* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry: From Triangles to Quadrilaterals and Polygons .
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Shapley–Folkman lemma wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
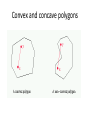
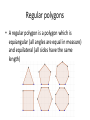
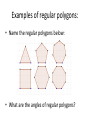
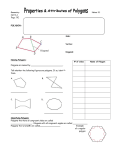
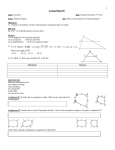
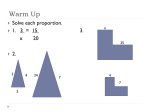
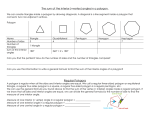
Geometry: From Triangles to Quadrilaterals and Polygons MA.912.G.2.1 Identify and describe convex, concave, regular, and irregular polygons. Block 22 Polygon Definition:A closed plane figure, having at least three side that are line segments and are connected at their endpoints • Sides of polygons are sides or edges, endpoints of sides are vertexes or corners Polygon • Examples of polygons: triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, hexagons etc. • Polygons play important role in Euclidean geometry, we can also see them in nature, science and everyday life Examples of polygon • Search the internet for other polygons: • Irregular triangles like isoscales triangles, right angle triangles • Quadrilaterals like rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids • Other irregular polygons: is a star a polygon? More definitions for polygons Convex polygon: Defines a shape that curves outward; opposite of concave. A geometric figure is convex if every line segment connecting interior points is entirely contained within the figure's interior Concave polygon: Defines a shape that curves inward; opposite of convex. Convex and concave polygons Regular polygons • A regular polygon is a polygon which is equiangular (all angles are equal in measure) and equilateral (all sides have the same length) Examples of regular polygons: • Name the regular polygons below: • What are the angles of regular polygons? Naming polygons: Calculating interior angles for regular polygons: • To calculate interior angle for a polygon we divide a regular polygon into triangles drawing diagonals from one vertex to all others • Each triangle has sum of angles 1800 Calculating interior angles for regular polygons: • To find an angle we multiply the number of triangles by angles 1800 and divide by the number of vertexes: for the pentagon that will be: (3* 1800 )/5=(540)/5=108 Calculating interior angles for regular polygons: Polygons and coordinate system • Question: if the three vertexes of a square are: A=(2,1), B=(1,3), C=(3,4) • What are the coordinates of forth vertex? What is the length of a side of this square? Solution: the picture below illustrates the situation Solution: the picture below illustrates the situation • • • • Answer: Fourth vertex D=(4,2) Side length: (1 2) 2 (3 1) 2 (1) 2 (2) 2 5 Challenge with polygons • Can we cut an equilateral triangle into four pieces that can be rearranged to make a square? • The Haberdasher's Puzzle, the greatest mathematical discovery of Henry Dudeney, was first published by him in the Weekly Dispatch in 1902 and then as problem no. 26 in The Canterbury Puzzles (1907) Haberdasher's puzzle Designing a Table Both Swinging and Stable Greg N. Frederickson Review and Discussion Basing on the lecture on reading: Designing a Table Both Swinging and Stable by Greg N. Frederickson How use the recourses form the module in a classroom setting?