* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The sum of the interior (=vertex) angles in a polygon
Survey
Document related concepts
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
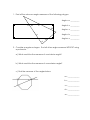
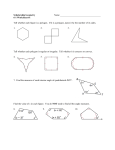
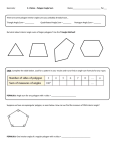
The sum of the interior (=vertex) angles in a polygon. We can create triangles inside a polygon by drawing diagonals. A diagonal is a line segment inside a polygon that connects two non-adjacent vertices. Polygon Name Number of sides Number of triangles Sum of the interior angles Triangle 3 Quadrilateral 4 Pentagon 5 Hexagon 6 Heptagon 7 1 triangle 180 360 = 2 180 Can you find the pattern? How do the number of sides and the number of triangles compare? _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Can you use this information to write a general formula to find the sum of the interior angles of a polygon? _______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ Regular Polygons A polygon is regular when all the sides and interior angles are equal. We call a regular three-sided polygon an equilateral triangle, a regular four-sides polygon is a square, a regular five-sided polygon is a regular pentagon, etc. We can use the general formula you found above to find the sum of the vertex (= interior) angles inside a regular polygon. If we know that all sides and interior angles are equal, we can divide the general formula by the number of side to find the measure of one interior angle. Measure of one interior (= vertex) angle in a regular polygon = ______________________ Measure of one exterior angle in a regular polygon = ______________________ Measure of one central angle in a regular polygon = ______________________ 1. Find all the unknown angle measures of the following polygon Angle a = __________ a c b 46˚ Angle b = __________ 64 Angle c = __________ Angle d = __________ e 35 Angle e = __________ d 2. Consider a regular octagon. Find all other angle measures WITHOUT using a protractor. a) What would be the measure of one interior angle? b) What would be the measure of one exterior angle? c) Find the measure of the angles below. a = _____________ b = _____________ c = _____________ d = _____________ e = _____________