* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inked
Quantitative comparative linguistics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Maximum parsimony (phylogenetics) wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
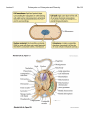
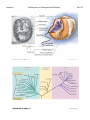
Lecture 2 Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes and Diversity Bacillus anthracis Last Lecture: 1. Introduction 2. History 3. Koch’s Postulates Today’s Today s Lecture: 1. Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote 2. Classifying prokaryotes 3 3. Ph l Phylogenetics ti Bio119 Lecture 2 Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes and Diversity Bio119 I. Basic Cell structure: (Fig. 1.5) A. All cells have B Many cells (plants B. (plants, prokaryotes prokaryotes, fungi) have: C. Eukaryotic cells 1. Major feature that is not in prokaryotic cells are: • • • 2. Generally larger and more complex than prokaryotes (Fig. 23.1) 3. DNA is contained in a __________________ compartment called the _______________ D. Prokaryotic cells (Fig. 4.43) 1. Two domains: ____________ and ________________ 2. Generally ____________ and _____________than eukaryotes 3. DNA is free in the cytoplasm. Lecture 2 Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes and Diversity II. Characteristics of the Domains of Life Characteristics of the primary domains (Table 1.2, 1.3, 1.4) Property p y Bacteria Archaea Eukaryote y Nuclear membrane Peptidoglycan cell walls Membrane Should be ester Lipids: glycerolglycerol linkage NOT hydrocarbon ether linkage Contain plastids Mitochondria Chloroplasts Transcription mRNA processing (capping, polyA t il) tail) mRNA splicing RNA Polymerase Genes in operons Transcription Factors Required Ribosome size Metabolism: Nitrogen Fixation Chemolithotrop hy Growth > 80˚C Bio119 Lecture 2 Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes and Diversity Bio119 III. Artificial vs. Phylogenetic Classification A. Artificial classification is based on: ________________________. E.g. g B. Phylogenetic classification is based on: ______________________. 1. Requires: 2. Preferred by bacteriologists 2 C. Two prokaryotic domains: IV. Nomenclature follows the binomial system of names. A. Domain, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species (Table 17.1) B. Example: Genus, Species: Escherichia coli must be Latin endings. 1. Genus is always capitalized and the species is lower case 2 Al 2. Always ititalicize li i or underline. d li 3. Name usually has some significance. C. How do identify a new isolate and classify it to the species level? 1. There are international guidelines: e.g. DNA-DNA hybridization IV. Phylogenetic Trees A. Basically two ways to create a phylogenic tree: 1. using: 2. using: B. The molecular-based system 1. Phylogenetic Tree shown in Fig 1.6 a)) b) The tree is derived from c) Pioneered by ________________________(Box 17.4) 2. This organization suggests that most of the diversity of life is in the ____________domains domains based on ribosomal RNA differences. differences a) Humans to corn: _________base changes/site. b) Between bacteria and archaea: ___________base changes/site. 3. Archaea are __________ closely related to Eukarya than Bacteria. 4. Eukaryotic microbes Lecture 2 Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes and Diversity Bio119 VI. The 16S or 18S rRNA gene is commonly used for phylogenetic classification of prokaryotes and eukaryotes: A. General features of a molecular marker? 1. 2. The function is: 3. There are ____________ and _______________regions 4. The gene tolerates: B. The gene encoding 16S ribosomal RNA (18S in eukaryotes) 1. The 16S rRNA is part of the ribosome a) Occurs in _______________________ b) c) Gene size: d) composed of many domains that can change independently of each other (Figure 17.1—SEQUENCED BY HARRY NOLLER) e) f) Large databases of sequences (Ribosome Database Project) VII. Methods for making a phylogenetic tree A. Phylogenetic trees: Figure 17.4 and 17.5, PCR and sequencing discussed in Boxs 16.1 and 16.3 1. Structure: nodes (internal vs. external), branches, and branch lengths (17.4) 2 T 2. Two main i ttypes: rooted t d and d unrooted t d (17 (17.3) 3) Lecture 2 Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes and Diversity B. Steps to make a 16S rRNA gene Phylogenetic Tree 1. 2. Use Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) to: What goes into a PCR: 1) 2) 3) 4)) 5) Put tubes in a thermocycler machinge. What does this do? Denature: Anneal: Extension: 3. Analyze by agarose gel electrophoresis 4. Sequence the 16S rRNA gene and compare the sequence to a database of sequences to see what prokaryote you’ve got by ALIGNING yours to others. 5. Turn 5 u tthe ea alignments g e ts into to a a: __________________________ Let’s go over Fig. 17.6 Bio119 Lecture 2 Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes and Diversity !"C l l t di !"Calculate distance t matrix ti !"Start an intermediate tree with most closely related strains. !"Calculate second distance matrix. !"Add other intermediate tree of closely related strains !"Calculate distance between two intermediate trees !"Then the average distance and draw the branches d(ab)(cd) Bio119 Lecture 2 Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes and Diversity Fig. 1.5, 23.1 Bio119 Lecture 2 Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes and Diversity Fig. 4.43, 1.6 Bio119 Lecture 2 Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes and Diversity Fig. 17.1 Bio119 Lecture 2 Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes and Diversity Box 16.1 Bio119