GA State Constitution that lasted until 1877. – Scalawags – White southerners who supported the Republican Party. • 1867 Rufus Bullock, a Radical Republican, became governor of GA until he was forced from office in 1871 by the Ku Klux Klan. • GA ratified the 14th Amendment in 1868. • 32 African-Americans were elected to the GA State House and Senate. Henry McNeal Turner Was one of the 32 African Americans elected to serve in GA’s Legislature in 1868. Was a Bishop in the African Methodist Episcopal Church. Doubted that whites and blacks could ever live together peacefully after slavery. He urged African Americans to move back to Africa rather than stay in the US. Few blacks listened, but Turner did draw a great deal of attention to the plight of African Americans in the South. Unrest in GA during Reconstruction A faction of conservative Democrats ousted 28 of the 32 African Americans who were voted into the State legislature. This group based their actions on the argument that blacks’ right to vote in the south did not give them the right to hold office. Some groups used violence to frighten African Americans. Ku Klux Klan Group who organized to terrorize African Americans and whites who assisted them. Klansmen would dress up in white sheets and hooded masks The KKK would often lynch those they targeted. Unrest in GA during Reconstruction Gov. Rufus Bullock was concerned about the unrest in GA and outraged at the ousting of the African American legislators. He asked the federal government to reinstitute martial law and in 1869 GA reorganized its government including the previously ousted African Americans. In January of 1870, GA ratified the 15th Amendment. In 1871, GA was readmitted to the Union. Presidential Election of 1876 In 1876, both Democrats and Republicans claimed their candidates had won the election. Republican Rutherford B. Hayes was named president after a compromise (Compromise of 1877). The compromise ended reconstruction and the Federal Government’s “occupation” of the south in exchange for Hayes becoming president. Presidential Election of 1876 Southern States could now run their own governments. GA and its neighbors became the “solid south”, a period of time in which only Democrats won elections for high offices. All civil rights efforts stopped in the south until the 1950’s because of Democrats’ control. Georgia would not have a Republican Governor again until 2002 when Sonny Perdue was elected.